CentOS7 运维 - Nginx配置教程
一、Nginx概述
一款高性能轻量级的Web服务软件
二、Nginx 服务状态
① 开启服务
nginx -t 检查配置文件语法结构是否正确
cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid 查看nginx的PID号
更多查看进程号的方法
lsof -i :80
netstat -natp | grep nginx
ss -tnlp | grep nginx
ps -ef | grep nginx
pgrep nginx

② 停止服务
kill后面跟pid号killall后面跟进程名
kill -3 <PID号>
kill -s QUIT <PID号>
killall -3 nginx
killall -s QUIT nginx

③ 重载服务
kill -1 <PID号>
kill -s HUP <PID号>
killall -1 nginx
killall -s HUP nginx
④ 日志分割
原理:当满足一定条件时,保存并删除旧的日志
kill -USR1 <PID号>
⑤ 平滑升级
kill -USR2 <PID号>
三、添加程序系统服务
方法一:systemctl
echo '
[Unit]
Description=nginx
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
ExecReload=/bin/kill -s HUP $MAINPID
ExecStop=/bin/kill -s QUIT $MAINPID
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target' > /lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
方法二:init.d
vim /etc/init.d/nginx
#!/bin/bash
#chkconfig: - 99 20
#description:Nginx 服务
COM="/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx"
PID="/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid"
case "$1" in
start)
$COM
;;
stop)
kill -s QUIT ${cat PID}
;;
restart)
$0 stop
$0 start
;;
reload)
kill -s HUP ${cat PID}
;;
*)
exit 1
esac
exit 0
添加系统服务并赋予执行权限
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nginx
chkconfig --add nginx
四、Nginx主配置文件
user_nobody 运行用户,若编译时未指定则默认为nobdy
worker_processes 1; 工作进程数量 可配置为内核数 * 2[一般1就够了]
error_log logs/error.log; 错误日志的位置
pid logs/nginx.pid PID文件位置
① 如何提高性能
I/O事件配置
events {
use epoll;
#2.6以上版本的系统核心建议使用epoll模型以提高性能
worker _connections 4095
#每个进程处理 4096 个连接
}
② 如何提高每个进程的连接数?
在Linux平台进行高并发TCP连接处理时,最高的并发数量都要受到系统对
用户单一进程同时可打开文件数量的限制。每个TCP连接都要创建一个socket
每个socket句柄同时也是一个文件句柄
ulimit -n 65535 临时修改本地每个进程可以同时打开的最大文件数
ulimit -a 可以查看当前系统用户可以打开最大文件数[open files项]
五、HTTP配置
http {
##文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include mime.types;
##默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
##日志格式设定
#log_format main '$remote_ addr - $remote. user [stime_ local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_ bytes_ sent "Shttp_ referer" '
# "$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
##访问日志位置
#access_Log logs/access.log main;
#支持文件发送(下载)
sendfile on;
##此选项允许或禁止使用socket的TCP_CORK的选项( 发送数据包前先缓存数据),此选项仅在使用sendfile的时候使用
#tcp_nopush on;
##连接保持超时时间,单位是秒
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive.timeout 65;
##gzip模块设置,设置是否开启gzip压缩输出
#gzip on;
#Web服务的监听配置
##Web服务的监听配置
server (
##监听地址及端口
listen 80;
##站点域名,可以有多个,用空格隔开
server.name www.benet.com;
##网页的默认字符集
charset utf-8;
##根目录配置
location / {
##网站根目录的位置/usr/local/nginx/html
root html;
##默认首页文件名
index index.html index.php;
}
##内部错误的反馈页而
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
#错误页而配置
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
六、日志格式设定
$remote_addr与$http_x_forwarded_for用以记录客户端的ip地址;
$remote_user: 用来记录客户端用卢名称;
$time_local: 用来记录访问时间与时区;
$request: 用来记录请求的url与http协议;
$status: 用来记录请求状态,成功是200;
$body_bytes_sent: 记录发送给客户端文件主体内容大小;
$http_referer: 用来记录从那个页面链接访问过来的;
$http_user_agent: 记录客户浏览器的相关信息;
通常web服务器放在反向代理的后面,这样就不能获取到客户的IP地址了,通过$remote_add拿到的IP地址是反向代理服务器的IP地址。反问代理服务器在转发请求的http头信息中,可以增加x_forwarded_for信息,用以记录原有客户端的IP地址和原来客户端的请求的服务器地址。
##location常见配置指令,root、alias、proxy_pass
root(根路径配置): 请求www.benet.com/1.jpg,会返回文件/usr/local/nginx/html/test/1.jpg
alias(别名配置): 请求ww . benet.com/test/1.jpg,会返回文件/usr/local/nginx/html/1.jpg
proxy_pass(反向代理配置>;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080/; 会转发请求到http://127.0.0.1:8080/1.jpg
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8080;
七、访问状态统计
查看是否有HTTP_STUB_STATUS模块
nginx -t

进入nginx主配置文件并添加stub_status
cd /usr/local/nginx/conf
cp nginx.conf{
,.bak}
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
.....
http {
.....
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.html;
}
##添加stub_status 配置##
location /status {
#访问位置为/status
stub_status on; #打开状态统计功能
access_log off; #关闭此位置的日志记录
}
}
}

八、Nginx访问控制
① 基于授权的访问控制
生成用户密码认证文件
也可通过在线生成
yum install -y httpd-tools
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db fox
如果删除了普通用户的权限就需要设置文件的属主
chown nginx /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db
chmod 700 /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db

修改主配置文件相对应目录,添加认证配置项
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
......
server {
location / {
......
##添加认证配置##
auth_basic "secret" ;
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db;
}
}

② 基于客户端的访问控制
访问控制规则如下
deny IP/IP 段:拒绝某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问
allow IP/IP 段:允许某个 IP 或 IP 段的客户端访问
规则从上往下执行,如匹配则停止,不再往下匹配
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
server {
location / {
#添加控制规则
deny 192.168.0.10;
#拒绝访问的客户端IP
allow all;
#允许其它IP客户端访问
}
}
systemctl restart nginx

九、Nginx虚拟主机
① 基于域名的虚拟主机
echo "192.168.0.50 www.benet.com www.accp.com" >> /etc/hosts
►为虚拟主机准备网页文档
mkdir -p /var/www/html/accp
mkdir -p /var/www/html/benet
echo "<h1>www.accp.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/accp/index.html
echo "<h1>www.benet.com</h1>" > /var/www/html/benet/index.html
►修改Nginx的配置文件
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.accp.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.accp.com.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/accp;
index index.html index.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.com.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/benet;
index index.html index.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
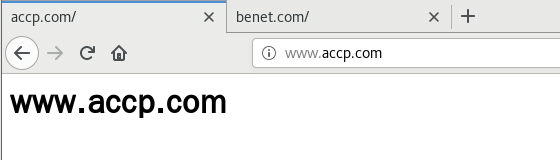
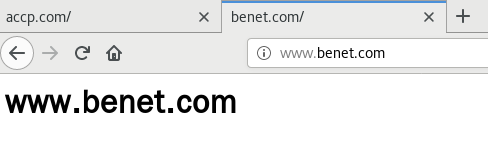
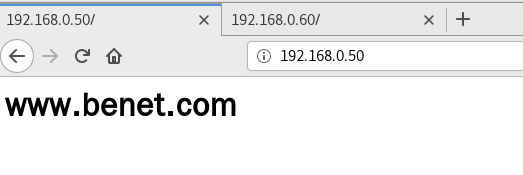
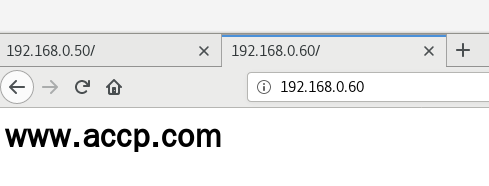
② 基于IP的虚拟主机
ifconfig ens33:0 192.168.0.60/24
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
server {
listen 192.168.0.50:80;
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/benet;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 192.168.0.60:80;
server_name www.accp.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.accp.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/accp;
index index.html index.html;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx
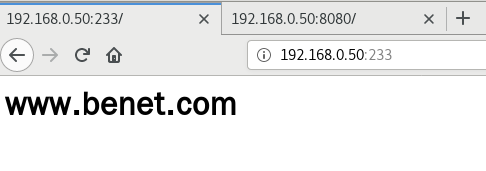
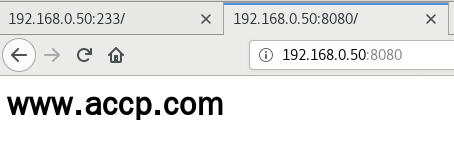
③ 基于端口的虚拟主机
vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
http {
server {
listen 192.168.0.50:233;
server_name www.accp.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.accp.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/accp;
index index.html index.html;
}
error_page 500 502. 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
server {
listen 192.168.0.50:8080;
server_name www.benet.com;
charset utf-8;
access_log logs/www.benet.access.log;
location / {
root /var/www/html/benet;
index index.html index.php;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = 50x.html{
root html;
}
}
}
nginx -t
systemctl restart nginx.service