1.问题描述:
复杂背景下目标检测存在诸多困难,主要为背景对目标检测的干扰,大量噪声存在导致传统导数边缘检测方法的失效等。本文正是针对上述两点,提出了分割区域图像、利用形态学方法检测目标的新算法;即首先利用目标与背景灰度差异性来确定目标的大致区域,将其分割出来,然后再结合多结构元素法进行目标的精确检测。通过与原图像分割、聚类算法分割实验比较,该算法在文中的应用实例中表现出了较好的抗干扰性和抗噪性能。
2.部分程序:
clc;clear;close all;
tic
I0= imread('D:\photo\01.jpg'); % 'D:\photo\5.10\DSC01587.JPG'
figure;imshow(I0);
I1=rgb2gray(I0);
I1=medfilt2(I1,[3 3]);
[x,y]=size(I1); %求出图象大小
%figure,imshow(I1);
s=strel('disk',15); %Top-Hat变换
I2=imopen(I1,s);
%figure,imshow(I2);
title('开运算');
I3=imsubtract(I1,I2);
figure, imshow(I3);title('高帽变换')
se2=strel('disk',4); %去除干扰及虚假目标点
I4=imerode(I3,se2);
%figure, imshow(I4);title('腐蚀运算');
se3=strel('diamond',3);
I5=imdilate(I4,se3);
%figure, imshow(I5);title('膨胀运算')
Seg=zeros(x,y);
z0=max(max(I1)); % 求出图象中最大的灰度
z1=min(min(I1)); % 最小的灰度
T=(z0+z1)*0.5; % 设定阈值
for i=1:x
for j=1:y
if(I5(i,j)>=T)
Seg(i,j)=1; % 阈值分割的图象
end
end
end
m=Seg;
figure,subplot(2,2,1),imshow(m);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%在原图上用矩形框标注%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%subplot(2,2,2),imshow(I1);
hold on;
cou=1;
for h=1:x
for w=1:y
if(m(h,w)>0.5)
toplen = h; % topIen 最上纵坐标
if (cou == 1)
tpln=toplen; % tpIn 最下纵坐标
end
cou=cou+1;
end
end
end
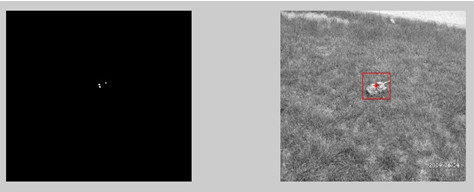
3.仿真结论:
D-10