大家好,我是小鱼,最近有些偷懒了,对了,ROS2的第一个五年支持版本发布了,动手学ROS2相关课程和文档也开始正式迁移至Humble版本啦~
本节是拓展章节,主要讲解一下如何给FishBot添加一个超声波传感器。
在实际的机器人开发过程中,我们可能会利用超声波传感器实现实时避障的功能,毕竟超声波的价格相较于激光雷达要便宜很多(便宜的几块钱)。
所以本节我们来说一下如何使用ROS2+Gazebo来仿真超声波传感器。
1.超声波传感器介绍
百科来一段:
超声波传感器是将超声波信号转换成其它能量信号(通常是电信号)的传感器。超声波是振动频率高于20kHz的机械波。它具有频率高、波长短、绕射现象小,特别是方向性好、能够成为射线而定向传播等特点。超声波对液体、固体的穿透本领很大,尤其是在阳光不透明的固体中。超声波碰到杂质或分界面会产生显著反射形成反射回波,碰到活动物体能产生多普勒效应。超声波传感器广泛应用在工业、国防、生物医学等方面。
接着看看长什么样子:

便宜的就长这样子,一共两个头,一个头用于发送波,一个头接收波。这个还稍微高级一点,带一个光敏电阻,可以为超声波数据做一些补偿。
超声波传感器原理是什么呢?
距离=(发送时间-接收时间)*速度/2
看了超声波的原理,你有没有发现和前面的激光雷达传感器是一样的,是的,所以超声波传感器插件和激光雷达传感器插件在Gazebo插件中是同一个:
libgazebo_ros_ray_sensor.so
2.超声波插件配置
直接上配置,接着再解释
2.1 添加超声波关节
超声波总要装在机器人身上某个位置,所以我们先添加一个关节和Joint,为了省事,link我们就只写个名字,你如果有需要可以按照前面的章节那样添加一下。
<link name="ultrasonic_sensor_link" />
<joint name="ultrasonic_sensor_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="ultrasonic_sensor_link"/>
<origin xyz="0.07 0.0 0.076" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</joint>
2.2 添加Gazebo插件
添加完了关节,我们就可以配置gazebo的插件了,gazebo插件配置如下
<gazebo reference="ultrasonic_sensor_link">
<sensor type="ray" name="ultrasonic_sensor">
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
<!-- 是否可视化,gazebo里能不能看到 -->
<visualize>true</visualize>
<!-- 扫描速率,也就是数据更新速率 -->
<update_rate>5</update_rate>
<ray>
<scan>
<!-- 水平扫描的点数 -->
<horizontal>
<samples>5</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-0.12</min_angle>
<max_angle>0.12</max_angle>
</horizontal>
<!-- 垂直方向扫描的点数 -->
<vertical>
<samples>5</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-0.01</min_angle>
<max_angle>0.01</max_angle>
</vertical>
</scan>
<!-- 超声波检测的范围和数据分辨率单位m -->
<range>
<min>0.02</min>
<max>4</max>
<resolution>0.01</resolution>
</range>
<!-- 数据噪声采用高斯噪声 -->
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
</noise>
</ray>
<plugin name="ultrasonic_sensor_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_ray_sensor.so">
<ros>
<!-- 重映射输出的话题名称 -->
<remapping>~/out:=ultrasonic_sensor_1</remapping>
</ros>
<!-- 输出消息的类型,注意与雷达区分,这里是sensor_msgs/Range -->
<output_type>sensor_msgs/Range</output_type>
<!-- 射线类型,这里要写ultrasound,注意和雷达区分 -->
<radiation_type>ultrasound</radiation_type>
<!-- frame名称,填写link名称即可 -->
<frame_name>ultrasonic_sensor_link</frame_name>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
3.编译运行测试
3.1Gazebo可视化
添加完成后就可以编译测试下代码
colcon build --packages-select fishbot_description
source install/setup.bash
ros2 launch fishbot_description gazebo.launch.py
没有物体的前面可以放个东西,因为本节是后面补充的,所有小鱼这里有个墙。
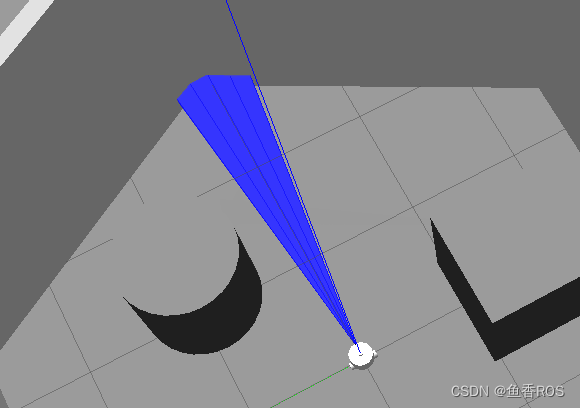
3.2话题数据
打开终端,输入下面指令
ros2 topic list
ros2 topic info /ultrasonic_sensor_1
ros2 topic echo /ultrasonic_sensor_1
不出意外可以看到下面的数据
header:
stamp:
sec: 4458
nanosec: 1000000
frame_id: ultrasonic_sensor_link
radiation_type: 0
field_of_view: 0.23999999463558197
min_range: 0.019999999552965164
max_range: 4.0
range: 2.6798219680786133
这里的range就是fishbot到墙之间的距离:2.67982
我们来讲一讲超声波传感器的数据类型sensor_msgs/msg/Range
# ros2 topic info /ultrasonic_sensor_1
Type: sensor_msgs/msg/Range
Publisher count: 1
Subscription count: 0
你可以使用ros2 interface show sensor_msgs/msg/Range看到详细的解释,我们翻译一下
# Single range reading from an active ranger that emits energy and reports
# one range reading that is valid along an arc at the distance measured.
# This message is not appropriate for laser scanners. See the LaserScan
# message if you are working with a laser scanner.
#
# This message also can represent a fixed-distance (binary) ranger. This
# sensor will have min_range===max_range===distance of detection.
# These sensors follow REP 117 and will output -Inf if the object is detected
# and +Inf if the object is outside of the detection range.
std_msgs/Header header # timestamp in the header is the time the ranger
# returned the distance reading
# Radiation type enums
# If you want a value added to this list, send an email to the ros-users list
uint8 ULTRASOUND=0
uint8 INFRARED=1
uint8 radiation_type # 传感器射线类型
# (sound, IR, etc) [enum]
float32 field_of_view # 距离数据对应的弧[rad]的大小,测量物体的范围介于
# -field_of_view/2 到 field_of_view/2 之间。
# 0 角度对应于传感器的 x 轴。
float32 min_range # 最小范围值 [m]
float32 max_range # 最大范围值 [m]
# 固定距离需要 min_range==max_range
float32 range # 范围数据 [m]
# (Note: values < range_min or > range_max should be discarded)
# Fixed distance rangers only output -Inf or +Inf.
# -Inf represents a detection within fixed distance.
# (Detection too close to the sensor to quantify)
# +Inf represents no detection within the fixed distance.
# (Object out of range)
结论,主要关注range就可以了。
3.3 在RVIZ2中可视化超声波数据
Add ->By topic->Range
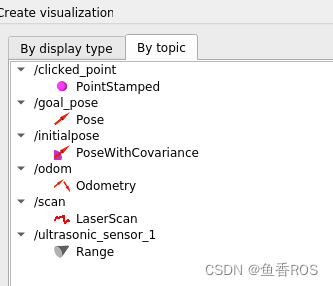
4.总结
本节主要介绍了如何对超声波传感器进行仿真,在导航的过程中我们通常把超声波放到一个代价地图中进行使用。所以学习其仿真还是很有用的。