由于计算性能的要求,特别需要使用并行计算,这里对TBB和OpenCL都进行了一些测试。
测试了TBB和OpenCL之后,我的感觉是如果真的要做高性能的异构计算,那还是选择CUDA吧,并且应该选用专用计算的GPU。
首先先把自己简单的描述写在前面:
1.TBB(Thread Building Blocks)线程构建模块,是Intel公司开发的并行编程开发工具,我在vs2015上测试了TBB的效果,
测试平台vs2015 release x86 + tbb2018_20180312oss,然后测试的时候是两个数相加的运算,实际测试结果,release模式下的计算耗时还小些,我觉得是vs的优化能力实现的。但是实际上TBB确实调用了多个CPU剂型计算。
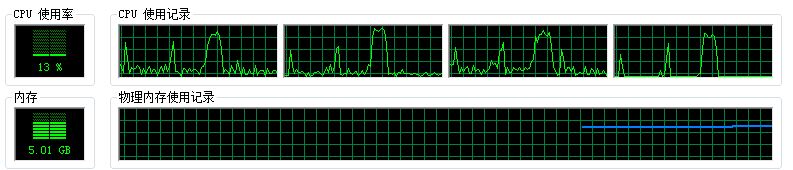
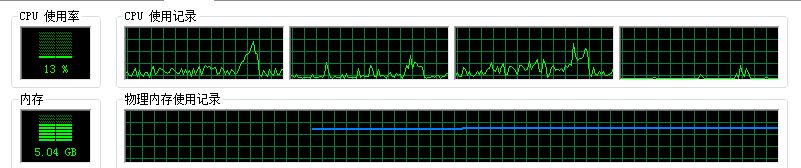
使用TBB并行计算时,CPU使用情况:
串行计算时,CPU的使用情况:
2.OpenCL,开始使用这个的时候,是因为这是一个现在在推行的异构计算标准,觉得它的计算能力,应该会有明显提升,然后也差强人意。主要的原因也还是手里没有一块像样的GPU,使用的作为显示的AMD GPU做的测试。
当然换用高性能的GPU时,使用OpenCL也是有性能提升的。

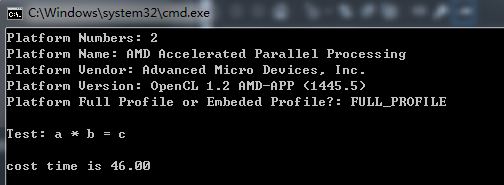
同样的计算,CPU耗时<10ms。
3.OpenCL的配置
TBB的配置:https://www.threadingbuildingblocks.org/,下载一个开发包即可,解压后添加路径即可。
OpenCL的配置,也是很简单,我这里使用的AMD的GPU,所以下载一个AMD APP SDK,在这里可以下载:http://hc.csdn.net/resources/classify?id=12
配置的方法:
(1)添加环境变量
(2)添加include目录
(3)添加lib目录
4.OpenCL测试代码
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/cloud_desktop/article/details/19107765
// amd_opencl_test.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#ifdef MAC
#include <OpenCL/cl.h>
#else
#include <CL/cl.h>
#endif
char* oclLoadProgSource(const char* cFilename, const char* cPreamble, size_t* szFinalLength);
int main()
{
cl_int errNum;
/******** 第一部分 选择OpenCL平台,创建一个上下文 ********/
cl_uint numPlatforms;
cl_platform_id *platformIds;
cl_context context = 0;
// 1. Select an OpenCL platform to run on.
errNum = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numPlatforms); // 1. 获取OpenCL平台数目
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS || numPlatforms <= 0) {
perror("Failed to find any OpenCL platforms.");
exit(1);
}
printf("Platform Numbers: %d\n", numPlatforms);
platformIds = (cl_platform_id *)malloc(
sizeof(cl_platform_id) * numPlatforms);
errNum = clGetPlatformIDs(numPlatforms, platformIds, NULL); // 2. 创建所有OpenCL平台
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Failed to find any OpenCL platforms.");
exit(1);
}
//------------------ 打印平台信息(Start) ------------------/
// Extension data
size_t ext_size = 0;
//输出生产商的名字
errNum = clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0],
CL_PLATFORM_NAME,
0, NULL, &ext_size);
if (errNum < 0) {
perror("Couldn't read CL_PLATFORM_NAME.");
exit(1);
}
char *name = (char*)malloc(ext_size);
clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0], CL_PLATFORM_NAME,
ext_size, name, NULL);
printf("Platform Name: %s\n", name);
//供应商信息
errNum = clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0],
CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR,
0, NULL, &ext_size);
if (errNum < 0) {
perror("Couldn't read CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR.");
exit(1);
}
char *vendor = (char*)malloc(ext_size);
clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0], CL_PLATFORM_VENDOR,
ext_size, vendor, NULL);
printf("Platform Vendor: %s\n", vendor);
//最高支持的OpenCL版本
errNum = clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0],
CL_PLATFORM_VERSION,
0, NULL, &ext_size);
if (errNum < 0) {
perror("Couldn't read CL_PLATFORM_VERSION.");
exit(1);
}
char *version = (char*)malloc(ext_size);
clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0], CL_PLATFORM_VERSION,
ext_size, version, NULL);
printf("Platform Version: %s\n", version);
//只有两个值:full profile 和 embeded profile
errNum = clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0],
CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE,
0, NULL, &ext_size);
if (errNum < 0) {
perror("Couldn't read CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE.");
exit(1);
}
char *profile = (char*)malloc(ext_size);
clGetPlatformInfo(platformIds[0], CL_PLATFORM_PROFILE,
ext_size, profile, NULL);
printf("Platform Full Profile or Embeded Profile?: %s\n", profile);
//------------------ 打印平台信息(End) ------------------/
// 2. Create an OpenCL context on the platform.
cl_context_properties contextProperties[] = {
CL_CONTEXT_PLATFORM,
(cl_context_properties)platformIds[0], // 3. 选择第一个OpenCL平台
0
};
context = clCreateContextFromType(contextProperties, // 4. 尝试为一个GPU设备创建一个上下文
CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU,
NULL, NULL, &errNum);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Could not create GPU context, trying CPU...");
context = clCreateContextFromType(contextProperties, // 5. 尝试为一个CPU设备创建一个上下文
CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, NULL, NULL, &errNum);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Failed to create an OpenCL GPU or CPU context.");
exit(1);
}
}
/******** 第二部分 选择设备,创建命令队列 ********/
cl_device_id *devices;
cl_device_id device = 0;
cl_command_queue commandQueue = NULL;
size_t deviceBufferSize = -1;
// 3. Get the size of the device buffer.
errNum = clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, 0, NULL, // 1. 查询存储上下文所有可用设备ID所需要的缓冲区大小
&deviceBufferSize);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Failed to get context infomation.");
exit(1);
}
if (deviceBufferSize <= 0) {
perror("No devices available.");
exit(1);
}
devices = new cl_device_id[deviceBufferSize / sizeof(cl_device_id)];
errNum = clGetContextInfo(context, CL_CONTEXT_DEVICES, // 2. 获取上下文中所有可用设备
deviceBufferSize, devices, NULL);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Failed to get device ID.");
exit(1);
}
// 4. Choose the first device
commandQueue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, // 3. 选择第一个设备,创建一个命令队列
devices[0], 0, NULL);
if (commandQueue == NULL) {
perror("Failed to create commandQueue for device 0.");
exit(1);
}
device = devices[0];
delete[] devices;
/******** 第三部分 读取OpenCL C语言,创建和构建程序对象 ********/
cl_program program;
size_t szKernelLength; // Byte size of kernel code
char* cSourceCL = NULL; // Buffer to hold source for compilation
// 5. Read the OpenCL kernel in from source file
cSourceCL = oclLoadProgSource( // 1. 从绝对路径读取HelloWorld.cl的源代码
"HelloWorld_Kernel.cl", "",
&szKernelLength);
if (cSourceCL == NULL) {
perror("Error in oclLoadProgSource\n");
exit(1);
}
// 6. Create the program
program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, // 2. 使用源代码创建程序对象
(const char **)&cSourceCL,
&szKernelLength, &errNum);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Error in clCreateProgramWithSource\n");
exit(1);
}
// 7. Build the program with 'mad' Optimization option
char* flags = "-cl-fast-relaxed-math";
errNum = clBuildProgram(program, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL); // 3. 编译内核源代码
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Error in clBuildProgram.\n");
exit(1);
}
/******** 第四部分 创建内核和内存对象 ********/
#define ARRAY_SIZE 1280*1024
cl_kernel kernel = 0;
cl_mem memObjects[3] = { 0, 0, 0 };
float *a = new float[ARRAY_SIZE];
float *b = new float[ARRAY_SIZE];
float *result = new float[ARRAY_SIZE];
// 8. Create the kernel
kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "helloworld", NULL); // 1. 创建内核对象
if (kernel == NULL) {
perror("Error in clCreateKernel.\n");
exit(1);
}
// 9. Create memory objects
for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++) {
a[i] = (float)i;
b[i] = (float)i;
}
time_t start, end;
double cost_time;
start = clock();
memObjects[0] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | // 2. 创建内存对象
CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE,
a, NULL);
memObjects[1] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY |
CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE,
b, NULL);
memObjects[2] = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_WRITE |
CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR,
sizeof(float) * ARRAY_SIZE,
result, NULL);
if (memObjects[0] == NULL || memObjects[1] == NULL ||
memObjects[2] == NULL) {
perror("Error in clCreateBuffer.\n");
exit(1);
}
/******** 第五部分 执行内核 ********/
size_t globalWorkSize[1] = { ARRAY_SIZE };
size_t localWorkSize[1] = { 1 };
// 10. Set the kernel arguments
errNum = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[0]); // 1. 设置内核参数
errNum |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[1]);
errNum |= clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), &memObjects[2]);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Error in clSetKernelArg.\n");
exit(1);
}
// 11. Queue the kernel up for execution across the array
errNum = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(commandQueue, kernel, 1, NULL, // 2. 执行内核排队
globalWorkSize, localWorkSize,
0, NULL, NULL);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Error in clEnqueueNDRangeKernel.\n");
exit(1);
}
// 12. Read the output buffer back to the Host
errNum = clEnqueueReadBuffer(commandQueue, memObjects[2], // 3. 读取运算结果到主机
CL_TRUE, 0,
ARRAY_SIZE * sizeof(float), result,
0, NULL, NULL);
if (errNum != CL_SUCCESS) {
perror("Error in clEnqueueReadBuffer.\n");
exit(1);
}
end = clock();
cost_time = end - start;
/******** 第六部分 测试结果 ********/
printf("\nTest: a * b = c\n\n");
//printf("Input numbers:\n");
//for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++)
// printf("a[%d] = %f, b[%d] = %f\n", i, a[i], i, b[i]);
//printf("\nOutput numbers:\n");
//for (int i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE; i++)
// printf("a[%d] * b[%d] = %f\n", i, i, result[i]);
printf("cost time is %.2f \n", cost_time);
while (1);
return 0;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//! Loads a Program file and prepends the cPreamble to the code.
//!
//! @return the source string if succeeded, 0 otherwise
//! @param cFilename program filename
//! @param cPreamble code that is prepended to the loaded file, typically a set of #defines or a header
//! @param szFinalLength returned length of the code string
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
char* oclLoadProgSource(const char* cFilename, const char* cPreamble, size_t* szFinalLength)
{
// locals
FILE* pFileStream = NULL;
size_t szSourceLength;
// open the OpenCL source code file
#ifdef _WIN32 // Windows version
if (fopen_s(&pFileStream, cFilename, "rb") != 0)
{
return NULL;
}
#else // Linux version
pFileStream = fopen(cFilename, "rb");
if (pFileStream == 0)
{
return NULL;
}
#endif
size_t szPreambleLength = strlen(cPreamble);
// get the length of the source code
fseek(pFileStream, 0, SEEK_END);
szSourceLength = ftell(pFileStream);
fseek(pFileStream, 0, SEEK_SET);
// allocate a buffer for the source code string and read it in
char* cSourceString = (char *)malloc(szSourceLength + szPreambleLength + 1);
memcpy(cSourceString, cPreamble, szPreambleLength);
if (fread((cSourceString)+szPreambleLength, szSourceLength, 1, pFileStream) != 1)
{
fclose(pFileStream);
free(cSourceString);
return 0;
}
// close the file and return the total length of the combined (preamble + source) string
fclose(pFileStream);
if (szFinalLength != 0)
{
*szFinalLength = szSourceLength + szPreambleLength;
}
cSourceString[szSourceLength + szPreambleLength] = '\0';
return cSourceString;
}
然后在新建一个HelloWorld_Kernel.cl文件,放到当前目录下,内容为异构计算的kernel:
// OpenCL Kernel Function
__kernel void helloworld(__global const float* a,
__global const float* b,
__global float* result)
{
// get index into global data array
int iGID = get_global_id(0);
// elements operation
result[iGID] = a[iGID] * b[iGID]; 至此结束!