一步一个脚印,从BIO到NIO
上次写了一篇BIO笔记 (查看),聊了BIO。这次接着聊NIO。
NIO三大元素
Channel 通道
个人感觉,通道有点类似于BIO的Stream。只不过stream只是单向的要么input,要么output。而Channel则是双向的并且支持非阻塞。具体实现包括 FileChannel,DatagramChannel,SocketChannel,ServerSocketChannel等。本文重点用到后面两个。
Buffer 缓存
用于保存数据的缓存,包括以下现实: ByteBuffer, CharBuffer, DoubleBuffer, FloatBuffer, IntBuffer, LongBuffer, ShortBuffer。具有非常灵添的操作。
Selector 多路复用器
可以通过多路复用器来管理多个通道,以及获取通道触发事件。
通道 通过注册的方式,添加侦听事件,通过select()方法获取可用的事件(比如可连接,可读,可写等操作)。
一步一个脚印,实例演示
1:实现多人聊天的工具,包括服务端,客户端。
引用上一篇的 Soket IO的通信工具的代码,如下:
服务端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ServerMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(4700);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
PrintWriter os=new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
BufferedReader is =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()) );
new Thread( ()->{
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println( is.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
while (true) {
String str=br.readLine();
os.println(str);
os.flush();
}
}
}
客户端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class ClientMain {
public static void main (String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket =new Socket("127.0.0.1",4700);
PrintWriter os=new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream());
BufferedReader br =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in) );
BufferedReader is =new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()) );
new Thread( ()->{
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println( is.readLine());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
while (true) {
String str=br.readLine();
os.println(str);
os.flush();
}
}
}
分码分析:
1:上面实例的服务端与客户端都是使用的BIO实现的。
2 :客户端与服务端是一对一的。
3:服务端在 Socket socket = ss.accept(); 的时候产生blocking,等待连接客户端连接。
4:服务端、客户端 在is.readLine() 的时候产生blocking。
总结:
聊天工具那肯定是要支持多个客户端的,不然跟服务端聊天多没意思。
服务端可以只有一个,必须支持同时响应多个人,那就必须是非blocking的。
使用NIO改造 :
服务端
import sun.nio.ch.ThreadPool;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class ServerMain {
static volatile HashMap<String, SocketChannel> clients = new HashMap<>();
static Queue<Msg> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Msg>(1000);
static ByteBuffer bfWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(4000);
static ByteBuffer bfRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(4000);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
connect();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "connection").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "read").start();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
trans();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "trans").start();
}
public static void connect() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("--------链接监听开始-------");
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//侦听 127.0.0.1 :11111
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 11111));
//设置为 非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//循环执行
while (true) {
//等待连接,非阻塞,如果没有连接,clien=null;
SocketChannel client = channel.accept();
//连接不为空时
if (client != null) {
//连接设置 非阻塞
client.configureBlocking(false);
//把链接添加到 链接列表
synchronized (clients) {
clients.put(String.valueOf(client.socket().getPort()), client);
}
System.out.println("添加链接:" + client.socket().getPort());
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
//读取
public static void read() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("--------信息监听开始-------");
while (true) {
synchronized (clients) {
for (Map.Entry<String, SocketChannel> it : clients.entrySet()) {
//断开连接的去掉
SocketChannel sc=it.getValue();
if (sc.isConnected() == false) {
clients.remove(it.getKey());
System.out.println("删除连接:" + sc);
continue;
}
//尝试读取数据
if (sc.read(bfRead) > 0) {
bfRead.flip();
byte[] arr = new byte[bfRead.limit()];
bfRead.get(arr);
String str = new String(arr);
String [] msgArr =str.split(":");
if (msgArr == null || msgArr.length < 2) {
System.out.println("忽略信息:" + str);
}
else
{
Msg msg= new Msg( String.valueOf(sc.socket().getPort()),msgArr[0],msgArr[1]);
queue.add(msg);
}
bfRead.clear();
}
}
}
java.lang.Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
//信息转发
public static void trans() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
System.out.println("--------信息转发开始-------");
while (true) {
Msg msg = queue.poll();
if (msg != null) {
SocketChannel c = clients.get(msg.to);
bfWrite.clear();
bfWrite.put( String.format("%s:%s",msg.from,msg.msg) .getBytes());
bfWrite.flip();
c.write(bfWrite);
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
public static class Msg {
public String to;
public String from;
public String msg;
public Msg( String from,String to, String msg) {
this.to = to;
this.from = from;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(String to) {
this.to = to;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
}
客户端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
public class ClientMain {
static SocketChannel sc;
static ByteBuffer bfWrite = ByteBuffer.allocate(4000);
static ByteBuffer bfRead = ByteBuffer.allocate(4000);
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.configureBlocking(false); //设置为非阻塞
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.01", 11111));
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
if (sc.finishConnect()) {
//启动读线程
new Thread(() -> {
try {
read();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}, "readThread").start();
//写入
while (true) {
String msg = br.readLine();
bfWrite.clear();
bfWrite.put(msg.getBytes());
bfWrite.flip();
System.out.println("发送信息:" + msg);
sc.write(bfWrite);
Thread.sleep(200);
}
}
} finally {
sc.finishConnect();
}
}
public static void read() throws InterruptedException, IOException {
while (true) {
if (sc.read(bfRead) > 0) {
bfRead.flip();
byte[] arr = new byte[bfRead.limit()];
bfRead.get(arr);
String str = new String(arr);
String[] msgArr = str.split(":");
//不符合格式的数据
if (msgArr == null || msgArr.length < 2) {
continue;
}
System.out.println(String.format("来自%s的信息:%s", msgArr[0], msgArr[1]));
bfRead.clear();
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
}
把它放到服务器上。并运行起来,开启一个服务器实例,开启两个客户端实例。运行效果如下:
服务器:
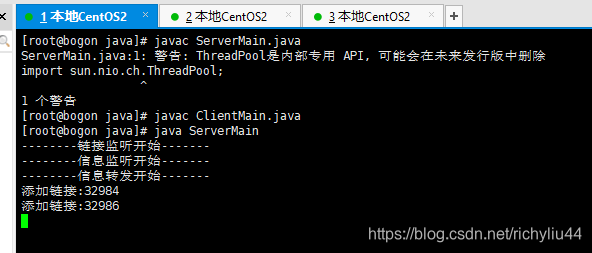
客户端1:
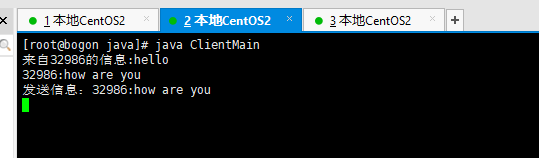
额户端2:
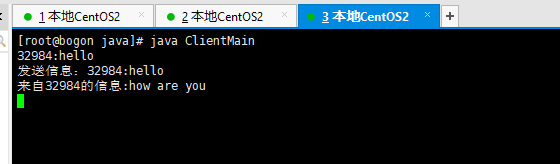
代码分析:
服务端
1:使用了NIO 的channel,并设置为 非阻塞。
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//侦听 127.0.0.1 :11111
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 11111));
//设置为 非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
2:因为是非阻塞的,资源的调用需要考虑多线程。多处引入synchronize
static volatile HashMap<String, SocketChannel> clients = new HashMap<>();
3:服务端包括分为三个线程,分别是,连接,读取信息,转发信息。
连接:如果有新的连接进来,则把连接放入clients。
读取:循环尝试去读取各个连接的数据,如有数据则写入转发队列。
转发:循环读取队列的数据,根据 消息to 找到目标连接,并把数据发送。
4:代码优化,为了更好的应对业务,引入队列、消息封装等。
客户端
1:同样使用了NIO 的channel,并设置为 非阻塞。
sc = SocketChannel.open();
sc.configureBlocking(false); //设置为非阻塞
sc.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.01", 11111));
总结:
1:聊天的功能基本能实现。
2:但是能效方面偏低,比如服务器的信息读取。假如说有10000个连接,那就得遍历10000次。如果能做到哪个连接有信息就读哪个连接,做到目标精确就好了。
引入多路复用器 selector
服务端
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class ServerMain2 {
static volatile HashMap<String, SocketChannel> clients = new HashMap<>();
static Queue<Msg> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Msg>(1000);
static Selector selector;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
selector = Selector.open();
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//侦听 127.0.0.1 :11111
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 11111));
//设置为 非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//通道注册到selector, 类型为连接
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
new Thread(()->{
try {
trans();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"trans").start();
while (true) {
if (selector.select(1000) == 0) {
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key);
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
public static void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-------handleAccept---------");
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel sc = ssChannel.accept();
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(key.selector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(4000));
//把链接添加到 链接列表
synchronized (clients) {
clients.put(String.valueOf(sc.socket().getPort()), sc);
}
System.out.println("添加链接:" + sc.socket().getPort());
}
public static void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
System.out.println("-------handleRead---------");
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer buf = (ByteBuffer) key.attachment();
long bytesRead = sc.read(buf);
while (bytesRead > 0) {
buf.flip();
while (buf.hasRemaining()) {
byte[] arr = new byte[buf.limit()];
buf.get(arr);
String str = new String(arr);
String[] msgArr = str.split(":");
if (msgArr == null || msgArr.length < 2) {
System.out.println("忽略信息:" + str);
} else {
Msg msg = new Msg(String.valueOf(sc.socket().getPort()), msgArr[0], msgArr[1]);
queue.add(msg);
}
}
System.out.println();
buf.clear();
bytesRead = sc.read(buf);
}
if (bytesRead == -1) {
sc.close();
}
}
//信息转发
public static void trans() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
ByteBuffer bfWrite =ByteBuffer.allocate(4000);
while (true) {
Msg msg = queue.poll();
if (msg != null) {
SocketChannel c = clients.get(msg.to);
bfWrite.clear();
bfWrite.put(String.format("%s:%s", msg.from, msg.msg).getBytes());
bfWrite.flip();
c.write(bfWrite);
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
}
public static class Msg {
public String to;
public String from;
public String msg;
public Msg(String from, String to, String msg) {
this.to = to;
this.from = from;
this.msg = msg;
}
public String getTo() {
return to;
}
public void setTo(String to) {
this.to = to;
}
public String getFrom() {
return from;
}
public void setFrom(String from) {
this.from = from;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
}
代码分析:
大概流程如下图所示:
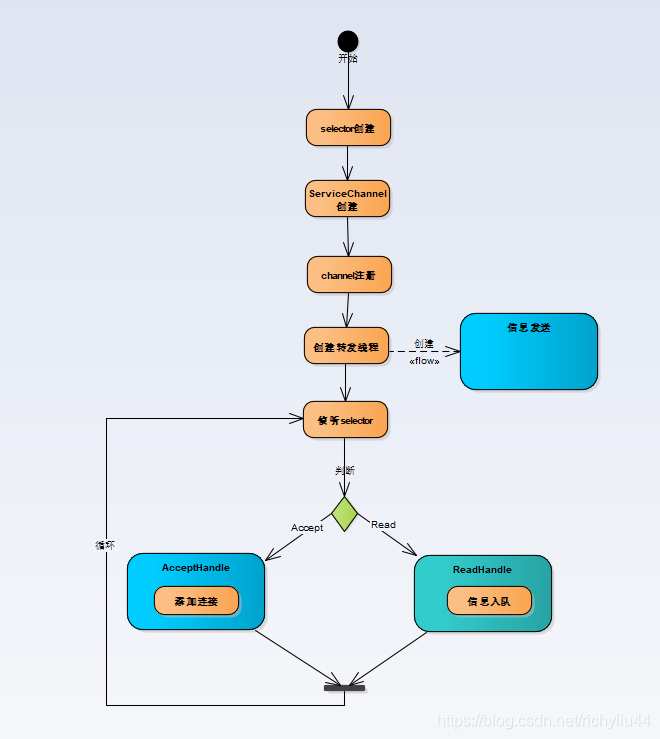
相对之前的版本,做了以下调整。
1:使用多路复用器。
selector = Selector.open();
2:通道注册到多路复用器
ServerSocketChannel channel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//侦听 127.0.0.1 :11111
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 11111));
//设置为 非阻塞
channel.configureBlocking(false);
//通道注册到selector, 类型为连接
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
3:侦听 连接以及可读事件。取代了原先开始两个线程(连接线程,读取线程)遍历的方式。
while (true) {
if (selector.select(1000) == 0) {
continue;
}
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
handleAccept(key);
}
else if (key.isReadable()) {
handleRead(key);
}
}
Thread.sleep(500);
}
演示效果:
服务端:

客户端1:
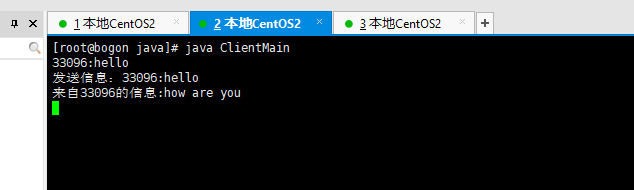
客户端2:
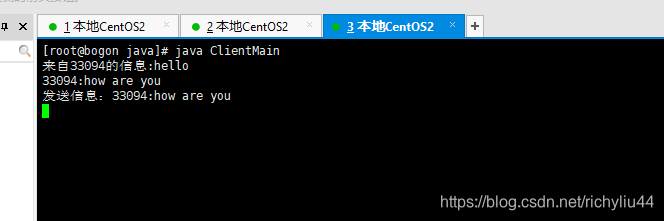
总结:
1:NIO的三大要素在本例子已经使用到了。
2:再次总结一下使用的好处。
1):channel ,支持not blocking。SeverSocketChanel 支持一个通道连接多个客户端。
2):Buffer,可以定义固定的一块内存,支持clear, flip等操作。可以重复利用,减少GC。
3):selector, 管理channel,侦听channel的事件。减少白忙添,增加能效。从以前的循环尝试读数据,到有数据才去读。同样连接也是。减少用户态/核生态的切换。
写在最后。
感觉NIO有点复杂,代码量有点多。。是不是应该有更好的封装呢?
未完,待续。。。。