Python编程特殊小技巧汇集
Python作为一种高级编辑语言,有很多使用的小技巧,分享一期。
1、变量值互换
a = 0b = 1a,b = b, a
2、连续赋值
a, b = 2, 13、自动解包赋值
a,b,c,d = [1,3,4,'domi']aa,*others = [1,3,4,'domi']>>> others[3, 4, 'domi']
4、链式比较
a = 10if 5<= a <= 15:print('Hello world')# 等价于if 5<= a and a <= 15:print('Hello world')
5、重复列表
a = [1,'domi']*2>>> a[1, 'domi', 1, 'domi']
6、重复字符串
>>> a[1]*2'domidomi'
7、三目运算
a = 10b = True if a==10 else False>>> bTrue等价于if a==10:b = Trueelse:b = False
8、字典合并
a = {"a":1}b = {"b":2}>>> {**a, **b}{'a': 1, 'b': 2}
9、字符串反转
s = "domi"s1 = s[::-1]
10、列表转为字符串
s = ['d','o','m','i']s1 = "".join(s)>>> s1'domi'
11、字典推导式
a = {x:x**2 for x in range(3)}>>> a{0: 0, 1: 1, 2: 4}
12、字典key和value互换
a_dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}{value:key for key, value in a_dict.items()}{1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
13、用counter查找列表中出现最多的元素
a = [1,2,3,3,0]from collections import Counterb = Counter(a)b.most_common(1)[(3, 2)] # 3出现的次数最多,为2次
14、赋值表达式,:=,可以将变量赋值和表达式放在一行
import res ="helloworld"match = re.search('o', s)if match:num = match.group(0)else:num = Nonenum
3和4可以合并为一行代码
if match := re.search('o', s):num = match.group(0)else:num = None
15、isintance函数用来判断实例的类型
a = 1.2isinstance(a, (int, float))b = "str"isinstance(a, int)
16、判断字符串是否某个字符开始或者结束,startswith,endswith
s = "123asdz"s.startswith("1")s.endswith(("z","a"))
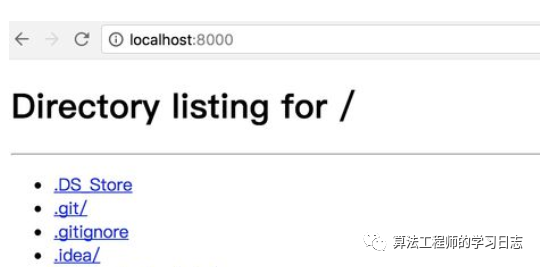
17、http.server共享文件
python3 -m http.server效果如下,方便在浏览器共享文件目录,方便在局域网共享文件
18、查找列表中出现次数最多的数字
a = [1,2,3,3,0]max(set(a), key=a.count)
19、扩展列表
a.extend(['domi','+1'])>>> a[1, 2, 3, 3, 0, 'domi', '+1']
20、列表负数索引
a[-2]'domi'
21、列表切片,
a = [1,2,3,'domi','mi']>>> a[2:4] # 提取第3个位置到第5个位置(不包含第5个位置)的数据[3, 'domi']>>> a[:3] # 提取前3个数据[1, 2, 3]>>> a[::2] # 提取偶数项[1, 3, 'mi']>>> a[1::2] # 提取奇数项[2, 'domi']>>> a[::-1] # 列表反转['mi', 'domi', 3, 2, 1]
22、二维数组转为一维数组
import itertoolsa = [[1,2],[3,4],[5,6]]b = itertools.chain(*a)>>> list(b)[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
23、带索引的迭代
a = ['d','o','m','i']for index, value in enumerate(a):print('第%d个数据为%s' %(index, value))第0个数据为d第1个数据为o第2个数据为m第3个数据为i
24、列表推导式
a = [x*3 for x in range(3)]>>> a[0, 3, 6]a = [x*3 for x in range(10) if x%2 == 0]>>> a[0, 6, 12, 18, 24]
25、生成器表达式
ge = (x*2 for x in range(10))>>> ge<generator object <genexpr> at 0x000001372D39F270>>>> next(ge)0>>>>>> next(ge)2>>> next(ge)4>>> next(ge)6>>> next(ge)8>>> next(ge)10>>> next(ge)12>>> next(ge)14>>> next(ge)16>>> next(ge)18>>> next(ge) # 迭代结束Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>StopIteration
26、集合推导式
>>> nums = {n**2 for n in range(10)}>>> nums{0, 1, 64, 4, 36, 9, 16, 49, 81, 25}
27、判断key是否存在字典中判断key是否存在字典中
>>> d = {"1":"a"}>>> d['2']Traceback (most recent call last):File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>KeyError: '2'>>> d['1']'a'>>> '1' in dTrue>>> '2' in dFalse>>> d.get('1')'a'>>> d.get('2')
28、打开文件
with open('foo.txt', 'w') as f:f.write("hello world")
29、两个列表组合成字典
a = ["One","Two","Three"]b = [1,2,3]dictionary = dict(zip(a, b))print(dictionary)
30、去除列表中重复元素
my_list = [1,4,1,8,2,8,4,5]my_list = list(set(my_list))
31、打印日历
import calendar
>>> print(calendar.month(2021, 1))January 2021Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su1 2 34 5 6 7 8 9 1011 12 13 14 15 16 1718 19 20 21 22 23 2425 26 27 28 29 30 31
32、匿名函数
def add(a, b):return a+b# 等同于add = lambda a,b:a+badd(1,2)
