ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
简介:ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor用于执行周期性或延时性的定时任务,它继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,在原有基础上实现的任务调度线程池,内部使用延时工作队列DelayedWorkQueue实现对任务的延时调度。
构造方法
简介: ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor类继承的是ThreadPoolExecutor。而且它的构造方法都是super调用父类方法。
由构造方法可以得知,ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的一些默认参数:
- 最大线程数是
Integer.MAX_VALUE - 默认空闲线程存活时间是0纳秒。
- 默认缓存队列是
DelayedWorkQueue(DelayedWorkQueue内部使用一个初始容量为16的数组来保存任务,容量不够时会按照现有容量的1.5倍进行扩容,最大容量可达Integer.MAX_VALUE。)
可设置的参数仅为核心线程数,拒绝策略和线程工厂
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue());
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler);
}
public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS,
new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler);
}
重要内部类
ScheduledFutureTask
谱系
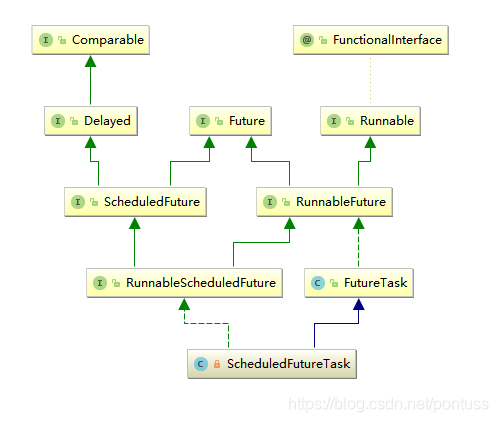
1.源码
1.1 成员变量
private class ScheduledFutureTask<V>
extends FutureTask<V>
implements RunnableScheduledFuture<V> {
/** Sequence number to break ties FIFO
* 任务在队列中的序号
*/
private final long sequenceNumber;
/** The time the task is enabled to execute in nanoTime units
* 任务应该执行的时间,以纳秒计算
* */
private long time;
/**
* Period in nanoseconds for repeating tasks.
* A positive value indicates fixed-rate execution.
* A negative value indicates fixed-delay execution.
* A value of 0 indicates a non-repeating task.
* 任务重复执行的时间间隔,以纳秒计算
* 当其为正值时,表示固定速率执行
* 当其为负值时,表示固定延迟执行
* 当其为0时,表示是非重复任务
*/
private final long period;
/** The actual task to be re-enqueued by reExecutePeriodic */
RunnableScheduledFuture<V> outerTask = this;
/**
* Index into delay queue, to support faster cancellation.
*/
int heapIndex;
/**
* Creates a one-shot action with given nanoTime-based trigger time.
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* Creates a periodic action with given nano time and period.
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns, long period) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = period;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* Creates a one-shot action with given nanoTime-based trigger time.
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Callable<V> callable, long ns) {
super(callable);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS);
}
public int compareTo(Delayed other) {
if (other == this) // compare zero if same object
return 0;
if (other instanceof ScheduledFutureTask) {
ScheduledFutureTask<?> x = (ScheduledFutureTask<?>)other;
long diff = time - x.time;
if (diff < 0)
return -1;
else if (diff > 0)
return 1;
else if (sequenceNumber < x.sequenceNumber)
return -1;
else
return 1;
}
long diff = getDelay(NANOSECONDS) - other.getDelay(NANOSECONDS);
return (diff < 0) ? -1 : (diff > 0) ? 1 : 0;
}
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this is a periodic (not a one-shot) action.
*
* @return {@code true} if periodic
*/
public boolean isPeriodic() {
return period != 0;
}
/**
* Sets the next time to run for a periodic task.
*/
private void setNextRunTime() {
long p = period;
if (p > 0)
time += p;
else
time = triggerTime(-p);
}
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
boolean cancelled = super.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning);
if (cancelled && removeOnCancel && heapIndex >= 0)
remove(this);
return cancelled;
}
/**
* Overrides FutureTask version so as to reset/requeue if periodic.
*/
public void run() {
boolean periodic = isPeriodic();
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic))
cancel(false);
else if (!periodic)
ScheduledFutureTask.super.run();
else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) {
setNextRunTime();
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
}
- sequenceNumber : 用于标识在等待队列中的顺序,因为可能会碰到多个任务的延时是一样的,所以需要另一个序号进行区分标记;
- time : 字段用于记录计算出来的任务执行时间;
- period:字段用于标识任务是否是定时任务,当该字段为正值时,表示是周期性重复任务,当该值为负值时,表示是延迟性重复任务,当该值为0时,表示是非重复任务;
- outerTask:用于记录当前任务,它的默认值就指向自己;该成员变量主要用在重复性任务中,当前一次任务执行结束时,任务会通过outerTask将自己再次加入到等待队列中,以实现重复执行,它的作用会在后面的源码中进行讲解;
- heapIndex:用于记录任务在队列中的堆排序顺序。ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor内部使用DelayedWorkQueue作为任务的等待队列,该队列的具体实现其实是一个小顶堆结构,heapIndex则记录了每个任务在堆中的排序顺序
1.2 构造方法
/**
* Creates a one-shot action with given nanoTime-based trigger time.
* 根据给定时间,创建一个执行一次的任务
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* Creates a periodic action with given nano time and period.
* 根据给定开始时间和间隔时间,创建周期性任务
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns, long period) {
super(r, result);
this.time = ns;
this.period = period;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
/**
* Creates a one-shot action with given nanoTime-based trigger time.
* 根据给定时间,创建一个执行一次的任务
*/
ScheduledFutureTask(Callable<V> callable, long ns) {
super(callable);
this.time = ns;
this.period = 0;
this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement();
}
DelayedWorkQueue等待队列
定义
DelayedWorkQueue是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的一个静态内部类
2.1 结构
/**
* Specialized delay queue. To mesh with TPE declarations, this
* class must be declared as a BlockingQueue<Runnable> even though
* it can only hold RunnableScheduledFutures.
* 延时队列,用于装载被执行的任务,然后根据调度配置进行入队和出队操作
* 小顶堆模式实现
*/
static class DelayedWorkQueue
extends AbstractQueue<Runnable>
implements BlockingQueue<Runnable>
DelayedWorkQueue 是实现了 BlockingQueue 的阻塞队列,且泛型指定的是Runnable。
2.2 成员变量
//初始容量为16
private static final int INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16;
//装任务的数组 扩容的时候按原有的1.5倍
private RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[] queue =
new RunnableScheduledFuture<?>[INITIAL_CAPACITY];
//可重入锁
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//已有元素个数
private int size = 0;
//试图执行队首任务的正处于等待状态的线程对象
private Thread leader = null;
//等待条件
private final Condition available = lock.newCondition();
2.3 DelayedWorkQueue堆结构
2.3.1 任务入队
DelayedWorkQueue中的元素会根据ScheduledFutureTask任务对象执行时间的先后以及其在初始化时获取的sequenceNumber从小到大进行排序,以便实现任务的先后调度。
我们首先关注与任务入队的相关的方法:
put(Runnable e)
add(Runnable e)
offer(Runnable e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
offer(Runnable x);
实际前三个方法内部都调用了offer(Runnable x),它们的源码如下:
// 添加任务,内部调用offer()
public void put(Runnable e) {
offer(e);
}
// 添加任务,内部调用offer()
public boolean add(Runnable e) {
return offer(e);
}
// 添加任务,内部调用offer()
public boolean offer(Runnable e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
return offer(e);
}
所以主要关注的点在于
// 添加任务
public boolean offer(Runnable x) {
// 检查任务
if (x == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//将任务转换为RunnableScheduledFuture对象
RunnableScheduledFuture e = (RunnableScheduledFuture)x;
// 加锁
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
// 如果任务个数大于等于队列数组容量,进行扩容操作
grow();
// size加1
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0) {
/**
* i为0,即原始size为0,没有任务
* 将e放在第0位置
*/
queue[0] = e;
// 设置e的heapIndex为0
setIndex(e, 0);
} else {
// 否则调用siftUp()对e进行添加及上浮操作
siftUp(i, e);
}
/**
* 如果第0个位置的任务是e,
* 表示此时入队的是队首元素,可以将leader清空了
* 同时可以通知其他线程可以竞争成为leader了
*/
if (queue[0] == e) {
// 将leader置为null
leader = null;
// 唤醒等待在available上的线程
available.signal();
}
} finally {
// 解锁
lock.unlock();
}
return true;
}
2.3.2 任务出队
DelayedWorkQueue的任务出队操作则相对比较麻烦,它提供了
poll()
poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
take()
三个出队方法。其中poll()方法最简单,它是无阻塞模式的出队操作,如果能获取到符合要求的任务就进行出队,否则直接返回null;

2.3.3. 任务移除
DelayedWorkQueue提供了remove(Object x)方法可以将队列中的任务进行移除;
remove方法无新颖套路,详情见源码;