Java基础 --- 终止线程 Terminate Threads
为什么要终止线程
- 线程消耗资源(包括内存,内核, CPU等资源).
- 只有当一个Java程序的所有线程都运行结束的时候,一个 Java 程序才算运行结束.
- 所以当一个线程不再被需要使用时或者运行不正常时需要清理掉.
- 下面代码中, 即使main方法已经运行完毕, 但是整个程序还是等待 BlockingTask运行结束.
public class Main1 {
public static void main(String [] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new BlockingTask());
thread.start();
}
private static class BlockingTask implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//do things
try {
Thread.sleep(500000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("Existing blocking thread");
}
}
}
}
终止线程的方法
return()
- 当一个线程的
run方法执行return语句时, 线程会自动结束
stop()
- 再以前的版本中, 使用stop和suspend可以立即结束一个线程
- 但是已经被废弃, 因为直接中断的方式,并没有让线程留下存储数据的时间,这也极容易导致线程的数据丢失或不一致性的问题
interrupt()
- java并没有提供任何机制来安全的停止线程,只提供了中断(interruption),这其实是一种协作机制,让一个线程去通知另外一个线程停止当前的工作。
- interrupt方法不是直接终止线程, 而是给目标线程发送一个中断信号,如果目标线程没有接收线程中断的信号并结束线程,线程则不会终止,具体是否退出或者执行其他逻辑由目标线程决定.
- When the interrupt method is called on a thread, the interrupted status of the thread is set. This is a boolean flag that is present in every thread.
interrupt() 和 isInterrupted()
- 可以使用
interrupt()和isInterrupted()从一个线程中断另一个线程并查看目前线程是否被中断
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(new LongComputationTask(new BigInteger("200000"), new BigInteger("100000000")));
thread.start();
//中断thread线程
thread.interrupt();
}
private static class LongComputationTask implements Runnable {
private BigInteger base;
private BigInteger power;
public LongComputationTask(BigInteger base, BigInteger power) {
this.base = base;
this.power = power;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(base + "^" + power + " = " + pow(base, power));
}
private BigInteger pow(BigInteger base, BigInteger power) {
BigInteger result = BigInteger.ONE;
for (BigInteger i = BigInteger.ZERO; i.compareTo(power) != 0; i = i.add(BigInteger.ONE)) {
// 查看目前线程是否被中断, 以及做出相应处理
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("Prematurely interrupted computation");
return BigInteger.ZERO;
}
result = result.multiply(base);
}
return result;
}
}
}
InterruptedException
- 当线程处于阻塞状态时(比如sleep和wait), 线程无法使用
isInterrupted()查看是否收到中断信号, 此时需要InterruptedExceptionInterruptedException会结束线程的阻塞状态
Runnable r = () -> {
try
{
. . .
while (more work to do)
{
//do more work
Thread.sleep(delay);
}
}
catch(InterruptedException e) {
// thread was interrupted during sleep
}
finally {
//cleanup, if required
}
// exiting the run method terminates the thread
};
- 当InterruptedException被抛出后, Interrupt status会被清除
- 下面代码就中断失败, 因为当InterruptedException被抛出后, Interrupt status被清除. 代码进入不到if语句
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
// 响应中断
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("青秧线程被中断,程序退出。");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("青秧线程休眠被中断,程序退出。");
}
}
});
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
thread.interrupt();
}
- 中断成功: 在catch中加入Thread.currentThread().interrupt(). 重新设置中断状态.
private static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
// 响应中断
if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("青秧线程被中断,程序退出。");
return;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("青秧线程休眠被中断,程序退出。");
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
});
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
thread.interrupt();
}
使用sleep时, 不要在底层代码中处理InterruptException
public class PassInterrupt implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("go");
throwInMethod();
}
}
private void throwInMethod() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread=new Thread (new PassInterrupt());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
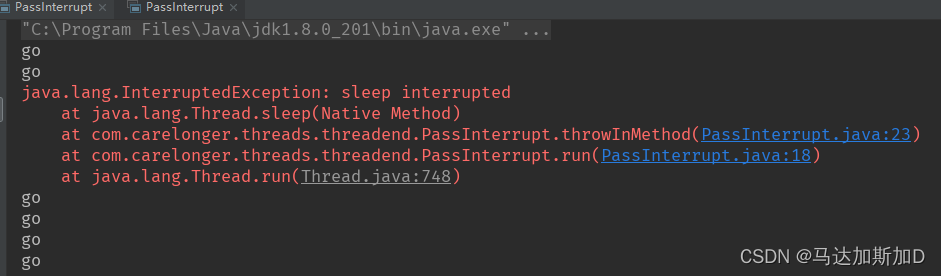
- 因为throwInMethod存在于底层方法中,如果在其中进行try/catch顶层方法可能无法感知,导致该中断被遗漏.
正确方式: 将exception抛给顶层方法处理
public class PassInterrupt implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
System.out.println("go");
try {
throwInMethod();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
//保存日志/停止程序等操作
System.out.println("日志已经保存");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void throwInMethod() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
//不在这里try/catch 是因为在这里的代码层次很深,run在较高层次,而throwInMethod较低层次
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread=new Thread (new PassInterrupt());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
isInterrupt() 和 interrupted的区别 (注意是interrupted不是interrupt)
- The
interruptedmethod is a static method that checks whether the current thread has
been interrupted. Furthermore, calling the interrupted method clears the interrupted
status of the thread.isInterruptedmethod is an instance method that you can use to check whether any thread has been interrupted.
Calling it does not change the interrupted status.