yarn cluster模式Application提交流程概述
yarn cluster模式Application提交流程如下图所示。
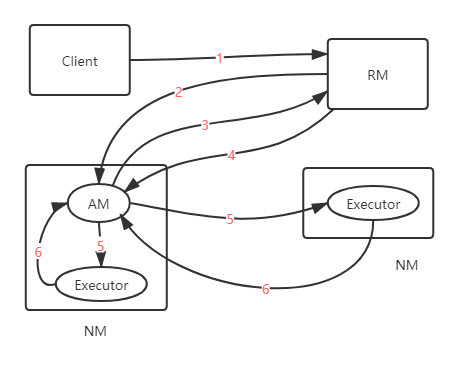
提交流程:
- Client 向ResourceManager申请启动ApplicationMaster。
- ResourceManager随机分配一个Container启动ApplicationMaster。
- ApplicationMaster向ResourceManager申请资源用于启动Executor。
- ResourceManager向ApplicationMaster返回用于启动Executor的资源。
- ApplicationMaster启动Executor。
- Executor反向注册到ApplicationMaster。
当以上步骤完成时,ApplicationMaster运行用户程序代码。此时就可以向Executor提交任务啦。
源码分析
下面通过源代码来分析具体的执行流程,本文中列出的代码为流程中的核心代码,并非全部,首先来分析spark-submit脚本。
if [ -z "${SPARK_HOME}" ]; then
source "$(dirname "$0")"/find-spark-home
fi
# disable randomized hash for string in Python 3.3+
export PYTHONHASHSEED=0
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
显然SparkSubmit是启动Spark应用程序的主入口类。
SparkSubmit.scala main方法
override def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to
// be reset before the application starts.
val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true)
val appArgs = new SparkSubmitArguments(args)
if (appArgs.verbose) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(appArgs)
// scalastyle:on println
}
appArgs.action match {
// 提交任务
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)
case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)
}
}
private def submit(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {
//准备提交环境,childMainClass返回值: YarnClusterApplication
val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
def doRunMain(): Unit = {
if (args.proxyUser != null) {
val proxyUser = UserGroupInformation.createProxyUser(args.proxyUser,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser())
try {
proxyUser.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {
override def run(): Unit = {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
})
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
if (e.getStackTrace().length == 0) {
// scalastyle:off println
printStream.println(s"ERROR: ${e.getClass().getName()}: ${e.getMessage()}")
exitFn(1)
} else {
throw e
}
}
} else {
runMain(childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass, args.verbose)
}
}
if (uninitLog) {
Logging.uninitialize()
}
if (args.isStandaloneCluster && args.useRest) {
try {
printStream.println("Running Spark using the REST application submission protocol.")
doRunMain()
} catch {
case e: SubmitRestConnectionException =>
printWarning(s"Master endpoint ${args.master} was not a REST server. " +
"Falling back to legacy submission gateway instead.")
args.useRest = false
submit(args, false)
}
} else {
// 提交任务
doRunMain()
}
}
prepareSubmitEnvironment方法childMainClass返回值YarnClusterApplication
private def prepareSubmitEnvironment(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {
...
if (isYarnCluster) {
// yarn cluster 设置childMainClass
childMainClass = YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS
if (args.isPython) {
childArgs += ("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource)
childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner")
} else if (args.isR) {
val mainFile = new Path(args.primaryResource).getName
childArgs += ("--primary-r-file", mainFile)
childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner")
} else {
if (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) {
childArgs += ("--jar", args.primaryResource)
}
childArgs += ("--class", args.mainClass)
}
if (args.childArgs != null) {
args.childArgs.foreach { arg => childArgs += ("--arg", arg) }
}
}
...
(childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass)
}
submit方法中最终将调用runMain方法
private def runMain(
childArgs: Seq[String],
childClasspath: Seq[String],
sparkConf: SparkConf,
childMainClass: String,
verbose: Boolean): Unit = {
....
try {
// 反射获取childMainClass YarnClusterApplication Class对象
mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)
} catch {
...
}
...
try {
// 实际调用YarnClusterApplication start方法
app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf)
} catch {
}
}
}
YarnClusterApplication start 方法
private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication {
override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = {
conf.remove("spark.jars")
conf.remove("spark.files")
new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf).run()
}
def run(): Unit = {
// 提交Application
this.appId = submitApplication()
}
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {
var appId: ApplicationId = null
try {
launcherBackend.connect()
setupCredentials()
//初始化yarn客户端
yarnClient.init(hadoopConf)
//启动yarn客户端
yarnClient.start()
// 为ApplicationMaster 创建上下文
val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)
val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext)
//提交Application
yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext)
appId
} catch {
...
}
}
在此方法中会初始化yarn客户端,最终提交ApplicationMaster,那么ApplicationMaster的启动类在哪里获取的呢?答案是createContainerLaunchContext方法。
createContainerLaunchContext方法
private def createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse: GetNewApplicationResponse) : ContainerLaunchContext = {
...
val amClass =
if (isClusterMode) {
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster").getName
} else {
Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher").getName
}
...
}
接着再看下ApplicationMaster 的启动类ApplicationMaster
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
SignalUtils.registerLogger(log)
val amArgs = new ApplicationMasterArguments(args)
master = new ApplicationMaster(amArgs)
// 启动Application Master
System.exit(master.run())
}
final def run(): Int = {
doAsUser {
runImpl()
}
exitCode
}
private def runImpl(): Unit = {
try {
val appAttemptId = client.getAttemptId()
...
//启动driver的核心代码
if (isClusterMode) {
runDriver()
} else {
runExecutorLauncher()
}
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
// catch everything else if not specifically handled
logError("Uncaught exception: ", e)
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,
ApplicationMaster.EXIT_UNCAUGHT_EXCEPTION,
"Uncaught exception: " + e)
}
}
runImpl方法中会启动Driver,Driver启动代码如下:
private def runDriver(): Unit = {
addAmIpFilter(None)
// 启动driver线程
userClassThread = startUserApplication()
// This a bit hacky, but we need to wait until the spark.driver.port property has
// been set by the Thread executing the user class.
logInfo("Waiting for spark context initialization...")
val totalWaitTime = sparkConf.get(AM_MAX_WAIT_TIME)
try {
val sc = ThreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future,
Duration(totalWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
if (sc != null) {
rpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnv
val driverRef = createSchedulerRef(
sc.getConf.get("spark.driver.host"),
sc.getConf.get("spark.driver.port"))
// executor注册到applicationMaster
registerAM(sc.getConf, rpcEnv, driverRef, sc.ui.map(_.webUrl))
registered = true
} else {
// Sanity check; should never happen in normal operation, since sc should only be null
// if the user app did not create a SparkContext.
throw new IllegalStateException("User did not initialize spark context!")
}
// 主线程等待driver线程
userClassThread.join()
} catch {
case e: SparkException if e.getCause().isInstanceOf[TimeoutException] =>
logError(
s"SparkContext did not initialize after waiting for $totalWaitTime ms. " +
"Please check earlier log output for errors. Failing the application.")
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,
ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SC_NOT_INITED,
"Timed out waiting for SparkContext.")
}
ApplicationMaster会启动一个线程运行用户Driver代码,那么ApplicationMaster怎么启动用户Driver代码呢?答案是反射。
ApplicationMaster用户submit时指定的 --class参数获取用户启动类,然后通过反射的方式启动用户Driver代码。
private def startUserApplication(): Thread = {
logInfo("Starting the user application in a separate Thread")
var userArgs = args.userArgs
if (args.primaryPyFile != null && args.primaryPyFile.endsWith(".py")) {
userArgs = Seq(args.primaryPyFile, "") ++ userArgs
}
if (args.primaryRFile != null && args.primaryRFile.endsWith(".R")) {
}
//通过反射获取spark-submit时提交的用户类
val mainMethod = userClassLoader.loadClass(args.userClass)
.getMethod("main", classOf[Array[String]])
//创建线程
val userThread = new Thread {
override def run() {
try {
mainMethod.invoke(null, userArgs.toArray)
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED, ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SUCCESS)
logDebug("Done running users class")
} catch {
case e: InvocationTargetException =>
e.getCause match {
case _: InterruptedException =>
case SparkUserAppException(exitCode) =>
val msg = s"User application exited with status $exitCode"
logError(msg)
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED, exitCode, msg)
case cause: Throwable =>
logError("User class threw exception: " + cause, cause)
finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,
ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EXCEPTION_USER_CLASS,
"User class threw exception: " + StringUtils.stringifyException(cause))
}
sparkContextPromise.tryFailure(e.getCause())
} finally {
sparkContextPromise.trySuccess(null)
}
}
}
userThread.setContextClassLoader(userClassLoader)
userThread.setName("Driver")
//启动driver线程
userThread.start()
userThread
}
runDriver中registerAM会启动executor并将executor反向注册到ApplicationMaster
private def registerAM(
_sparkConf: SparkConf,
_rpcEnv: RpcEnv,
driverRef: RpcEndpointRef,
uiAddress: Option[String]) = {
...
allocator = client.register(driverUrl,
driverRef,
yarnConf,
_sparkConf,
uiAddress,
historyAddress,
securityMgr,
localResources)
rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("YarnAM", new AMEndpoint(rpcEnv, driverRef))
// 为executor分配资源,启动executors
allocator.allocateResources()
...
}
def allocateResources(): Unit = synchronized {
updateResourceRequests()
...
//调用YARN接口,分配container
val allocateResponse = amClient.allocate(progressIndicator)
//获取分派container资源状态
val allocatedContainers = allocateResponse.getAllocatedContainers()
if (allocatedContainers.size > 0) {
logDebug(("Allocated containers: %d. Current executor count: %d. " +
"Launching executor count: %d. Cluster resources: %s.")
.format(
allocatedContainers.size,
numExecutorsRunning.get,
numExecutorsStarting.get,
allocateResponse.getAvailableResources))
// container分配完毕处理函数:初始化executor,等待分配task
handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala)
}
}
总结
本文通过走读源代码的方式分析了yarn cluster模式Application的提交流程,如有错误敬请指正。