1.1 项目目录

1.2 代码示例
持久层(Dao)
CustomerDao
package cn.guardwhy.dao;
/**
* 客户dao接口
*/
public interface CustomerDao {
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
void saveCustomer();
}
CustomerDaoImpl
package cn.guardwhy.dao.impl;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.CustomerDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 客户dao实现类
*/
@Component("customerDao")
public class CustomerDaoImpl implements CustomerDao {
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
@Override
public void saveCustomer() {
System.out.println("保存客户操作");
}
}
业务层(Service)
CustomerService
package cn.guardwhy.service;
/**
* 客户service接口
*/
public interface CustomerService {
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
void saveCustomer();
}
CustomerServiceImpl
package cn.guardwhy.service.impl;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.CustomerDao;
import cn.guardwhy.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 客户service实现类
*/
@Component("customerService")
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
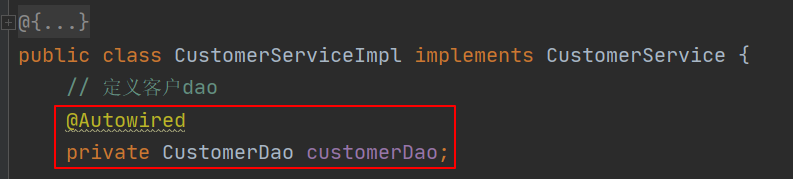
// 定义客户dao
@Autowired
private CustomerDao customerDao;
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
@Override
public void saveCustomer() {
customerDao.saveCustomer();
}
}
配置bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置包扫描注解配置dao/service
第一步:导入context名称空间和约束
第二步:
通过<context:component-scan>标签配置包扫描。spring框架在创建IOC容器的时候,
会扫描指定的包,和它的子包
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="cn.guardwhy"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
表现层(Controller)
CustomerController
package cn.guardwhy.controller;
import cn.guardwhy.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 客户controller
*/
public class CustomerController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.加载spring配置文件,创建spring ioc容器
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.实例工厂方法实例化对象
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) context.getBean("customerService");
// 3.保存用户
customerService.saveCustomer();
}
}
执行结果
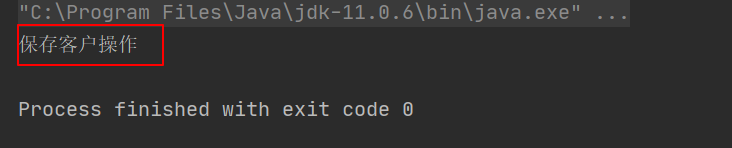
1.3 常用注解
1.3.1 创建对象注解
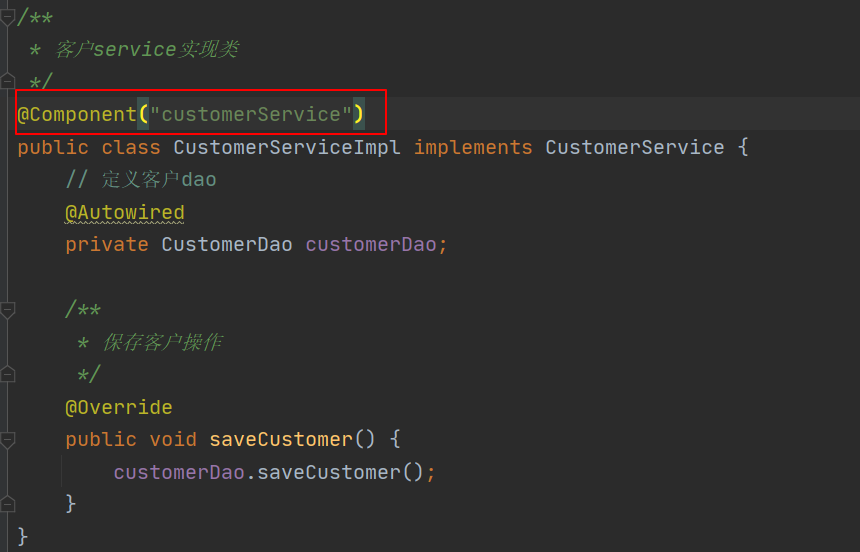
@Component
#作用:
配置javaBean对象。相当于xml配置方式中的bean标签。
#属性:
value:给bean一个唯一标识名称。
#细节:
1.value属性可以省略。
2.默认使用类的名称首字母小写,作为bean的名称。
代码示例
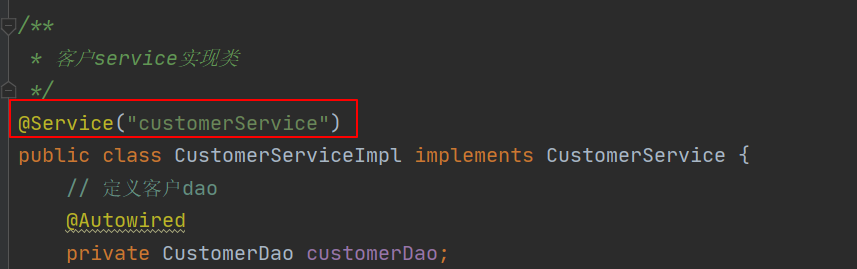
@Controller、@Service、@Repository
@Component演化的三个注解
- @Controller:一般用于表现层
- @Service:一般用于业务层
- @Repository:一般用于持久层
代码示例
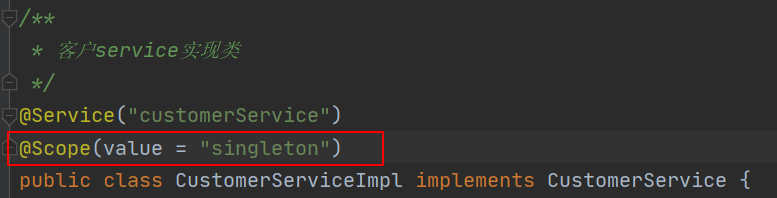
1.3.2 bean作用范围注解
@Scope
#作用:
设置bean的作用范围。相当于xml配置方式中bean标签的scope属性
#属性:
value:指定作用范围取值
#属性取值:
singleton:单例。默认值
prototype:多例
代码示例
1.3.3 注入数据注解
@Autowired
#作用:
默认按照bean的类型注入数据
#属性:
required:指定目标bean是否必须存在于spring的IOC容器(true必须存在;false:可以不存在;默认true)
#细节:
- 在spring容器中,如果同一个类型存在多个bean实例对象。
- 则先按照bean的类型进行注入,再按照bean的名称进行匹配。
- 匹配上注入成功;匹配不上注入失败。
代码示例
@Resource
#作用:
默认按照bean的名称注入数据
#属性:
name:指定bean的名称注入数据
type:指定bean的类型注入数据
#细节:
默认按照bean的名称匹配注入数据。如果注入失败,再按照bean的类型注入。
代码示例
@Value
给java简单类型成员变量注入数据
代码示例
1.3.4 bean生命周期注解
@PostConstruct @PreDestroy
#@PostConstruct:
初始化操作,相当于xml配置方式中bean标签的init-method属性。
#@PreDestroy:
销毁操作,相当于xml配置方式中bean标签的destroy-method属性。
代码示例
1.4 代码示例
持久层(Dao)
CustomerDaoImpl
package cn.guardwhy.dao.impl;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.CustomerDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
/**
* 客户dao实现类
*/
@Repository("customerDao")
public class CustomerDaoImpl implements CustomerDao {
/**
* 初始化方法
*/
public void init(){
System.out.println("正在执行初始化操作......");
}
/**
* 销毁方法
*/
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("正在执行销毁操作......");
}
/**
* 无参数构造方法
*/
public CustomerDaoImpl(){
System.out.println("正在创建客户CustomerDaoImpl对象.");
}
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
@Override
public void saveCustomer() {
System.out.println("保存客户操作");
}
}
业务层(Service)
CustomerServiceImpl
package cn.guardwhy.service.impl;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.CustomerDao;
import cn.guardwhy.dao.impl.CustomerDaoImpl;
import cn.guardwhy.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* 客户service实现类:
*/
@Service("customerService")
@Scope(value = "singleton")
public class CustomerServiceImpl implements CustomerService {
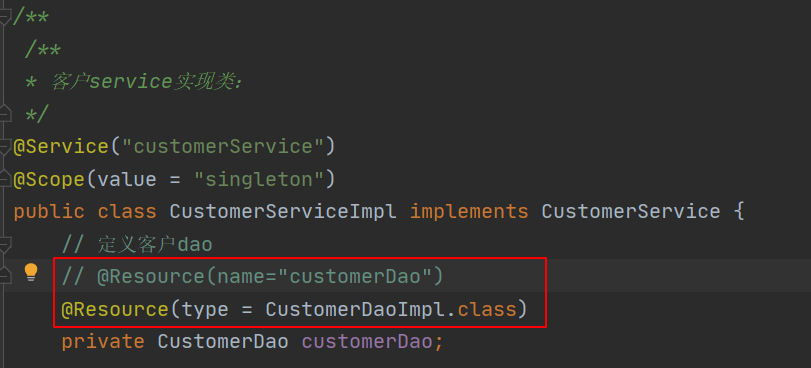
// 定义客户dao
// @Resource(name="customerDao")
@Resource(type = CustomerDaoImpl.class)
private CustomerDao customerDao;
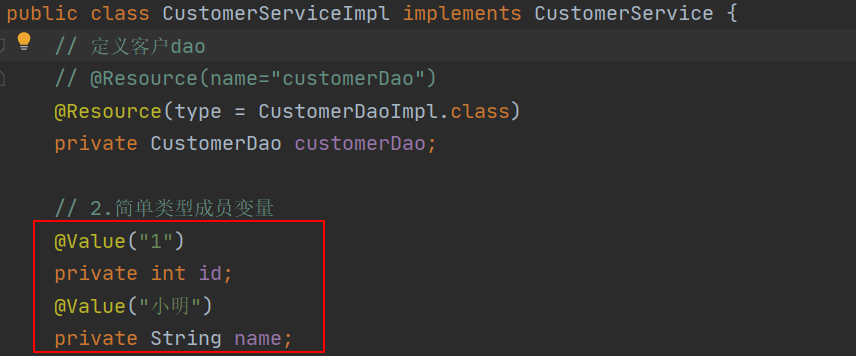
// 2.简单类型成员变量
@Value("1")
private int id;
@Value("小明")
private String name;
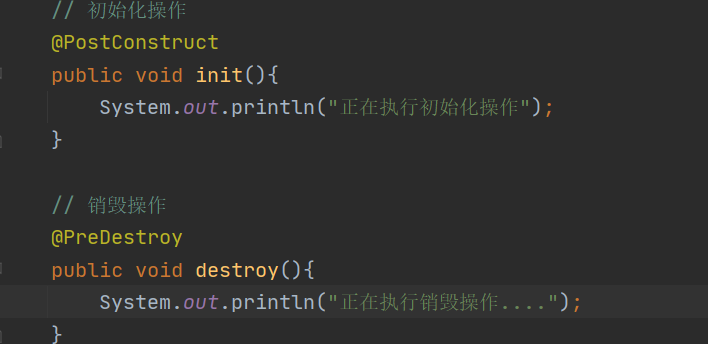
// 初始化操作
@PostConstruct
public void init(){
System.out.println("正在执行初始化操作");
}
// 销毁操作
@PreDestroy
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("正在执行销毁操作....");
}
/**
* 保存客户操作
*/
@Override
public void saveCustomer() {
System.out.println("id="+id+",name="+name);
customerDao.saveCustomer();
}
}
表现层(Controller)
CustomerController
package cn.guardwhy.controller;
import cn.guardwhy.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* 客户controller
*/
public class CustomerController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1.加载spring配置文件,创建spring ioc容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 2.实例工厂方法实例化对象
CustomerService customerService = (CustomerService) context.getBean("customerService");
// 3.保存用户
customerService.saveCustomer();
// 4.销毁容器
context.close();
}
}
执行结果
