superpoint 论文原文,先过一遍论文。
superpoint 官方源代码,基于 pytorch 的,不过遗憾的是训练代码和相应的渲染的训练数据没提供。
superpoint 大佬复现带训练版本,基于tensorflow。
1.官方源码效果
命令行下载源码,也可以点上面链接下载。
git clone https://github.com/magicleap/SuperPointPretrainedNetwork.git 先配置环境(强烈建议安装anaconda配置虚拟环境,方便管理)
pip install opencv-python
pip install torch
我的实现版本:opencv-python 4.4 torch1.8.1
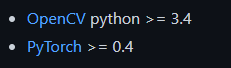
官方要求:
运行图片模式(其他模式github都有对应命令代码,输入为摄像头或视频)
./demo_superpoint.py assets/给到图片文件夹的路径上一级/
注意图片不是png格式则需要做修改,在img_glob default里修改,运行卡顿也可以改HW调整输入图片大小。

跟踪效果(检测对应特征点在图片上的移动)


源码只有跟踪效果,我在源码的基础上做了一些修改,写了匹配和用时匹配数等数据的可视化。
import argparse
import glob
import numpy as np
import os
import time
import cv2
from numpy.core.records import array
from numpy.distutils.system_info import x11_info
import torch
if int(cv2.__version__[0]) < 3: # pragma: no cover
print('Warning: OpenCV 3 is not installed')
class SuperPointNet(torch.nn.Module):#
def __init__(self):
super(SuperPointNet, self).__init__() # 第一句话,调用父类的构造函数 也就是nn.module
self.relu = torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.pool = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)
c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, d1 = 64, 64, 128, 128, 256, 256
# Shared Encoder.
self.conv1a = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, c1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)# 编码卷集层
self.conv1b = torch.nn.Conv2d(c1, c1, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv2a = torch.nn.Conv2d(c1, c2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv2b = torch.nn.Conv2d(c2, c2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv3a = torch.nn.Conv2d(c2, c3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv3b = torch.nn.Conv2d(c3, c3, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv4a = torch.nn.Conv2d(c3, c4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv4b = torch.nn.Conv2d(c4, c4, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
# Detector Head.
self.convPa = torch.nn.Conv2d(c4, c5, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)# 解码卷集层
self.convPb = torch.nn.Conv2d(c5, 65, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
# Descriptor Head.
self.convDa = torch.nn.Conv2d(c4, c5, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)# 解码卷集层
self.convDb = torch.nn.Conv2d(c5, d1, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
# Shared Encoder.
x = self.relu(self.conv1a(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv1b(x))
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.relu(self.conv2a(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv2b(x))
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.relu(self.conv3a(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv3b(x))
x = self.pool(x)
x = self.relu(self.conv4a(x))
x = self.relu(self.conv4b(x))
# Detector Head.
cPa = self.relu(self.convPa(x))
semi = self.convPb(cPa)
# Descriptor Head.
cDa = self.relu(self.convDa(x))
desc = self.convDb(cDa)
dn = torch.norm(desc, p=2, dim=1) # Compute the norm.
desc = desc.div(torch.unsqueeze(dn, 1)) # Divide by norm to normalize.
return semi, desc #网络结构 返回值
class SuperPointFrontend(object): #
#superpoint前端类 继承了object
#包含住了superpoint类
""" Wrapper around pytorch net to help with pre and post image processing. """
def __init__(self, weights_path, nms_dist, conf_thresh, nn_thresh,
cuda=False):
self.name = 'SuperPoint'
self.cuda = cuda
self.nms_dist = nms_dist
self.conf_thresh = conf_thresh#传参
self.nn_thresh = nn_thresh # L2 descriptor distance for good match.
self.cell = 8 # Size of each output cell. Keep this fixed.每个输出单元格的大小。保持固定的。
self.border_remove = 4 # Remove points this close to the border. 边界点
# Load the network in inference mode.
self.net = SuperPointNet() #子类
if cuda:
# Train on GPU, deploy on GPU.
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path))
self.net = self.net.cuda()
else:
# Train on GPU, deploy on CPU.
self.net.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path,
map_location=lambda storage, loc: storage))
self.net.eval()
def nms_fast(self, in_corners, H, W, dist_thresh):#非极大值抑制 ,dis thresh 默认4
grid = np.zeros((H, W)).astype(int) # Track NMS data. #array
inds = np.zeros((H, W)).astype(int) # 存储点的索引。
# 根据特征点信心值排序 四舍五入最接近的int。
inds1 = np.argsort(-in_corners[2,:])
#argsort返回数组值从小到大的索引值 ,前是行索引 后面是列 取第三行的信心值全切片 从大到小排序
corners = in_corners[:,inds1]#取出所有特征点信值
rcorners = corners[:2,:].round().astype(int) # 取出特征点xy 0-2 列全部
# Check for edge case of 0 or 1 corners.检查0或1个角的边缘情况。
if rcorners.shape[1] == 0:
return np.zeros((3,0)).astype(int), np.zeros(0).astype(int)
if rcorners.shape[1] == 1:
out = np.vstack((rcorners, in_corners[2])).reshape(3,1)
return out, np.zeros((1)).astype(int)
# Initialize the grid.
for i, rc in enumerate(rcorners.T):
#enumerate就是枚举的意思,把元素一个个列举出来, 所以他返回的是元素rc以及对应的索引i。
grid[rcorners[1,i], rcorners[0,i]] = 1 #有哪些点 有就给1
inds[rcorners[1,i], rcorners[0,i]] = i #给点对应的特征点序号
# Pad the border of the grid, so that we can NMS points near the border.
pad = dist_thresh #距离4 int
grid = np.pad(grid, ((pad,pad), (pad,pad)), mode='constant')#pad填充边缘网格 constant default=0
# Iterate through points, highest to lowest conf, suppress neighborhood.
#遍历点,从最高到最低的conf,抑制邻域。
count = 0
for i, rc in enumerate(rcorners.T):
# Account for top and left padding.
pt = (rc[0]+pad, rc[1]+pad)#4*4领域 因为要考虑边界
if grid[pt[1], pt[0]] == 1: # If not yet suppressed.
grid[pt[1]-pad:pt[1]+pad+1, pt[0]-pad:pt[0]+pad+1] = 0
grid[pt[1], pt[0]] = -1 #抑制完了取-1
count += 1
# Get all surviving -1's and return sorted array of remaining corners.
#获取所有幸存的-1,并返回剩余角的排序数组。
keepy, keepx = np.where(grid==-1) #-1的xy where返回坐标
keepy, keepx = keepy - pad, keepx - pad#真实的xy坐标 因为前面加4了
inds_keep = inds[keepy, keepx]
out = corners[:, inds_keep] #取出xy和conf
values = out[-1, :] #出conf
inds2 = np.argsort(-values) #排序conf 返回索引
out = out[:, inds2]
out_inds = inds1[inds_keep[inds2]]
return out, out_inds#剩下点的3*n 和索引
def run(self, img):
assert img.ndim == 2, 'Image must be grayscale.'
assert img.dtype == np.float32, 'Image must be float32.'
H, W = img.shape[0], img.shape[1]
inp = img.copy()
inp = (inp.reshape(1, H, W))
inp = torch.from_numpy(inp)
inp = torch.autograd.Variable(inp).view(1, 1, H, W)
if self.cuda:
inp = inp.cuda()
# Forward pass of network.
outs = self.net.forward(inp)
semi, coarse_desc = outs[0], outs[1]
# Convert pytorch -> numpy.
semi = semi.data.cpu().numpy().squeeze()
# --- Process points.
dense = np.exp(semi) # Softmax.
dense = dense / (np.sum(dense, axis=0)+.00001) # Should sum to 1.
# Remove dustbin.
nodust = dense[:-1, :, :]
# Reshape to get full resolution heatmap.
Hc = int(H / self.cell)
Wc = int(W / self.cell)
nodust = nodust.transpose(1, 2, 0)
heatmap = np.reshape(nodust, [Hc, Wc, self.cell, self.cell])
heatmap = np.transpose(heatmap, [0, 2, 1, 3])
heatmap = np.reshape(heatmap, [Hc*self.cell, Wc*self.cell])
xs, ys = np.where(heatmap >= self.conf_thresh) # Confidence threshold.
if len(xs) == 0:
return np.zeros((3, 0)), None, None
pts = np.zeros((3, len(xs))) # Populate point data sized 3xN.
pts[0, :] = ys
pts[1, :] = xs
pts[2, :] = heatmap[xs, ys]
pts, _ = self.nms_fast(pts, H, W, dist_thresh=self.nms_dist) # Apply NMS.
inds = np.argsort(pts[2,:])
pts = pts[:,inds[::-1]] # Sort by confidence.
# Remove points along border.
bord = self.border_remove
toremoveW = np.logical_or(pts[0, :] < bord, pts[0, :] >= (W-bord))
toremoveH = np.logical_or(pts[1, :] < bord, pts[1, :] >= (H-bord))
toremove = np.logical_or(toremoveW, toremoveH)
pts = pts[:, ~toremove]
# --- Process descriptor.
D = coarse_desc.shape[1]
if pts.shape[1] == 0:
desc = np.zeros((D, 0))
else:
# Interpolate into descriptor map using 2D point locations.
samp_pts = torch.from_numpy(pts[:2, :].copy())
samp_pts[0, :] = (samp_pts[0, :] / (float(W)/2.)) - 1.
samp_pts[1, :] = (samp_pts[1, :] / (float(H)/2.)) - 1.
samp_pts = samp_pts.transpose(0, 1).contiguous()
samp_pts = samp_pts.view(1, 1, -1, 2)
samp_pts = samp_pts.float()
if self.cuda:
samp_pts = samp_pts.cuda()
desc = torch.nn.functional.grid_sample(coarse_desc, samp_pts)
desc = desc.data.cpu().numpy().reshape(D, -1)
desc /= np.linalg.norm(desc, axis=0)[np.newaxis, :]
return pts, desc, heatmap
def nn_match_two_way(desc1, desc2, nn_thresh):
assert desc1.shape[0] == desc2.shape[0]
if desc1.shape[1] == 0 or desc2.shape[1] == 0:
return np.zeros((3, 0))
if nn_thresh < 0.0:
raise ValueError('\'nn_thresh\' should be non-negative')
# Compute L2 distance. Easy since vectors are unit normalized.
dmat = np.dot(desc1.T, desc2)
dmat = np.sqrt(2-2*np.clip(dmat, -1, 1))
# Get NN indices and scores.
idx = np.argmin(dmat, axis=1)
scores = dmat[np.arange(dmat.shape[0]), idx]
# Threshold the NN matches.
keep = scores < nn_thresh
# Check if nearest neighbor goes both directions and keep those.
idx2 = np.argmin(dmat, axis=0)
keep_bi = np.arange(len(idx)) == idx2[idx]
keep = np.logical_and(keep, keep_bi)
idx = idx[keep]
scores = scores[keep]
# Get the surviving point indices.
m_idx1 = np.arange(desc1.shape[1])[keep]
m_idx2 = idx
# Populate the final 3xN match data structure.
matches = np.zeros((3, int(keep.sum())))
matches[0, :] = m_idx1
matches[1, :] = m_idx2
matches[2, :] = scores
return matches
class VideoStreamer(object):
def __init__(self, basedir, camid, height, width, skip, img_glob):#img_glod *.png
# 构造函数
# 图模式中主要用来得到self.list 所有图片的路径
#
self.cap = [] #list
self.camera = False
self.video_file = False
self.listing = []
self.sizer = [height, width]
self.i = 0
self.skip = skip
self.maxlen = 1000000
# If the "basedir" string is the word camera, then use a webcam.
if basedir == "camera/" or basedir == "camera": #使用相机
print('==> Processing Webcam Input.')
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(camid)
self.listing = range(0, self.maxlen)
self.camera = True
else:
# Try to open as a video.
self.cap = cv2.VideoCapture(basedir) #使用视屏
lastbit = basedir[-4:len(basedir)] #len str的长度 string[-4:最后] 切片 切最后四个字符
if (type(self.cap) == list or not self.cap.isOpened()) and (lastbit == '.mp4'):
raise IOError('Cannot open movie file')
elif type(self.cap) != list and self.cap.isOpened() and (lastbit != '.txt'):
print('==> Processing Video Input.')
num_frames = int(self.cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT)) #视频总帧数
self.listing = range(0, num_frames) #生成list
self.listing = self.listing[::self.skip] #切片 0-num_frame 10步一切
self.camera = True
self.video_file = True
self.maxlen = len(self.listing) #更新总帧数
else:
print('==> Processing Image Directory Input.')
search = os.path.join(basedir, img_glob)#前后str拼起来 得到*图片路径 名字用*.png
#type(search)=str
self.listing = glob.glob(search) #找到所有符合search格式的图片路径
self.listing.sort() #从小到大排序
self.listing = self.listing[::self.skip] ##切片 遍历list skip步一切
self.maxlen = len(self.listing) #更新总帧数
if self.maxlen == 0:
raise IOError('No images were found (maybe bad \'--img_glob\' parameter?)')
def read_image(self, impath, img_size): #读图的成员函数
""" Read image as grayscale and resize to img_size.
Inputs
impath: Path to input image.
img_size: (W, H) tuple specifying resize size.
Returns
grayim: float32 numpy array sized H x W with values in range [0, 1].
"""
grayim = cv2.imread(impath, 0) #0 gray
if grayim is None:
raise Exception('Error reading image %s' % impath)
# Image is resized via opencv.
interp = cv2.INTER_AREA#一种插值方法 一般用来缩小
grayim = cv2.resize(grayim, (img_size[1], img_size[0]), interpolation=interp) #把图片缩小到指定HW
grayim = (grayim.astype('float32') / 255.) #格式转换
return grayim
def next_frame(self): #依次给图的成员函数
""" Return the next frame, and increment internal counter.
Returns
image: Next H x W image.
status: True or False depending whether image was loaded.
"""
if self.i == self.maxlen:#到最后一帧了
return (None, False)
if self.camera: #相机模式
ret, input_image = self.cap.read()
if ret is False:
print('VideoStreamer: Cannot get image from camera (maybe bad --camid?)')
return (None, False)
if self.video_file: #video模式
self.cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_POS_FRAMES, self.listing[self.i])
input_image = cv2.resize(input_image, (self.sizer[1], self.sizer[0]),
interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA)
input_image = cv2.cvtColor(input_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
input_image = input_image.astype('float')/255.0
else:
image_file = self.listing[self.i] #切当前片
input_image = self.read_image(image_file, self.sizer)
# Increment internal counter.
self.i = self.i + 1#内部的计数器
input_image = input_image.astype('float32')
return (input_image, True)
def match_descriptors(kp1, desc1, kp2, desc2):
# Match the keypoints with the warped_keypoints with nearest neighbor search
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_L2, crossCheck=True)
##是一个暴力匹配的对象,取desc1中一个描述子,再与desc2中的所有描述子计算欧式距离
matches = bf.match(desc1, desc2)
##上一行的返回值类似元组的集合(i,j)代表第一个集合的第i个点的最佳匹配是第二个集合的第j个点
matches_idx = np.array([m.queryIdx for m in matches])
m_kp1 = [kp1[idx] for idx in matches_idx]
matches_idx = np.array([m.trainIdx for m in matches])
m_kp2 = [kp2[idx] for idx in matches_idx]
####m_kp1是第一张图片的特征点,m_kp2是第二张图片的特征点,此时它们已经一一对应了(至少是最对应的,距离最小的
return m_kp1, m_kp2, matches
def showpoint(img,ptx):
for i in range(ptx.shape[1]):
x=int(round(ptx[0,i]))
y=int(round(ptx[1,i]))
# if x>20 and y>20 and x<640 and y <450:
# None
cv2.circle(img,(x,y),3,color=(255,0,0))
return img
def drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches):
"""
My own implementation of cv2.drawMatches as OpenCV 2.4.9
does not have this function available but it's supported in
OpenCV 3.0.0
This function takes in two images with their associated
keypoints, as well as a list of DMatch data structure (matches)
that contains which keypoints matched in which images.
An image will be produced where a montage is shown with
the first image followed by the second image beside it.
Keypoints are delineated with circles, while lines are connected
between matching keypoints.
img1,img2 - Grayscale images
kp1,kp2 - Detected list of keypoints through any of the OpenCV keypoint
detection algorithms
matches - A list of matches of corresponding keypoints through any
OpenCV keypoint matching algorithm
"""
# Create a new output image that concatenates the two images together
# (a.k.a) a montage
rows1 = img1.shape[0]
cols1 = img1.shape[1]
rows2 = img2.shape[0]
cols2 = img2.shape[1]
#out = np.zeros((max([rows1,rows2]),cols1+cols2,3), dtype='uint8')
# Place the first image to the left
i1= np.dstack([img1, img1, img1])
i2=np.dstack([img2, img2, img2])
cv2.imshow("sdd",i1)
cv2.imshow("sd",i1)
out = np.hstack([i1,i2])
print("sdsdsd",out.shape)
# Place the next image to the right of it
#out[0:480,640:1280] = np.dstack([img2, img2, img2])
# For each pair of points we have between both images
# draw circles, then connect a line between them
for i in range(matches.shape[1]):
# Get the matching keypoints for each of the images
img1_idx = matches[0,i]
img2_idx = matches[1,i]
x11=int(img1_idx)
y11=int(img1_idx)
x22=int(img2_idx)
y22=int(img2_idx)
# x - columns
# y - rows
x1= kp1[0,x11]
y1= kp1[1,y11]
x2= kp2[0,x22]
y2= kp2[1,y22]
# Draw a small circle at both co-ordinates
# radius 4
# colour blue
# thickness = 1
a = np.random.randint(0,256)
b = np.random.randint(0,256)
c = np.random.randint(0,256)
cv2.circle(out, (int(np.round(x1)),int(np.round(y1))), 2, (a, b, c), 1) #画圆,cv2.circle()参考官方文档
cv2.circle(out, (int(np.round(x2)+cols1),int(np.round(y2))), 2, (a, b, c), 1)
# Draw a line in between the two points
# thickness = 1
# colour blue
cv2.line(out, (int(np.round(x1)),int(np.round(y1))), (int(np.round(x2)+cols1),int(np.round(y2))), (a, b, c), 1, shift=0) #画线,cv2.line()参考官方文档
# Also return the image if you'd like a copy
return out
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Parse command line arguments.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch SuperPoint Demo.')
parser.add_argument('input', type=str, default='',
help='Image directory or movie file or "camera" (for webcam).')
parser.add_argument('--weights_path', type=str, default='superpoint_v1.pth',
help='Path to pretrained weights file (default: superpoint_v1.pth).')
parser.add_argument('--img_glob', type=str, default='*.png',#################pgm
help='Glob match if directory of images is specified (default: \'*.png\').')
parser.add_argument('--skip', type=int, default=1,
help='Images to skip if input is movie or directory (default: 1).')
parser.add_argument('--show_extra', action='store_true',
help='Show extra debug outputs (default: False).')
parser.add_argument('--H', type=int, default=480,
help='Input image height (default: 120).')
parser.add_argument('--W', type=int, default=640,
help='Input image width (default:640).')
parser.add_argument('--display_scale', type=int, default=2,
help='Factor to scale output visualization (default: 2).')
parser.add_argument('--min_length', type=int, default=2,
help='Minimum length of point tracks (default: 2).')
parser.add_argument('--max_length', type=int, default=5,
help='Maximum length of point tracks (default: 5).')
parser.add_argument('--nms_dist', type=int, default=4,
help='Non Maximum Suppression (NMS) distance (default: 4).')
parser.add_argument('--conf_thresh', type=float, default=0.015,
help='Detector confidence threshold (default: 0.015).')
parser.add_argument('--nn_thresh', type=float, default=0.7,
help='Descriptor matching threshold (default: 0.7).')
parser.add_argument('--camid', type=int, default=0,
help='OpenCV webcam video capture ID, usually 0 or 1 (default: 0).')
parser.add_argument('--waitkey', type=int, default=1,
help='OpenCV waitkey time in ms (default: 1).')
parser.add_argument('--cuda', action='store_true',
help='Use cuda GPU to speed up network processing speed (default: False)')
parser.add_argument('--no_display', action='store_true',
help='Do not display images to screen. Useful if running remotely (default: False).')
parser.add_argument('--write', action='store_true',
help='Save output frames to a directory (default: False)')
parser.add_argument('--write_dir', type=str, default='tracker_outputs/',
help='Directory where to write output frames (default: tracker_outputs/).')
opt = parser.parse_args()
print(opt)
#读图 读下一张图
vs = VideoStreamer(opt.input, opt.camid, opt.H, opt.W, opt.skip, opt.img_glob)
print('==> Loading pre-trained network.')
# This class runs the SuperPoint network and processes its outputs.
fe = SuperPointFrontend(weights_path=opt.weights_path,#权重的路径str
nms_dist=opt.nms_dist,#非极大值抑制 int距离4
conf_thresh=opt.conf_thresh,#探测器阈值0.015
nn_thresh=opt.nn_thresh,#匹配器阈值0.7
cuda=opt.cuda) #GPU加速 默认false
print('==> Successfully loaded pre-trained network.')
# Create a window to display the demo.
if not opt.no_display:
win = 'SuperPoint Tracker'
cv2.namedWindow(win)
else:
print('Skipping visualization, will not show a GUI.')
# Font parameters for visualizaton.
font = cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX#设置可视化字体
font_clr = (255, 255, 255)
font_pt = (4, 12)
font_sc = 0.4
#创建输出目录
if opt.write:#默认false
print('==> Will write outputs to %s' % opt.write_dir)
if not os.path.exists(opt.write_dir):
os.makedirs(opt.write_dir)
print('==> Running Demo.')
img1, status = vs.next_frame()#读第一张图
start1 = time.time()
pts, desc, heatmap = fe.run(img1)
end1 = time.time()
c2=end1-start1
print("第一张图提取用时",c2,"提取特征点数目",pts.shape[1])
imgx=img1.copy()
img11=showpoint(imgx,pts)
cv2.imshow("imgone",img11)
img2, status = vs.next_frame()#读第二张图
start1 = time.time()
pts1, desc1, heatmap1 = fe.run(img2)
end1 = time.time()
c2=end1-start1
print("第二张图提取用时",c2,"提取特征点数目",pts1.shape[1])
imgx=img2.copy()
img22=showpoint(imgx,pts1)
cv2.imshow("imgtwo",img22)
match=nn_match_two_way(desc,desc1,0.7)
print("图1与图2匹配对数",match.shape[1])
# cv_kpts1 = [cv2.KeyPoint(pts[0,i], pts[1,i], 1)
# for i in range(pts.shape[1])]
# cv_kpts2 = [cv2.KeyPoint(pts1[0,i], pts1[1,i], 1)
# for i in range(pts1.shape[1])]
# sift_matched_img = cv2.drawMatches(img1, cv_kpts1, img2,
# cv_kpts2, matches, None,
# matchColor=(0, 255, 0),
# singlePointColor=(0, 0, 255))
#手写匹配 有些问题
out=sift_matched_img = drawMatches(img1, pts, img2,
pts1, match)
cv2.namedWindow("matcher",0)
cv2.imshow("matcher",out)
cv2.waitKey(0)
print('==> Finshed Demo.')
代码运行效果


