1. OutputFormat 数据输出
-
相关方法
getRecordWriter(): 获取RecordWriter对象,负责数据的写出操作.
checkOutputSpecs(): 检查输出路径 -
子抽象类 FileOutputFormat
checkOutputSpecs(): 对该方法做了具体的实现.
相关异常: Output directory " + outDir + " already exists" -
具体实现类
TextOutputFormat hadoop默认使用的
LineRecordWriter
SequenceFileOutputFormat : 最终写出的文件是二进制格式的,所谓的sequenceFile -
自定义的OutputFormat
(1). 自定义类继承 FileOutputFormat
(2). 自定义RecordWriter对象, 完成数据的写出操作.
2. MR源码解读:
Job提交流程
一. 从Driver类中的提交job开始
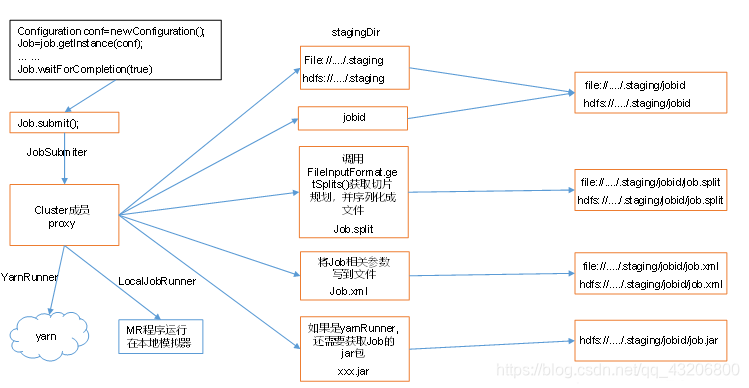
job.waitForCompletion(true);
1. submit(); 进行提交
1.1 > ensureState(JobState.DEFINE); 再次确认Job的状态
1.2 > setUseNewAPI(); 设置使用新的API
1.3 > connect(); 明确当前提交的Job运行的环境是本地还是集群
1.3.1 > return new Cluster(getConfiguration()); 创建 Cluster对象
1.3.1.1 > initialize(jobTrackAddr, conf);
① > initProviderList(); 获取Job运行的环境列表
YarnClientProtocolProvider ==>集群环境
LocalClientProtocolProvider==>本地环境
② > 根据Provider结合当前的conf判断是哪个环境
YarnClientProtocolProvider ==> YarnRunner
LocalClientProtocolProvider==> LocalJobRunner
1.4 > final JobSubmitter submitter =
getJobSubmitter(cluster.getFileSystem(), cluster.getClient()); //构造Job提交器对象
1.5 > return submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster); 通过JobSubmitter提交Job
1.5.1 > checkSpecs(job); 校验输出路径
1.5.2 > Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, conf); //获取Job的临时工作目录
D:/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/Administrator1590679188/.staging
1.5.3 > JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID(); //为当前Job生成JodId
job_local11590679188_001
1.5.4 > Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString()); //生成Job提交路径
D:/tmp/hadoop/mapred/staging/Administrator1590679188/.staging/job_local11590679188_001
1.5.5 > copyAndConfigureFiles(job, submitJobDir); //拷贝Job相关的配置信息
① 将job的提交路径在磁盘中创建出来
1.5.6 > int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir); //生成切片信息
1.5.6.1 > maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir); //生成切片
① InputFormat<?, ?> input =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf); // 获取InputFormat
② List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job); //生成切片
切片对象: file:///D:/input/inputWord/JaneEyre.txt:0+36306679
③ return array.length; //返回切片的个数
最终在job的提交路径中有两个文件:
job.split
job.splitmetainfo
1.5.7 > conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps); //根据切片的个数设置启动多少个MapTask
1.5.8 > writeConf(conf, submitJobFile); //把job的所有配置信息写到job的提交路径下
最终在job的提交路径下有一个文件:
job.xml
1.5.9 > status = submitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials()); // 真正将job提交进行执行
1.5.10> jtFs.delete(submitJobDir, true); // 最后删除Job提交路径.
MapTask流程
一. 从Job提交流程的 1.5.9 开始进入到MapTask的执行
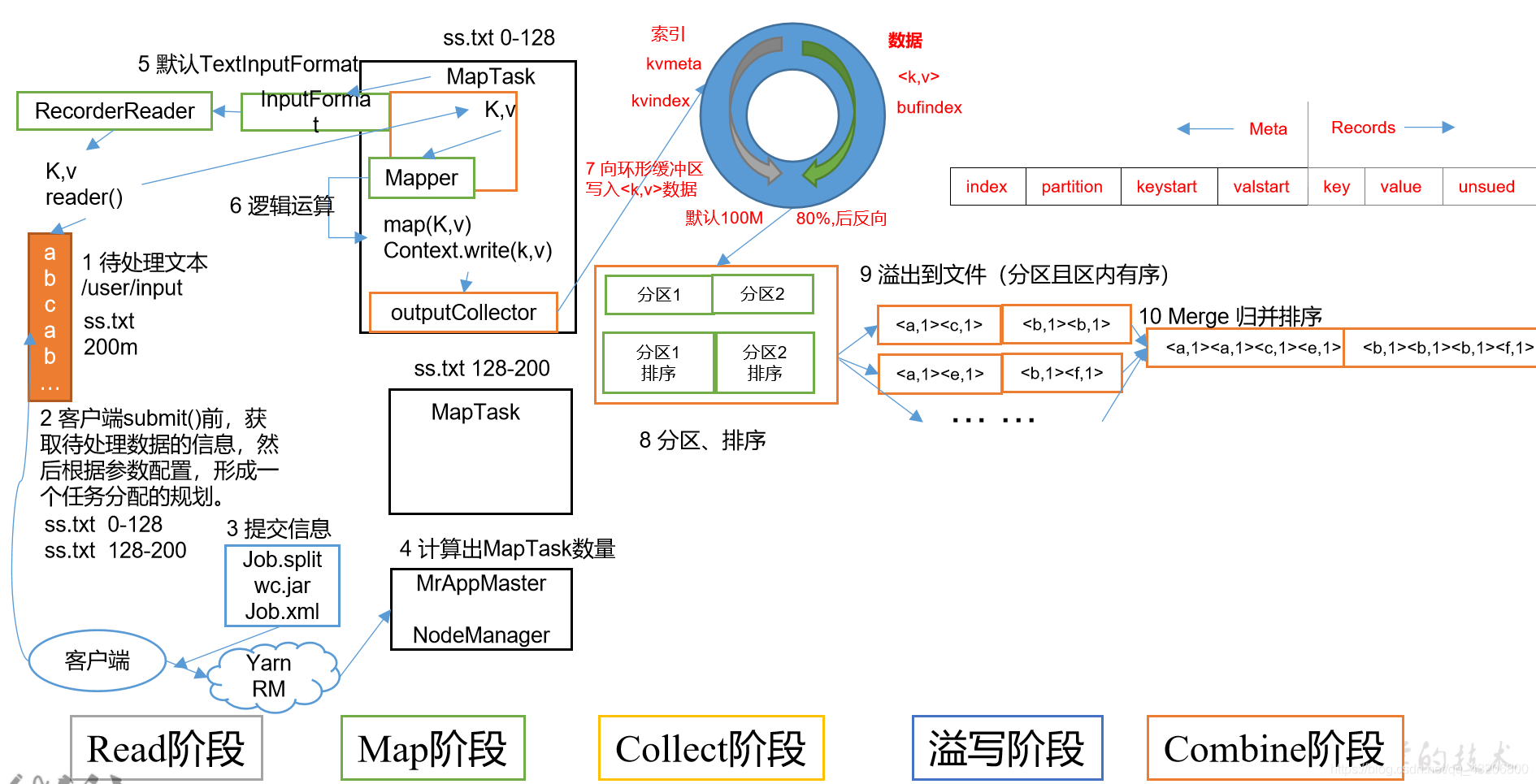
status = submitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials());
1 >. Job job = new Job(JobID.downgrade(jobid), jobSubmitDir); //创建一个可以真正执行的Job
Job: LocalJobRunner$Job , 且 是一个线程
2 >. 因为当前的Job对象是一个线程,所有执行线程要执行run方法,因此直接找到Job的run方法进行查看
2.1 > TaskSplitMetaInfo[] taskSplitMetaInfos =
SplitMetaInfoReader.readSplitMetaInfo(jobId, localFs, conf, systemJobDir);
// 读取切片的metainfo信息.
2.2 > List<RunnableWithThrowable> mapRunnables = getMapTaskRunnables(
taskSplitMetaInfos, jobId, mapOutputFiles);
//根据切片的metainfo信息,可以得出有多少个切片,再生成对应个数的Runnable对象.
Runnable : LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable
2.3 > ExecutorService mapService = createMapExecutor(); // 创建线程池对象
2.4 > runTasks(mapRunnables, mapService, "map"); // 将所有的LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable对象提交给线程池执行
2.4.1 > for (Runnable r : runnables) {
service.submit(r);
}
//取出每个LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable,交给一个线程去执行.
2.4.2 > LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable交给每个线程执行时,会执行到 LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable的run方法
因此接下来看LocalJobRunnber$Job$MapTaskRunnable的run方法
2.4.2.1 > MapTask map = new MapTask(systemJobFile.toString(), mapId, taskId,
info.getSplitIndex(), 1); //创建MapTask对象
2.4.2.2 > map.run(localConf, Job.this); //执行MapTask的run方法
2.4.2.2.1 > runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
1). mapper = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
//反射的方式创建Mapper对象. 例如: WordCountMapper
2). inputformat = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// 反射的方式创建Inputformat对象, 例如: TextInputFormat
3). split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
// 获取当前MapTask所负责的切片
4). input = new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
// 获取RecordReader对象
5). output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
//创建缓冲区对象
① collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
//收集器对象,可以理解为缓冲区对象
[1]. collector.init(context); //初始化缓冲区对象
collector: MapTask$MapOutputBuffer
{1}. final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
// 获取溢写百分比 80%
// 通过mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent参数来配置
{2}. final int sortmb = job.getInt(MRJobConfig.IO_SORT_MB,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_IO_SORT_MB);
// 获取缓冲区大小 100M
// 通过 mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb 参数来配置
{3}. sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass(
MRJobConfig.MAP_SORT_CLASS, QuickSort.class,
IndexedSorter.class), job);
// 获取排序对象 QuickSort.class, 只排索引.
{4}. comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
// 获取key的比较器对象
{5}. k/v serialization 获取kv的序列化对象
{6}. output counters 获取计数器
{7}. compression 获取编解码器,进行压缩操作
{8}. combiner 获取Combiner对象,在溢写及归并可以使用combiner
{9}. spillThread.start(); 启动溢写线程
② partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
// 根据ReduceTask的个数,获取分区器对象
6). mapper.run(mapperContext);
// 执行Mapper对象的run方法,例如WordCountMapper中的run方法
① setup(context);
② map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
//调用到WordCountMapper中的map方法,是一个循环调用的过程
[4] context.write(outk,outv);
//将map方法中处理好的kv写出去.
③ cleanup(context);
Shuffle流程
一. 从WordCountMapper类中的map方法中写出kv后,进入shuffle流程

context.write(outk,outv);
1. mapContext.write(key, value);
2. output.write(key, value);
3. collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
// 收集器对象 将kv收集到缓冲区. 收集前要将kv的分区号计算出来.
3.1 > startSpill();
// WordCountMapper持续往缓冲区写数据,当达到溢写条件80%时,开始溢写
3.1.1 > spillReady.signal(); //线程通信, 通知溢写线程开始干活
3.1.1.1 > 执行溢写线程的run方法, run方法中调用MapTask$MapOutputBuffer中的sortAndSpill()方法
①> final SpillRecord spillRec = new SpillRecord(partitions); //按照分区数创建溢写记录对象
final Path filename =
mapOutputFile.getSpillFileForWrite(numSpills, size); // 获取溢写文件的文件名
///tmp/hadoop-Administrator/mapred/local/localRunner/Administrator/jobcache/job_local1440922619_0001/attempt_local1440922619_0001_m_000000_0/output/spill0.out
out = rfs.create(filename); // 创建
②> sorter.sort(MapOutputBuffer.this, mstart, mend, reporter); // 溢写前排序
③> for (int i = 0; i < partitions; ++i) { //按照分区进行溢写
④> writer = new Writer<K, V>(job, partitionOut, keyClass, valClass, codec,
spilledRecordsCounter); // 通过writer对象进行溢写操作
⑤> 溢写会有combiner的判断。
⑥> writer.close(); // 本次溢写结束,查看磁盘的溢写文件是有数据的。
⑦> if (totalIndexCacheMemory >= indexCacheMemoryLimit) {
// 如果索引数据超过指定的内存大小,也需要溢写到文件中.(该现象一般情况很难发生.)
3.1.1.2 如上写溢写过程,在整个mapTask中会出现N次,具体多少看数据量.
如果map中最后的数据写到缓冲区,但是没有满足80%溢写条件的情况,
最终也需要将缓冲区的数据刷写到磁盘(最后一次写)
最后一次会发生在 MapTask中关闭 NewOutputCollector对象的时候.
output.close(mapperContext);
① collector.flush(); // 将缓冲区的数据刷写的磁盘
[1] . sortAndSpill()
[2] . 最终所有的数据都写到磁盘中后,在磁盘上是多个溢写文件,例如:
spill0.out
spill1.out
..........
spillN.out
② mergeParts(); // 归并,将多个溢写文件归并成一个大文件
[1] . final Path[] filename = new Path[numSpills];
// 创建数组,用于存储多个溢写文件的文件路径
filename[0]: /tmp/hadoop-Administrator/mapred/local/localRunner/Administrator/jobcache/job_local1440922619_0001/attempt_local1440922619_0001_m_000000_0/output/spill0.out
......
[2] . Path finalOutputFile =
mapOutputFile.getOutputFileForWrite(finalOutFileSize);
//最终输出文件的路径
/tmp/hadoop-Administrator/mapred/local/localRunner/Administrator/jobcache/job_local1440922619_0001/attempt_local1440922619_0001_m_000000_0/output/file.out
[3]. Path finalIndexFile =
mapOutputFile.getOutputIndexFileForWrite(finalIndexFileSize);
//最终输出文件的索引文件
/tmp/hadoop-Administrator/mapred/local/localRunner/Administrator/jobcache/job_local1440922619_0001/attempt_local1440922619_0001_m_000000_0/output/file.out.index
[4]. for (int parts = 0; parts < partitions; parts++) { //按照分区进行归并
[5]. RawKeyValueIterator kvIter = Merger.merge(job, rfs,
keyClass, valClass, codec,
segmentList, mergeFactor,
new Path(mapId.toString()),
job.getOutputKeyComparator(), reporter, sortSegments,
null, spilledRecordsCounter, sortPhase.phase(),
TaskType.MAP);
// 归并操作
[6]. if (combinerRunner == null || numSpills < minSpillsForCombine(3)) {
Merger.writeFile(kvIter, writer, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector.setWriter(writer);
combinerRunner.combine(kvIter, combineCollector);
}
//归并也可以使用combiner,但是前提条件是设置了combiner,并且溢写次数大于等于3
[7]. writer.close(); //归并完成
[8]. spillRec.writeToFile(finalIndexFile, job); //写出索引文件
[9]. for(int i = 0; i < numSpills; i++) {
rfs.delete(filename[i],true);
}
//删除所有的溢写文件spillN.out ,只保留最终的输出文件。
[10]. 最终的文件就是 file.out 和 file.out.index ,等待reduce的拷贝.
ReduceTask流程
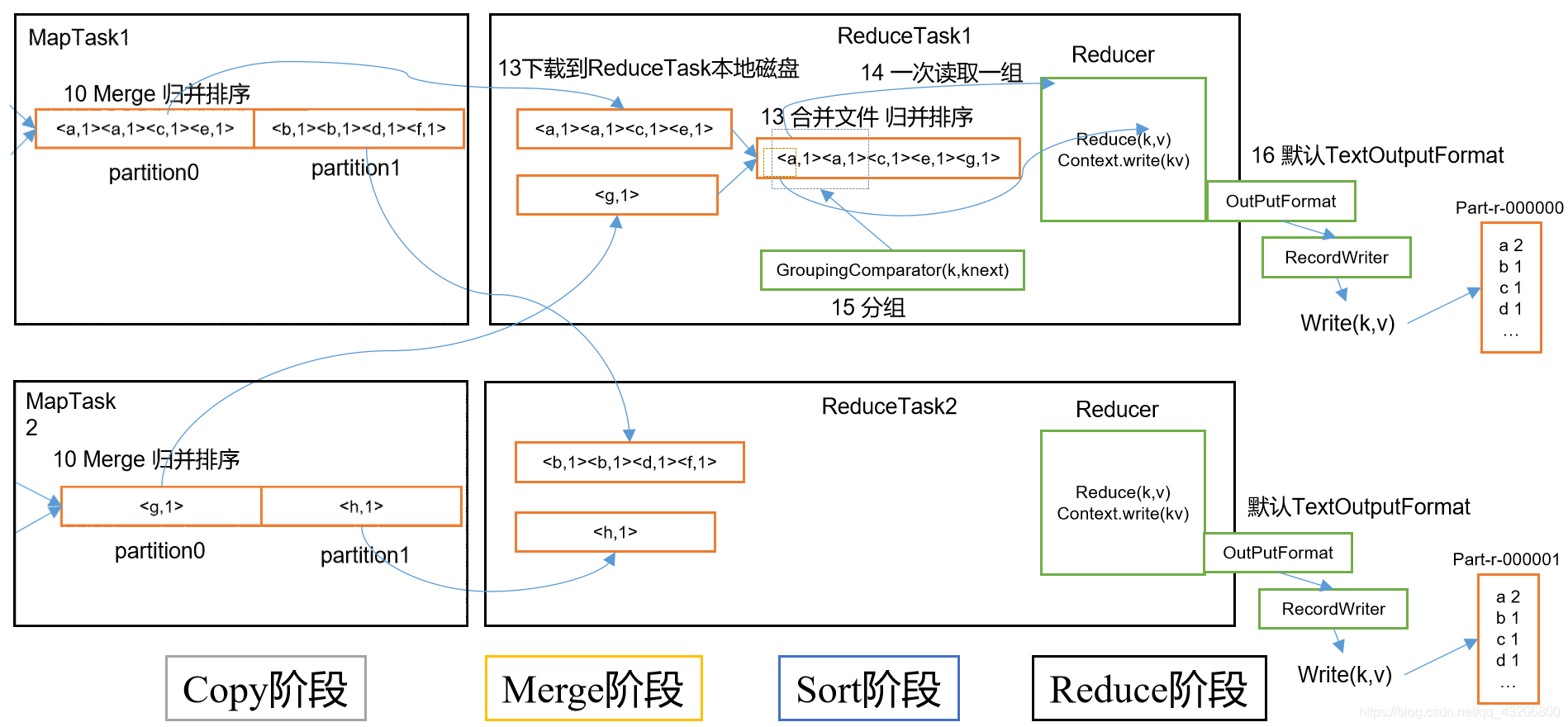
一. 在LocalJobRunner$Job中的run方法中:
1.
if (numReduceTasks > 0) { // 判断reduceTask的个数
List<RunnableWithThrowable> reduceRunnables = getReduceTaskRunnables(
jobId, mapOutputFiles);
// 创建Runnable对象: LocalJobRunner$Job$ReduceTaskRunnable
ExecutorService reduceService = createReduceExecutor();
//创建线程池
runTasks(reduceRunnables, reduceService, "reduce");
//将所有的LocalJobRunner$Job$ReduceTaskRunnable 提交到线程池执行.
}
2. for (Runnable r : runnables) {
service.submit(r);
}
//循环每个Runnable,提交给线程池去执行.
3. 线程执行的时候,要运行LocalJobRunner$Job$ReduceTaskRunnable 中run方法
3.1 > ReduceTask reduce = new ReduceTask(systemJobFile.toString(),
reduceId, taskId, mapIds.size(), 1);
//创建ReduceTask对象
3.2 > reduce.run(localConf, Job.this);
//执行ReduceTask中的run方法
3.2.1 > RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator();
// 获取分组比较器
3.2.2 > runNewReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
3.2.2.1 > reducer = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getReducerClass(), job);
//反射的操作创建reduce对象 ,例如: WordCountReducer
3.2.2.2 > trackedRW = new NewTrackingRecordWriter<OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(this, taskContext);
//创建RecordWriter对象
3.2.2.3 > reducer.run(reducerContext);
//执行WordCouontReducer中的run方法.
① setup(context);
② reduce(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getValues(), context);
//执行到WordCountReducer中的reduce方法,是一个循环调用过程.
[1]. context.write(key,outv);
//将处理好的kv写出
{1} reduceContext.write(key, value);
{2} output.write(key, value);
{3} real.write(key,value);
real :TextOutputFormat$LineRecordWriter
{4} writeObject(key); //写出key
writeObject(value); //写出value
{5} private void writeObject(Object o) throws IOException {
if (o instanceof Text) {
Text to = (Text) o;
out.write(to.getBytes(), 0, to.getLength());
} else {
out.write(o.toString().getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
//调用对象的toString方法,将返回的字符串转换成字节,通过流写出
}
}
③ cleanup(context);
源码总结:
.在整个MR中 ,会有N个MapTask 和 N 个ReduceTask ,
在集群中的效果是多个MapTask并行运行, 并行数由集群的资源的来决定.
多个ReduceTask并行运行,并行数由集群的资源来决定. 一般来说,ReduceTask的
数量比较少,基本上都能够同时并行.