目录
2.3链表的操作(在链表中是没有扩容操作的,因为是链表数据结构,所以直接插入元素就可以了)
3.front()&&back()(获取首/尾元素可以直接对其进行更改)
1.STL中的list的底层结构
- STL中的list底层是一个带头节点双向循环链表
- 双向:的可以从前往后,也可以从后往前遍历。
- 循环:找尾节点的时间复杂度为O(1)
- 带头节点:1.代码实现简单。2.因为要放end()迭代器(end:是最后一个元素的下一个位置:auto it=end();--it;//it要指向最后一个元素)
2.list的使用
-
2.1构造对象:

-
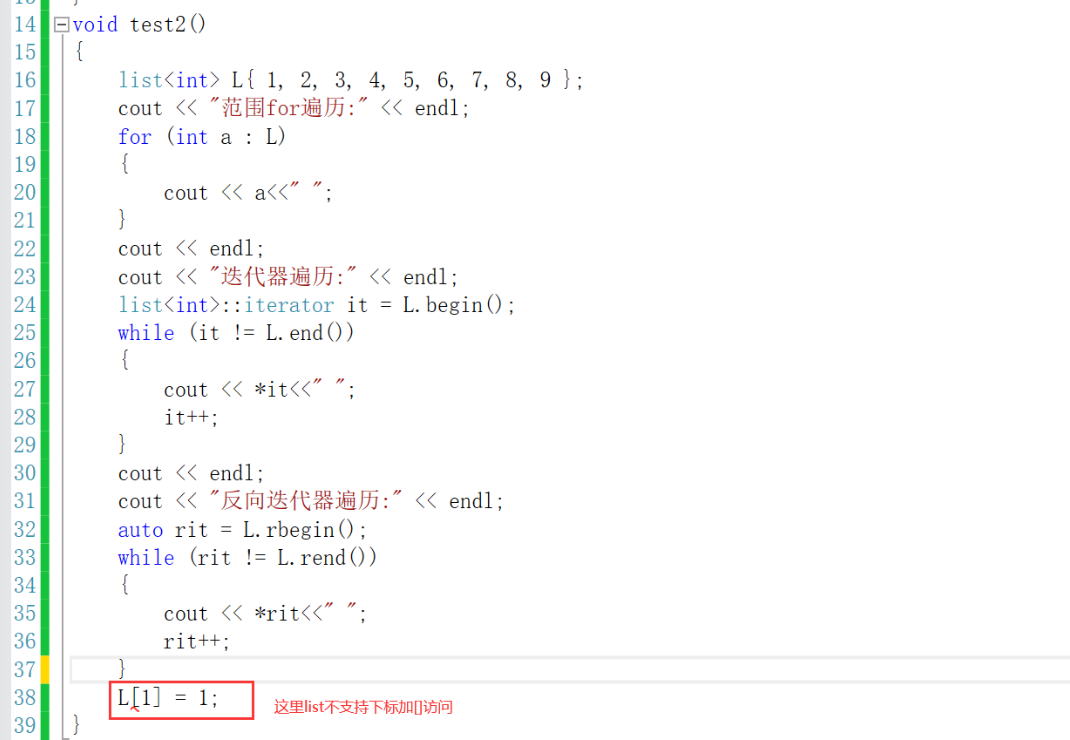
2.2链表的遍历方式:
- 这里链表不可以用[下标]访问(因为链表这种结构不支持随机访问)
-
2.3链表的操作(在链表中是没有扩容操作的,因为是链表数据结构,所以直接插入元素就可以了)
-
1.resize()

-
2.clear()清空链表

-
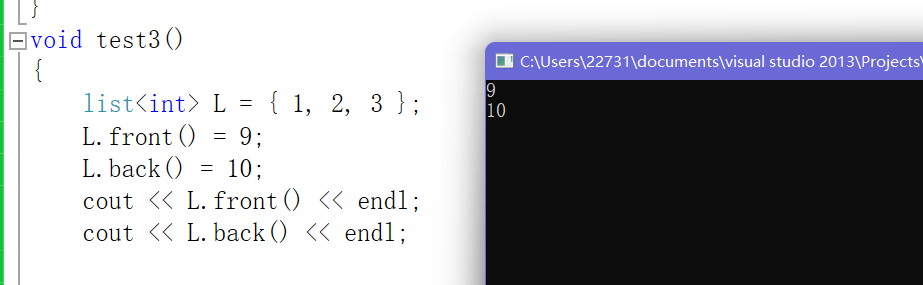
3.front()&&back()(获取首/尾元素可以直接对其进行更改)
-
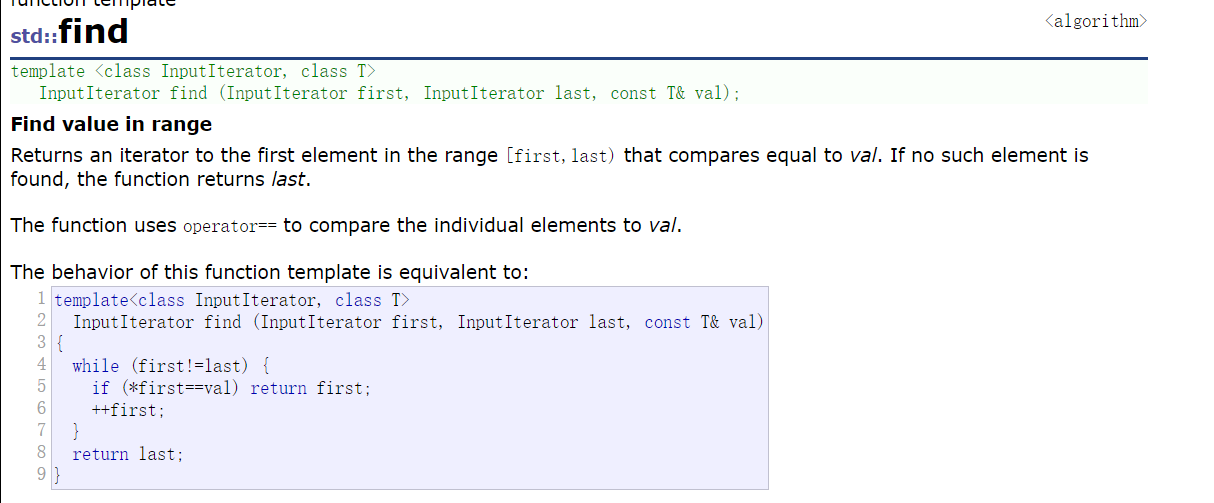
4.插入和删除元素

- 注意这里面使用的find函数不是list中的成员函数,list中没有没有find成员函数,这里的find函数是全局的而vector中也没有实现find查找的方法
-
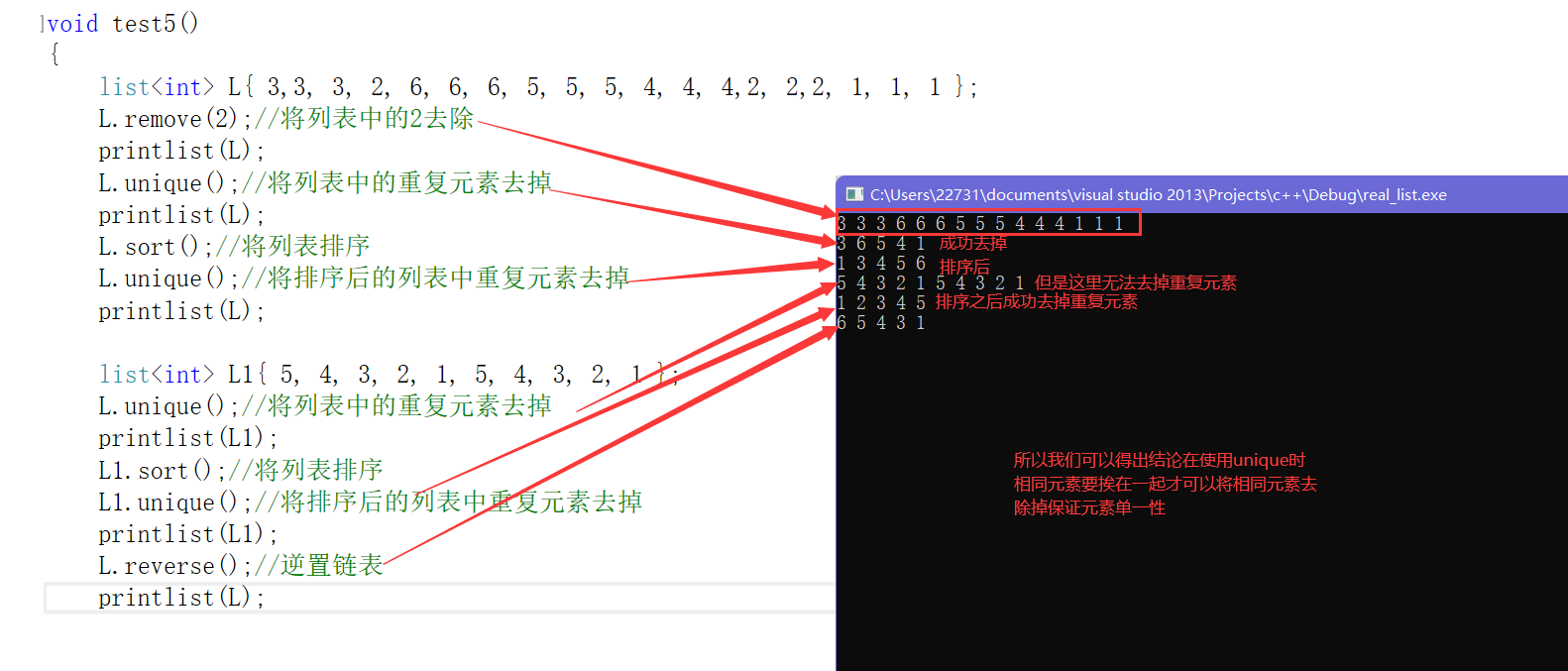
remove()和unique的使用:
-
remove_if()//按条件删除
3.list的模拟实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
#if 1
namespace wbx
{ ///链表节点
template<class T>
class listnode
{
public:
listnode(const T&value = T())
:prev(nullptr),
next(nullptr),
val(value)
{}
listnode<T>* prev;
listnode<T>* next;
T val;
};
迭代器类
template <class T,class Ref,class Ptr>
struct List_iterator//这里将名字不要直接取名为iterator因为在下面给模版重命名为iterator时有可能冲突
{
public:
//friend class list;
typedef Ref Reference;
typedef Ptr Pointer;
typedef listnode<T> node;
typedef List_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> list_iterator;
List_iterator(node* t = nullptr)
:p(t)
{}
Reference operator*()//这里要返回Ref,不要直接写成T&,因为不是所有的数据类型都是T&
{
return p->val;
}
Pointer operator->()//当T为内置类型时没有意义,当T为自定义类型的时候才有用
{
return &p->val;
}
List_iterator& operator++()//前置++//这里引用返回可以减少拷贝构造效率更高
{
p = p->next;
return *this;
}
List_iterator operator++(int)//后置++//这里不可以引用返回因为temp返回的是临时的对象出了作用域就销毁了
{
iterator temp(*this);
p = p->next;
return temp;
}
List_iterator operator--()
{
p = p->prev;
return *this;
}
List_iterator operator--(int)
{
iterator temp(*this);
p = p->prev;
return temp;
}
bool operator==(const List_iterator&it2)
{
return p == it2.p;
}
bool operator!=(const List_iterator&it2)
{
return p != it2.p;
}
node *p;
};
///反向迭代器
template<class iterator>//包装正向迭代器
struct list_reserver_iterator
{
public:
typedef typename iterator::Reference Reference1;//这里在类外定义类中的类型时要加上typename因为在类外用类型加::
typedef typename iterator::Pointer Pionter1;//也可以访问类中的静态成员变量
//typedef list_reserver_iterator<iterator> self;
list_reserver_iterator(iterator it)
:_it(it)
{}
Reference1 operator*()
{
return *_it;
}
Pionter1 operator->()
{
//return &_it.p->val;
//return _it->;
return _it.operator->();
}
list_reserver_iterator<iterator>& operator++()
{
--_it;
return *this;
}
list_reserver_iterator<iterator> operator++(int)
{
list_reserver_iterator<iterator> temp(_it);
--_it;
return temp;
}
list_reserver_iterator<iterator>& operator--()
{
++_it;
return *this;
}
list_reserver_iterator<iterator> operator--(int)
{
list_reserver_iterator<iterator> temp(_it);
++_it;
return *this;
}
bool operator==(const list_reserver_iterator<iterator> &r)
{
return _it == r._it;
}
bool operator!=(const list_reserver_iterator<iterator> &r)
{
return _it != r._it;
}
iterator _it;
};
//链表模板
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
///
typedef listnode<T> node;
typedef List_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef List_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
typedef list_reserver_iterator<List_iterator<T, T&, T*>> reserver_iterator;
typedef list_reserver_iterator<const_iterator> const_reserver_iterator;
//typedef iterator<T> iterator;
public:
list()
{
createhead();
}
list(int n, const T &val = T())
{
createhead();
while (n--)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
///插入删除元素
iterator insert(iterator pos,const T& date)
{
node* temp = new node(date);
node* inpos = pos.p;
temp->next = inpos;
temp->prev = inpos->prev;
temp->prev->next = temp;
temp->next->prev = temp;
return iterator(temp);
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
node* temp = pos.p;
temp->prev->next = temp->next;
temp->next->prev = temp->prev;
node* ret = temp->next;
delete temp;
return iterator(ret);
}
iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last)
{
auto it = first;
while (it != last)
{
it = erase(it);
}
return it;
}
void clear()
{
erase(begin(), end());
}
void push_back(const T& date)
{
insert(end(),date);
}
void push_front(const T& date)
{
insert(begin(), date);
}
void pop_back()
{
if (empty())
{
std::cout << "链表已为空" << std::endl;
return;
}
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
if (empty())
{
std::cout << "链表已为空" << std::endl;
return;
}
erase(begin());
}
bool empty()
{
return begin() == end();
}
容量相关
void resize(int n,const T &val=T())
{
if (n >=size())
{
int count = n - size();
while (count--)
{
push_back(val);
}
}
else
{
int count = size() - n;
while (count--)
{
pop_back();
}
}
}
int size()
{
int count=0;
for (auto a : *this)
{
count++;
}
return count;
}
迭代器
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(phead->next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(phead);
}
const_iterator cbegin()const//这里不加const也可以编译通过因为非const成员也可以调用const成员函数
{
return const_iterator(phead->next);
}
const_iterator cend()const
{
return const_iterator(phead);
}
reserver_iterator rbegin()
{
return reserver_iterator((--end()));
}
reserver_iterator rend()
{
return reserver_iterator((--begin()));
}
const_reserver_iterator rcbegin()
{
return const_reserver_iterator(--cend());
}
const_reserver_iterator rcend()
{
return const_reserver_iterator(--cbegin());
}
void printlist()
{
for (auto a : *this)
{
std::cout << a << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
获取元素
T& front()
{
return *begin();
}
T& back()
{
return *(--end());
}
private:
void createhead()
{
phead = new node();
phead->next = phead;
phead->prev = phead;
}
listnode<T> *phead;
};
}
void test1()
{
wbx::list<int> L(3, 5);
L.printlist();
L.pop_back();
L.printlist();
L.push_back(1);
L.printlist();
L.push_back(2);
L.printlist();
L.push_back(3);
L.printlist();
L.push_back(4);
L.printlist();
L.push_front(6);
L.printlist();
L.pop_front();
L.printlist();
cout << L.size() << endl;
L.resize(10);
cout << L.size() << endl;
L.printlist();
L.resize(20,99);
cout << L.size() << endl;
L.printlist();
L.front() = 111;
L.back() = 999;
L.printlist();
cout << L.front() << endl;
cout << L.back() << endl;
wbx::list<int>::iterator it = L.begin();
cout << *it << endl;
cout << "zhengxaing dayin" << endl;
L.printlist();
auto it2 = L.rbegin();
while (it2 != L.rend())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
it2++;
}
cout << "fanxiangdayin" << endl;
auto it3 = L.rend();
while (it3 != L.begin())
{
cout << *it3 << " ";
it3--;
}
L.clear();
L.printlist();
}
struct A
{
int a;
int b;
int c;
};
void test2()//->运算符重载的使用
{
A aa{ 1, 2, 3 };
A bb{ 4, 5, 6 };
A cc{ 7, 8, 9 };
wbx::list<A> L;
L.push_back(aa);
L.push_back(bb);
L.push_back(cc);
wbx::list<A>::iterator it = L.begin();
auto it2 = L.rbegin();
cout << it->a << it->b << it->c << endl;//这里原本是要写为it->->的形式但是这里编译器帮我们优化了,只需要写一个->就可以了。
cout << it2->a << it2->b << it2->c << endl;
}
void test3()
{
wbx::list<int> L;
L.push_back(1);
L.push_back(2);
L.push_back(3);
L.push_back(4);
L.push_back(5);
L.printlist();
cout << "fanxiangdayin" << endl;
auto it2 = L.rbegin();
while (it2 != L.rend())
{
cout << *it2 << " ";
it2++;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "fanxiangdayin" << endl;
auto it3 = L.rend();
while (it3 != L.rbegin())
{
cout << *it3 << " ";
it3--;
}
}
int main()
{
//test1();
test2();
//test3();
return 0;
}
#endif