类图
代码
深克隆
浅克隆
总结
1. 类图
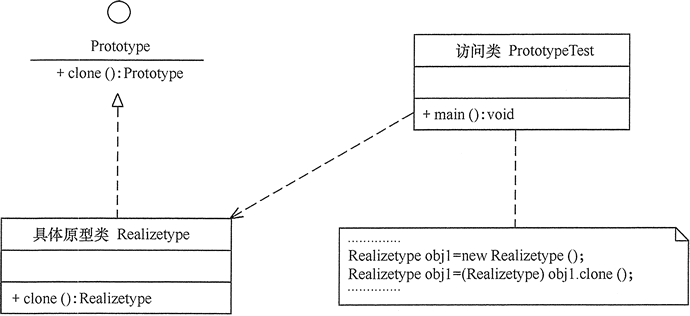
2. 代码
- 浅克隆:实现Cloneable接口,重写clone()方法(格式固定)
- 深克隆:实现Serializable接口,通过序列化将对象写到一个流中,再从流里将其读出来,可以实现深克隆
2.1 浅克隆
- 需要被克隆的类
-
class Prototype implements Cloneable{ public Prototype clone(){ Object object = null; try { object = super.clone(); }catch(CloneNotSupportedException exception){ System.err.println("Not support cloneable"); } return (Prototype)object; } }
-
- 客户端调用
-
public class PrototypeTest { public static void main(String[] args)throws CloneNotSupportedException { Prototype obj1 = new Prototype(); Prototype obj2 = (Prototype )obj1.clone(); System.out.println("obj1==obj2?"+(obj1==obj2)); //false } }
-
2.2 深克隆
-
import java.io.*; class WeeklyLog implements Serializable{ private Attachment attachment; //attachment为引用类型 private String name; public void setAttachment(Attachment attachment) { this.attachment = attachment; } public Attachment getAttachment(){ return (this.attachment); } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getName() { return (this.name); } //使用序列化技术实现深克隆 public WeeklyLog deepClone() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, OptionalDataException{ ByteArrayOutputStream bao=new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //将对象写入流中 ObjectOutputStream oos=new ObjectOutputStream(bao); oos.writeObject(this); ByteArrayInputStream bis=new ByteArrayInputStream(bao.toByteArray()); //将对象从流中取出 ObjectInputStream ois=new ObjectInputStream(bis); return (WeeklyLog)ois.readObject(); } }
3. 总结
浅克隆
- 类本身:不同地址
- 成员变量——值类型:不同地址
- 成员变量——引用类型:相同地址
深克隆
- 类本身:不同地址
- 成员变量——值类型:不同地址
- 成员变量——引用类型:不同地址
clone()方法:
- 任何对象x,都有x.clone() != x,即克隆对象与原型对象不是同一个对象
- 任何对象x,都有x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass(),即克隆对象与原型对象的类型一样
原型模式优缺点:
- 优点:基于内存二进制流的复制,性能大于new关键字
- 缺点:需要为每一个类都配置一个 clone 方法;代码修改比较麻烦