命名实体识别是AllenNLP的核心模块之一。在官网上介绍如下:
Named Entity Recognition
The named entity recognition model identifies named entities (people, locations, organizations, and miscellaneous) in the input text. This model is the "baseline" model described in Peters, Ammar, Bhagavatula, and Power 2017 . It uses a Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU) character encoder as well as a GRU phrase encoder, and it starts with pretrained GloVe vectors for its token embeddings. It was trained on the CoNLL-2003 NER dataset. It is not state of the art on that task, but it's not terrible either. (This is also the model constructed in our Creating a Model tutorial.)
1、命名实体采用论文原理
命名实体识别(Named Entity Recognition,NER)就是从一段自然语言文本中找出相关实体,并标注出其位置以及类型,它是 NLP 领域中一些复杂任务(例如关系抽取,信息检索等)的基础。那么AllenNLP采用的模型是ACL2017 刚录用的一篇论文《Semi-supervised sequence tagging with bidirectional language models》。该论文使用海量无标注语料库训练了一个双向神经网络语言模型,然后使用这个训练好的语言模型来获取当前要标注词的语言模型向量(LM embedding),然后将该向量作为特征加入到原始的双向 RNN-CRF 模型中。
论文的模型流程如下:即分为三个步骤:1是训练词向量和语言模型向量(LM);2是对每个输入句子用1的结果进行向量化;3是基于两个向量进行序列标注。
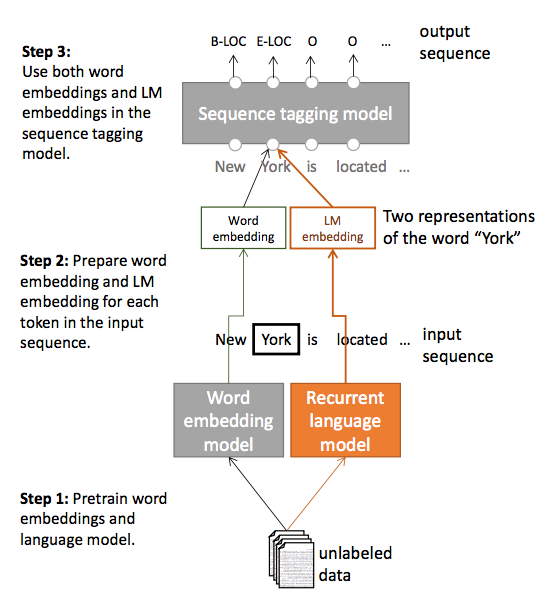
实验结果表明,在少量标注数据上,加入这个语言模型向量能够大幅度提高 NER 效果,即使在大量的标注训练数据上,加入这个语言模型向量仍能提供原始 RNN-CRF 模型的效果。
2、AllenLP+NER实践
官网上的测试DEMO运行如下:
利用重构代码运行如下:
echo '{"sentence": "Did Uriah honestly think he could beat The Legend of Zelda in under three hours?"}' > examples.json
python -m allennlp.run predict ./models/ner-model-2018.02.12.tar.gz ./data/examples.json
后续结果:
速度非常地快,后续可以研究一下其支持中文的问题


