从本系列文章开始,作者正式开始研究Python深度学习、神经网络及人工智能相关知识。前四篇文章讲解了神经网络基础概念、Theano库的安装过程及基础用法、theano实现回归神经网络、theano实现分类神经网络,这篇文章讲解Overfitting问题及正规化解决方法,采用theano实现。主要是学习"莫烦大神" 网易云视频的在线笔记,后面随着深入会讲解具体的项目及应用。基础性文章和在线笔记,希望对您有所帮助,也建议大家一步步跟着学习,同时文章中存在错误或不足之处,还请海涵~
"莫烦大神" 网易云视频地址:http://study.163.com/provider/1111519/course.html
从2014年开始,作者主要写了三个Python系列文章,分别是基础知识、网络爬虫和数据分析。
- Python基础知识系列:Pythonj基础知识学习与提升
- Python网络爬虫系列:Python爬虫之Selenium+Phantomjs+CasperJS
- Python数据分析系列:知识图谱、web数据挖掘及NLP

前文参考:
[Python人工智能] 一.神经网络入门及theano基础代码讲解
[Python人工智能] 二.theano实现回归神经网络分析
[Python人工智能] 三.theano实现分类神经网络及机器学习基础
[Python人工智能] 四.神经网络和深度学习入门知识
一. 正规化-Regularization
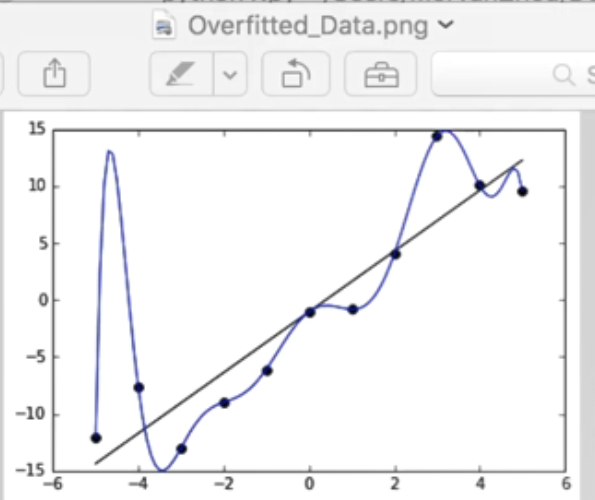
但是Overfitting会产生一个问题:在学习过程中会不断减小与真实值的误差,得到这条蓝色的线条,它能非常完美的预测这些点,与真实值的误差非常小,误差cost甚至为0,而黑色的直线的会与真实值产生误差。例如,x为-4这个点,蓝色线对应值为-7,基本吻合,而黑色线预测值为-12,存在一定误差。
但真实预测时,我们会觉得黑色线比蓝色线更为准确,因为如果有其他数据点时,将来的数据用黑色的线能更好的进行预测或概括。比如x为2.5时,蓝色线这个点的误差可能会比黑色线更大。Overfitting后的误差会非常小,但是测试数据时误差会突然变得很大,并且没有黑线预测的结果好。
分类问题,看下面这张图。第一张图通过一条曲线将data分割开来,注意有两个X在class2里面;第二张图是Over-fitting完全把数据点分离开来,一堆点为class1、另一堆点为class2。虽然训练时图2误差更小,但是使用图2去预测时,其误差可能会更大,而图1的误差会更小,更倾向于用图1的方法。

避免Over-fitting的方法主要是正规化,包括Regularization L1和L2,下面开始讲解。
二. 定义Layer类及增加数据集
1.定义Layer类
神经网络首先需要添加神经层,将层(Layer)定义成类,通过类来添加神经层。神经层是相互链接,并且是全连接,从第一层输入层传入到隐藏层,最后传输至输出层。假设接下来需要定义两层内容:
L1 = Layer(inputs, in_size=13, out_size=50, activation_function)
参数包括输入值,输入节点数,输出节点数和激励函数
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
参数中L1的输出作为输入值,L1的输出10个节点作为输入节点,输出节点1个,激励函数为None。
定义类的代码如下,包括权重和bias,其中参数为随机变量更有利于我们后面的更新,乱序更能促进神经网络的学习。
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
2.增加数据集
需要注意,机器学习通常将数据data划分为两组,train data-训练神经网络、test data-检验预测神经网络。这里所采用的数据集是sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集(load_boston),该数据集包括500多个数据点,每个sample有13个特征去描述房价。
再导入数据集之前,作者补充一个知识点——Nnormalization。
通过 "x_data = load_boston().data" 代码导入波士顿房价数据集,但是x_data变化范围非常之广,比如有一个特征是占地面积,其范围从0到500,而另一个特征到市中心的距离,值为1、2公里,由于0到500和0到2取值范围变化幅度较大,这里使用机器学习机器一种技巧 Normalization 进行处理。将x的特征进行正常化,把每个特征的取值范围都浓缩到0-1的范围,这样能使机器学习更方便的学习东西,这里我主要通过自定义函数minmax_normalization()实现。代码如下:
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
输出结果如下图所示,包括13个特征Normalization后的结果,y类标及划分为训练集和预测集的形状。
[[0.00000000e+00 1.80000000e-01 6.78152493e-02 ... 2.87234043e-01 1.00000000e+00 8.96799117e-02] [2.35922539e-04 0.00000000e+00 2.42302053e-01 ... 5.53191489e-01 1.00000000e+00 2.04470199e-01] [2.35697744e-04 0.00000000e+00 2.42302053e-01 ... 5.53191489e-01 9.89737254e-01 6.34657837e-02] ... [6.11892474e-04 0.00000000e+00 4.20454545e-01 ... 8.93617021e-01 1.00000000e+00 1.07891832e-01] [1.16072990e-03 0.00000000e+00 4.20454545e-01 ... 8.93617021e-01 9.91300620e-01 1.31070640e-01] [4.61841693e-04 0.00000000e+00 4.20454545e-01 ... 8.93617021e-01 1.00000000e+00 1.69701987e-01]] [[24. ] [21.6] [34.7] [33.4] [36.2] ... [16.8] [22.4] [20.6] [23.9] [22. ] [11.9]] (400, 13) (400, 1) (106, 13) (106, 1)
三. theano实现回归神经网络正规化
1.定义变量和Layer
包括两个Layer,如下:
L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
#定义x和y
x = T.dmatrix("x")
y = T.dmatrix("y")
#定义两个Layer
#L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
#L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
2.计算误差
(1)普通方法
定义cost变量计算误差,即预测值与真实值的差别。常用的方法如下,通过计算输出结果(预测值)和真实结果误差的平方平均自实现。
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
但是该方法会产生Overfitting问题。为了解决Overfitting,在计算cost时,我要做一些手脚,加上一个东西。
(2)L2 Regularization
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
它是0.1乘以L1的权重平方求和加上L2的权重平方和,注意尽量用一个小于1的值来乘,如这里的0.1。
上面这个就是L2 Regularization方法,相当于有一个 0.1乘以所有的weight平方和,它称为惩罚机制。快要进入Overfitting时,通过这个机制来惩罚,不进入Overfitting,另一种方法是L1 Regularization。
(3)L1 Regularization
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())
根据流行程度来看,L2比L1更普及,这篇文章也主要使用L2进行实验,0.1可以取不同值,去分别测试对比实验。
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
#定义x和y
x = T.dmatrix("x")
y = T.dmatrix("y")
#定义两个Layer
#L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
#L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
#the way to compute cost
#计算误差 但该方法的结果会产生Overfitting问题
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
#L2 regularization
#0.1乘以L1的权重平方求和加上L2的权重平方和
#惩罚机制: 快要进入Overfitting时,通过这个机制来惩罚不进入Overfitting
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
#L1 regularization
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())
3.梯度下降更新
再定义梯度下降变量,其误差越大,降低趋势越大,通过梯度下降让预测值更接近真实值。代码中通过theano.function()函数更新神经网络的四个参数,计算公式如下啊:
L1.W, L1.W-learnging_rate*gW1:
(原始的权重-学习效率*下降幅度)并且更新为L1.W,通过该方法将L1.W、L1.b、L2.W、L2.b更新。
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
#print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
#定义x和y
x = T.dmatrix("x")
y = T.dmatrix("y")
#定义两个Layer
#L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
#L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
#the way to compute cost
#计算误差 但该方法的结果会产生Overfitting问题
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
#L2 regularization
#0.1乘以L1的权重平方求和加上L2的权重平方和
#惩罚机制: 快要进入Overfitting时,通过这个机制来惩罚不进入Overfitting
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
#L1 regularization
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())
#对比正规化和没有正规化的区别
#梯度下降定义
gW1, gb1, gW2, gb2 = T.grad(cost, [L1.W, L1.b, L2.W, L2.b])
#学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
#训练 updates
train = theano.function(
inputs=[x,y],
updates=[(L1.W, L1.W - learning_rate * gW1),
(L1.b, L1.b - learning_rate * gb1),
(L2.W, L2.W - learning_rate * gW2),
(L2.b, L2.b - learning_rate * gb2)])
#计算误差
compute_cost = theano.function(inputs=[x,y], outputs=cost)
print(compute_cost)
4.预测结果
最后是预测结果,训练时会给出x和y求cost,而预测时只给出输入x,用来做预测。最后每隔50步输出err,如果err不断减小,说明神经网络在学到东西,因为预测值与真实值误差在不断减小。
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
#print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
#定义x和y
x = T.dmatrix("x")
y = T.dmatrix("y")
#定义两个Layer
#L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
#L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
#the way to compute cost
#计算误差 但该方法的结果会产生Overfitting问题
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
#L2 regularization
#0.1乘以L1的权重平方求和加上L2的权重平方和
#惩罚机制: 快要进入Overfitting时,通过这个机制来惩罚不进入Overfitting
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
#L1 regularization
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())
#对比正规化和没有正规化的区别
#梯度下降定义
gW1, gb1, gW2, gb2 = T.grad(cost, [L1.W, L1.b, L2.W, L2.b])
#学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
#训练 updates
train = theano.function(
inputs=[x,y],
updates=[(L1.W, L1.W - learning_rate * gW1),
(L1.b, L1.b - learning_rate * gb1),
(L2.W, L2.W - learning_rate * gW2),
(L2.b, L2.b - learning_rate * gb2)])
#计算误差
compute_cost = theano.function(inputs=[x,y], outputs=cost)
print(compute_cost)
#存储cost误差
train_err_list =[]
test_err_list = []
learning_time = [] #计算每一步的i
#训练1000次 每隔10次输出
for i in range(1000):
train(x_train, y_train)
if i % 10 == 0:
#训练误差
cost1 = compute_cost(x_train, y_train)
train_err_list.append(cost1)
#预测误差
cost2 = compute_cost(x_test, y_test)
test_err_list.append(cost2)
learning_time.append(i) #对应i
print(cost1)
print(cost2)
print(i)
注意:cost前面定义了三次,我们注释掉其他两个,分别进行对比实验,结果每隔10步输出。
76.95290841879309 64.23189302430346 0 50.777745719854 32.325523689775714 10 37.604371357212884 20.74023271455164 20 ...
5.绘制图形对比
红色线为训练误差,蓝色虚线为测试结果。完整代码如下所示:
#coding:utf-8
import numpy as np
import theano.tensor as T
import theano
from theano import function
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#首先定义神经网络Layer类
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None):
#权重: 平均值为0 方差为1 行数为in_size 列数为out_size
self.W = theano.shared(np.random.normal(0,1,(in_size,out_size)))
#bias
self.b = theano.shared(np.zeros((out_size,) ) + 0.1)
#乘法加bias
self.Wx_plus_b = T.dot(inputs, self.W) + self.b #dot乘法
#激励函数
self.activation_function = activation_function
#默认为None,否则进行激活
if activation_function is None:
self.outputs = self.Wx_plus_b
else:
self.outputs = self.activation_function(self.Wx_plus_b)
#正常化处理 数据降为0-1之间
def minmax_normalization(data):
xs_max = np.max(data, axis=0)
xs_min = np.min(data, axis=0)
xs = (1-0) * (data - xs_min) / (xs_max - xs_min) + 0
return xs
#导入sklearn中的波士顿房价数据集
#500多个数据点 每个sample有13个特征去描述房价
np.random.seed(100)
x_data = load_boston().data #数据集
#minmax normalization, rescale the inputs
x_data = minmax_normalization(x_data)
print(x_data)
#增加一个维度 定义成矩阵的形式
y_data = load_boston().target[:, np.newaxis]
#print(y_data)
#cross validation, train test data split
#划分训练集和测试集
#前400个sameple或样本行作为训练集, 剩余的作为预测集
x_train, y_train = x_data[:400], y_data[:400]
x_test, y_test = x_data[400:], y_data[400:]
print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape)
print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape)
#定义x和y
x = T.dmatrix("x")
y = T.dmatrix("y")
#定义两个Layer
#L1: 13个属性,神经层有50个神经元,激活函数用tanh
L1 = Layer(x, 13, 50, T.tanh)
#L2: 输入为L1输出,输入个数为50,输出为1即房价
L2 = Layer(L1.outputs, 50, 1, None)
#the way to compute cost
#计算误差 但该方法的结果会产生Overfitting问题
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
#L2 regularization
#0.1乘以L1的权重平方求和加上L2的权重平方和
#惩罚机制: 快要进入Overfitting时,通过这个机制来惩罚不进入Overfitting
#cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
#L1 regularization
#cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())
#对比正规化和没有正规化的区别
#梯度下降定义
gW1, gb1, gW2, gb2 = T.grad(cost, [L1.W, L1.b, L2.W, L2.b])
#学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
#训练 updates
train = theano.function(
inputs=[x,y],
updates=[(L1.W, L1.W - learning_rate * gW1),
(L1.b, L1.b - learning_rate * gb1),
(L2.W, L2.W - learning_rate * gW2),
(L2.b, L2.b - learning_rate * gb2)])
#计算误差
compute_cost = theano.function(inputs=[x,y], outputs=cost)
print(compute_cost)
#存储cost误差
train_err_list =[]
test_err_list = []
learning_time = [] #计算每一步的i
#训练1000次 每隔10次输出
for i in range(1000):
train(x_train, y_train)
if i % 10 == 0:
#训练误差
cost1 = compute_cost(x_train, y_train)
train_err_list.append(cost1)
#预测误差
cost2 = compute_cost(x_test, y_test)
test_err_list.append(cost2)
learning_time.append(i) #对应i
print(cost1)
print(cost2)
print(i)
#plot cost history
plt.plot(learning_time, train_err_list, 'r-') #红色线为训练误差
plt.plot(learning_time, test_err_list, 'b--') #蓝色虚线为测试结果
plt.show()
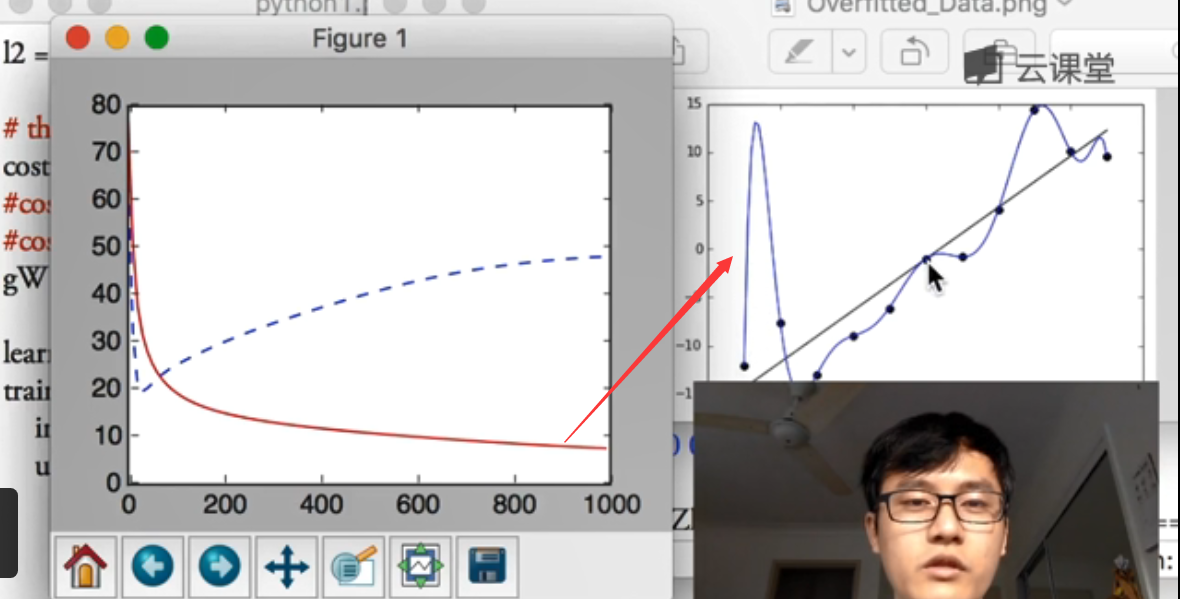
(1)Overfitting问题对应曲线,红色线为训练误差,蓝色虚线为测试结果,会发现预测的误差在不断变大。cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y))
参考莫烦大神视频原图,对应的蓝色曲线就没有黑色直线预测效果好,也看看大神风貌吧,也推荐大家去学习,哈哈!
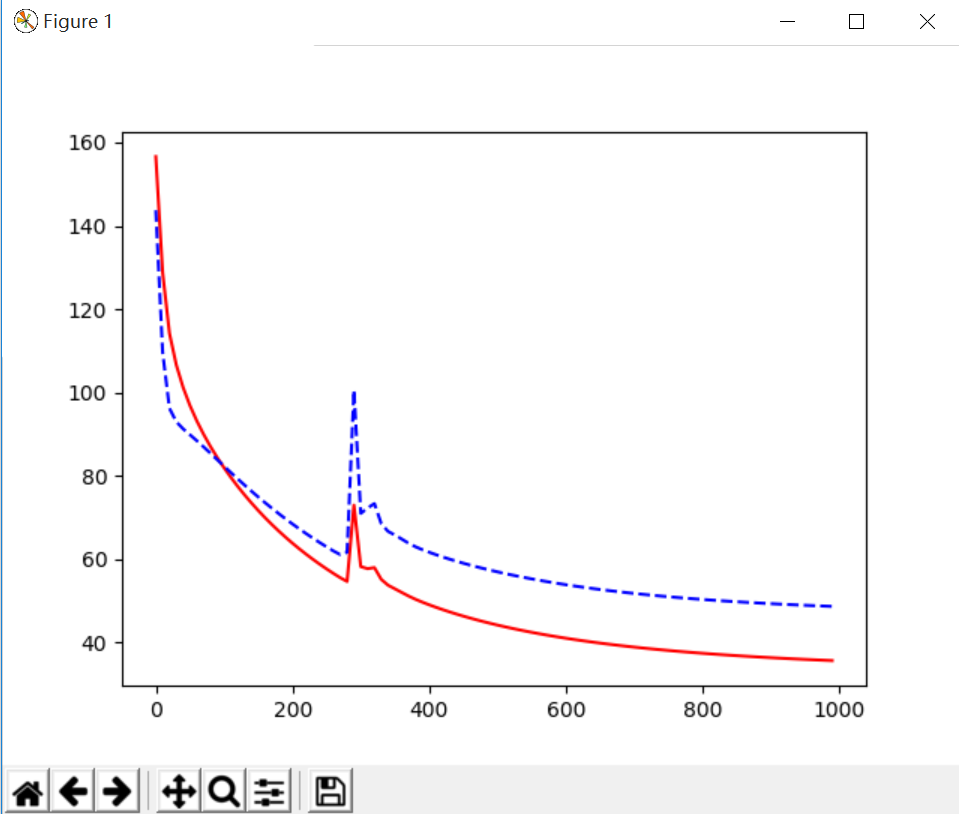
(2)L2 Regularization,通过正规化处理后的结果,发现预测结果和训练结果的误差变化基本一致,其效果更好。
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*((L1.W**2).sum() + (L2.W**2).sum())
这里输出了1000个,而输出100个值如下所示:
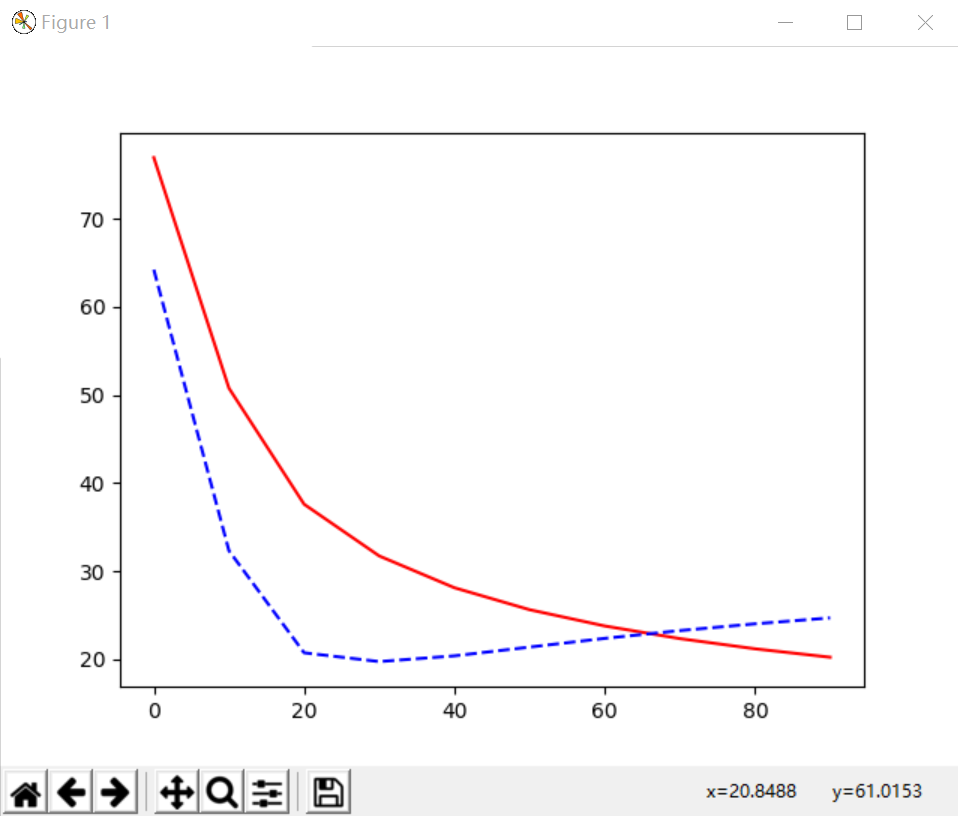
(3)L1 regularization输出结果如下图所示:
cost = T.mean(T.square(L2.outputs-y)) + 0.1*(abs(L1.W).sum() + abs(L2.W).sum())

一个人如果总是自己说自己厉害,那么他就已经再走下坡路了,最近很浮躁,少发点朋友圈和说说吧,更需要不忘初心,砥砺前行。珍惜每一段学习时光,也享受公交车的视频学习之路,加油,最近兴起的傲娇和看重基金之心快离去吧,平常心才是更美,当然娜最美,早安。
(By:Eastmount 2018-06-01 下午5点 http://blog.csdn.net/eastmount/ )