学习笔记04-第五章 类和对象
用书参考:孙连英,刘畅,彭涛所著的Java面向对象程序设计。
我的所有代码你都可以通过GitHub获取,
以下为我的GitHub地址:[[https://github.com/MrNeoJeep/java-code.git]]
(1)下图描述了student类的设计,编写代码
下图描述了student类的设计,编写代码编写一个用于测试student类的测试类,测试类中可以创建两个或三个学生(或学生数组更好)并且使用student类测试他们是否按照声明执行操作
代码
public class Text5_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*下图描述了student类的设计,编写代码
* 编写一个用于测试student类的测试类,测试类中可以创建两个或三个学生(或学生数组更好)
* 并且使用student类测试他们是否按照声明执行操作
* */
//测试
testStudent test1 = new testStudent();
test1.setMarks1(98, 97, 90);
test1.setMarks2(95, 94, 92);
test1.setMarks3(88, 97, 93);
test1.settings();
test1.testCal();
}
}
//测试student类的设计
class testStudent
{
Student s1 = new Student("①", "Tom");
Student s2 = new Student("②", "Kitti");
Student s3 = new Student("③", "Lili");
String Num[] = new String[3];
String Name[] = new String[3];
int mathsMark[] = new int[3];
int EngMark[] = new int[3];
int SciMark[] = new int[3];
public void setMarks1(int mathsMark,int EngMark,int SciMark)
{
s1.enterMarks(mathsMark, EngMark, SciMark);
}
public void setMarks2(int mathsMark,int EngMark,int SciMark)
{
s2.enterMarks(mathsMark, EngMark, SciMark);
}
public void setMarks3(int mathsMark,int EngMark,int SciMark)
{
s3.enterMarks(mathsMark, EngMark, SciMark);
}
public void settings()
{
Num[0] = s1.getNumber();
Num[1] = s2.getNumber();
Num[2] = s3.getNumber();
Name[0] = s1.getName();
Name[1] = s2.getName();
Name[2] = s3.getName();
mathsMark[0] = s1.getMarkForMaths();
mathsMark[1] = s2.getMarkForMaths();
mathsMark[2] = s3.getMarkForMaths();
EngMark[0] = s1.getMarkForEnglish();
EngMark[1] = s2.getMarkForEnglish();
EngMark[2] = s3.getMarkForEnglish();
SciMark[0] = s1.getMarkForScience();
SciMark[1] = s2.getMarkForScience();
SciMark[2] = s3.getMarkForScience();
}
public void testCal()
{
System.out.printf("%s同学的平均成绩是:%.2f\n",s1.getName(),s1.calculateAverageMark());
System.out.printf("%s同学的平均成绩是:%.2f\n",s2.getName(),s2.calculateAverageMark());
System.out.printf("%s同学的平均成绩是:%.2f\n",s3.getName(),s3.calculateAverageMark());
}
}
//student类的设计
class Student
{
private String studentNumber;
private String studentName;
private int markForMaths = -1;
private int markForEnglish = -1;
private int markForScience = -1;
//构造方法
public Student(String studentNumber,String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentNumber = studentNumber;
}
public String getNumber() {
return studentNumber;
}
public String getName() {
return studentName;
}
public void enterMarks(int markForMaths,int markForEnglish,int markForScience )
{
this.markForEnglish = markForEnglish;
this.markForMaths = markForMaths;
this.markForScience = markForScience;
}
public int getMarkForMaths() {
return markForMaths;
}
public int getMarkForEnglish() {
return markForEnglish;
}
public int getMarkForScience() {
return markForScience;
}
public double calculateAverageMark()
{
return (double)(this.markForEnglish+this.markForMaths+this.markForScience)/3;
}
}
运行结果

(2)开发一个电器商店管理系统。系统中有名为StockItem(商品)的类
stockItem有以下属性:货品编号,货品名称,商品价格和当前存储的商品总数
前三个属性需要在对象创建时被设定(即构造方法中设置)。库存品总数在对象创建时设置为0
货品创建后库存变化与货品名不应该被修改
类中的方法有:
1、在对象生命周期内允许重设价格的方法、
2、接受一个整型参数,将它添加到同类商品的总数中
3、返回商品总价值的方法
4、读取四个属性的方法
5、编写stockItem类的方法
6、编写测试stockItem类的测试程序,要求创建一个电器TV,将库存量增加200台,显示库存总价值
7、添加一个属性salasTax。该属性的值对于类的每一个对象都一样编写该语句的声明语句
8、添加一个名为setSalesTax的方法,他接收double类型的参数,
将该值赋值给商品税款。编写一行代码,将该类所有对象的商品税款设定为8,
但不能引用任何的特定对象。
代码
public class Text5_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*开发一个电器商店管理系统。系统中有名为StockItem(商品)的类。
* stockItem有以下属性:货品编号,货品名称,商品价格和当前存储的商品总数
* 前三个属性需要在对象创建时被设定(即构造方法中设置)。库存品总数在对象创建时设置为0
* 货品创建后库存变化与货品名不应该被修改
* 类中的方法有:
* 1、在对象生命周期内允许重设价格的方法、
* 2、接受一个整型参数,将它添加到同类商品的总数中
* 3、返回商品总价值的方法
* 4、读取四个属性的方法
* 5、编写stockItem类的方法
* 6、编写测试stockItem类的测试程序,要求创建一个电器TV,将库存量增加200台,显示库存总价值
* 7、添加一个属性salasTax。该属性的值对于类的每一个对象都一样编写该语句的声明语句
* 8、添加一个名为setSalesTax的方法,他接收double类型的参数,
* 将该值赋值给商品税款。编写一行代码,将该类所有对象的商品税款设定为8,
但不能引用任何的特定对象。
* */
TestStockItem T1 = new TestStockItem();
T1.test();
}
}
//测试类程序
class TestStockItem
{
StockItem item_TV = new StockItem(1, "TV", 1999);
public void test()
{
item_TV.increaseTotalStock(200);
item_TV.setM_SalesTax(8);
System.out.println("库存总价值:"+item_TV.calculateTotalPrice());
}
}
//stockItem类
class StockItem
{
private int m_ItemSerialNum;
private String m_ItemName;
private double m_ItemPrice;
private int m_TotalNum = 0;
private double m_salesTax;
public StockItem(int ItemSerialNum,String ItemName,double ItemPrice)
{
this.m_ItemSerialNum = ItemSerialNum;
this.m_ItemName = ItemName;
this.m_ItemPrice = ItemPrice;
}
public double getM_ItemPrice() {
return m_ItemPrice;
}
public void setM_ItemPrice(double m_ItemPrice) {
this.m_ItemPrice = m_ItemPrice;
}
public int getM_ItemSerialNum() {
return m_ItemSerialNum;
}
public String getM_ItemName() {
return m_ItemName;
}
public int getM_TotalNum() {
return m_TotalNum;
}
public void setM_SalesTax(double tax)
{
this.m_salesTax = tax;
}
public void increaseTotalStock(int num)
{
this.m_TotalNum += num;
}
public double calculateTotalPrice()
{
double price;
price = this.m_ItemPrice*this.m_TotalNum;
return price;
}
}
运行结果

(3)编写一个studentList类用来存储练习(1)中描述的student对象。下面的UML图描述了StudentList对象和student对象的关系。
代码
package demo.USTS.chapter5;
public class Text5_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*编写一个studentList类用来存储练习(1)中描述的student对象。
* 下面的UML图描述了StudentList对象和student对象的关系。
* */
StudentList list1 = new StudentList(4);
student stu1 = new student("①", "Tom",30,20,30);
student stu2 = new student("②", "Kitti",89,88,49);
student stu3 = new student("③", "Lili",89,76,77);
list1.add(stu1);
list1.add(stu2);
list1.add(stu3);
System.out.println("总数为:"+list1.getTotal());
list1.getItem("①");
list1.getItem("②");
list1.getItem("③");
}
}
//学生列表
class StudentList
{
student[] list;
int total = 0;
StudentList(int length)
{
list = new student[length];//长度
}
//判断数组是否为空
public boolean isEmpty()
{
if(total == 0)
{
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
//判断数组是否满
public boolean isFull()
{
if(total == list.length-1)
{
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
//添加函数
public boolean add(student stu)
{
if(isFull())
{
return false;
}
else {
list[total] = new student(stu.studentNumber, stu.studentName,stu.markForMaths,stu.markForEnglish,stu.markForScience);
total++;
return true;
}
}
//移除函数
public boolean remove(String number)
{
if(isEmpty())
{
return false;
}
else {
for(int i = 0; i < total;i++)
{
if(list[i].studentNumber == number)
{
for(int j = i; j < total-1;j++)
{
list[j] = list[j+1];
}
}
total--;
}
return true;
}
}
student [] arr = new student[5];
public void getItem(String number)
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
for(int i = 0;i <= total;i++)
{
if(list[i].studentNumber == number)
{
System.out.println(list[i].studentNumber);
System.out.println(list[i].studentName);
System.out.println("英语成绩:"+list[i].markForEnglish);
System.out.println("数学成绩:"+list[i].markForMaths);
System.out.println("科学成绩:"+list[i].markForScience);
return;
}
}
}
else {
System.out.println("空");
}
}
public int getTotal() {
return total;
}
}
class student
{
String studentNumber;
String studentName;
int markForMaths = -1;
int markForEnglish = -1;
int markForScience = -1;
//构造方法
public student(String studentNumber,String studentName,int markForMaths,int markForEnglish,int markForScience) {
this.studentName = studentName;
this.studentNumber = studentNumber;
this.markForEnglish = markForEnglish;
this.markForMaths = markForMaths;
this.markForScience = markForScience;
}
public String getNumber() {
return studentNumber;
}
public String getName() {
return studentName;
}
public int getMarkForMaths() {
return markForMaths;
}
public int getMarkForEnglish() {
return markForEnglish;
}
public int getMarkForScience() {
return markForScience;
}
public double calculateAverageMark()
{
return (double)(this.markForEnglish+this.markForMaths+this.markForScience)/3;
}
}
运行结果
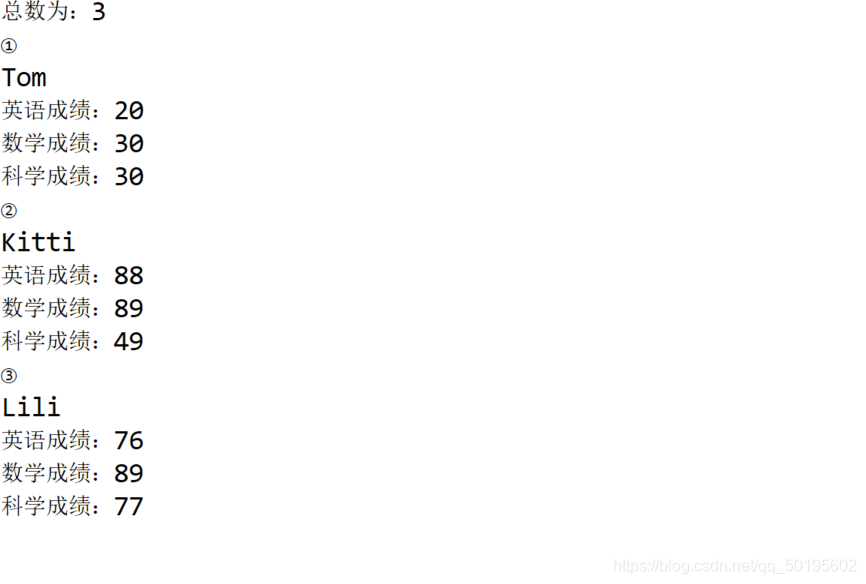
(4)设计并实现一个Day类用于表示一周中的某一天
Day类可以表示出是星期几,
例如sun是表示星期天。对一个Day类型的对象
程序可以实现以下操作
1、设置星期几
2、显示星期几
3、返回星期几
4、返回下一天
5、返回前一天
6、计算并返回当天之后的某一天是星期几。
7、添加适当的构造方法
8、定义一组方法实现在上面(1)~(7)中指定的对Day类的操作。
9、编写一段程序来测试对Day类的各种操作。
代码
public class Text5_4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*设计并实现一个Day类用于表示一周中的某一天。Day类可以表示出是星期几,
* 例如sun是表示星期天。对一个Day类型的对象
程序可以实现以下操作
1、设置星期几
2、显示星期几
3、返回星期几
4、返回下一天
5、返回前一天
6、计算并返回当天之后的某一天是星期几。
7、添加适当的构造方法
8、定义一组方法实现在上面(1)~(7)中指定的对Day类的操作。
9、编写一段程序来测试对Day类的各种操作。
* */
Day day = new Day("星期四");
day.show();
String nextdayString = day.nextDay();
String frontdayString = day.frontDay();
System.out.println("星期四后一天: " + nextdayString);
System.out.println("星期四前一天: " + frontdayString);
String calString = day.calculate(13);
System.out.println("13天后为: " + calString);
}
}
//day类
class Day
{
String []arr = {
"星期一","星期二","星期三","星期四","星期五","星期六","星期日"};
//表示星期几
String week;
int num;
//构造方法,设置星期几
Day(String week)
{
this.week = week;
for(int i = 0 ;i < arr.length;i++)
{
if(arr[i] == this.week)
{
this.num = i;
}
}
}
//显示星期几
public void show()
{
System.out.println("今天是"+this.week );
}
//返回星期几
public String returnWeek()
{
return this.week;
}
//返回下一天
public String nextDay()
{
if(this.num == 6)
{
return arr[0];
}
else {
return arr[this.num+1];
}
}
//返回前一天
public String frontDay()
{
if(this.num == 0)
{
return arr[6];
}
else {
return arr[this.num-1];
}
}
//计算这一天后的之后某一天是星期几
public String calculate(int in_num)
{
int temp = (this.num + in_num) % 7;
return arr[temp];
}
}
运行结果

初学java,代码多有不足,如有错误,非常感谢你的指正。