1002 Blow up the Enemy
题意
张三父子俩对狙。有n把狙击枪,每个人选中了枪就不能换,每把枪有两个属性,一个是攻击值,一个是延迟时间,开枪之后要等延迟时间之后才能打第二枪,这里规定第一枪没有延迟时间。每个人血量初始值为100,被击中一枪,血量就被扣对方枪的攻击值。现在开始选枪,如果张三当前选的枪最终能够击败对方,那么赢得概率为1,如果打平手,那么赢得概率为0.5。问张三能赢得最大概率。
解题思路
贪心+概率。求出所有枪能够击败对方需要花的时间,然后按照时间从小到大排序,张三就选第一把枪,概率最大了。那么概率怎么算呢,遍历所有枪,如果时间相同,那么概率就加0.5,否则概率加1(张三一定能赢),最后对累加的结果除以n就是最终的概率了。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define sc(a) scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc2(a, b) scanf("%d%d", &a, &b)
#define sc3(a, b, c) scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c)
#define scl(a) scanf("%lld", &a)
#define scl2(a, b) scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b)
#define ss(a) scanf("%s", a)
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define PII pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
int a[2005], b[2005], c[2005];
int main()
{
int t;
sc(t);
while (t--)
{
int n;
sc(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
sc2(a[i], b[i]);
c[i] = (100 + a[i] - 1) / a[i] * b[i] - b[i]; //由于第一枪是瞬狙的,就不需要考虑延迟时间,所以要减去
}
sort(c + 1, c + n + 1); //时间从小到大排序
double ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (c[i] == c[1]) //平局
ans += 0.5;
else //胜局
ans += 1;
}
printf("%.6lf\n", ans / n); //最后的概率
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}1004 Deliver the Cake
题意
张三送蛋糕。n个城镇,m条边,每条边有个权值,表示从u城镇走到v城镇需要花的时间。张三要从s走到t,每个城镇对手捧蛋糕都有要求,L表示一定要左手捧蛋糕,R表示一定要右手捧蛋糕,M表示都可以,如果对不上的话,那么就要花额外的x时间换手,问从s走到t需要花的最少时间。
解题思路
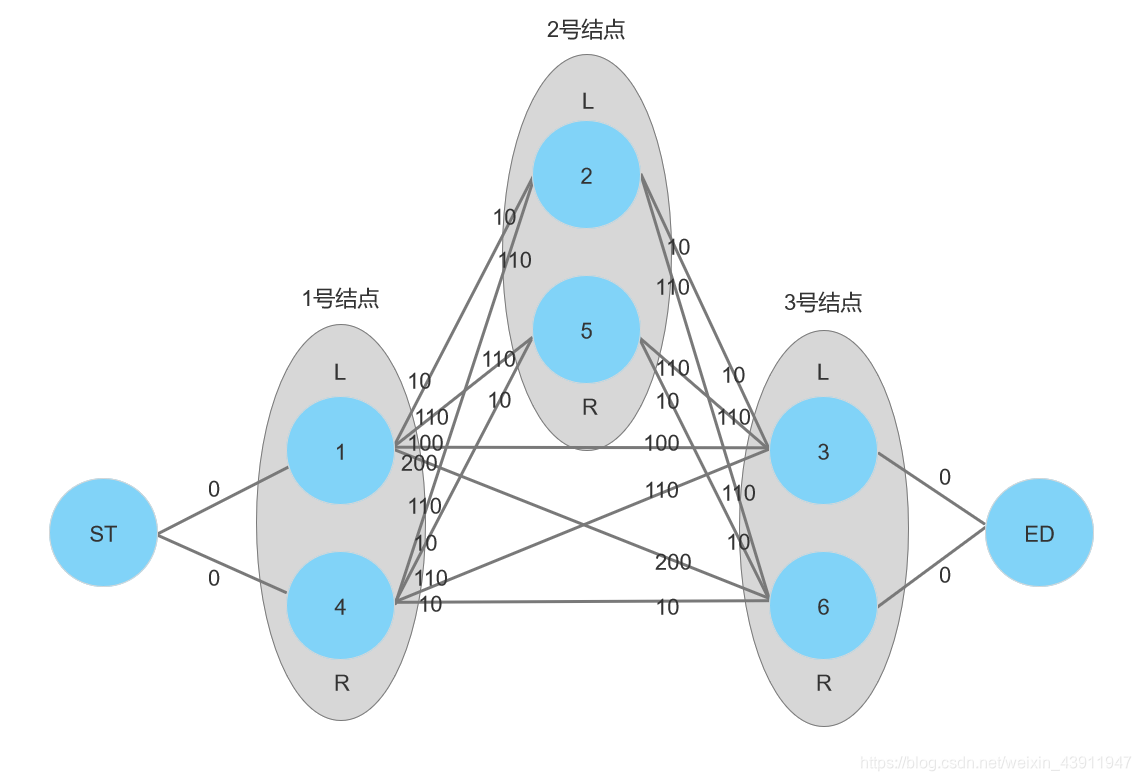
拆点+dijkstra。如果没有M这样的限制的话,那么就直接跑一边dijkstra就好了,但是有这个M的话,一个点就要分两种情况,那我们就把一个点拆成两个点,分别表示左右,然后建立双向边就好了呀,然后可以在s点之前加一个初始点st,在t之后加一个末尾点ed。如下图。最后跑一边dijkstra就完结啦!!
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define sc(a) scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc2(a, b) scanf("%d%d", &a, &b)
#define sc3(a, b, c) scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c)
#define scl(a) scanf("%lld", &a)
#define scl2(a, b) scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b)
#define ss(a) scanf("%s", a)
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define PII pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int N = 2e5 + 5;
const int M = 2e5 + 5;
const LL inf = 1e17;
struct node
{
int u;
LL w;
bool operator<(const node &a) const
{
return w > a.w;
}
};
struct eage
{
int u;
LL w;
};
vector<eage> v[N];
bool vis[N];
LL dis[N];
int st, ed;
char str[N];
void add(int a, int b, LL c) //加边
{
v[a].push_back({b, c});
v[b].push_back({a, c});
}
LL dijkstra()
{
fill(vis, vis + N, false);
fill(dis, dis + N, inf);
dis[st] = 0;
priority_queue<node> q;
q.push({st, 0});
while (q.size())
{
node t = q.top();
q.pop();
int from = t.u;
if (vis[from])
continue;
vis[from] = true;
for (auto i : v[from])
{
int to = i.u;
LL w = i.w;
if (!vis[to] && dis[from] + w < dis[to])
{
dis[to] = dis[from] + w;
q.push({to, dis[to]});
}
}
}
return dis[ed];
}
int main()
{
int t;
sc(t);
while (t--)
{
int n, m, s, t;
LL x;
sc2(n, m);
sc2(s, t);
scl(x);
ss(str + 1);
st = 0;
ed = n * 2 + 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= n * 2 + 1; i++) //初始化
v[i].clear();
//加初始点st
if (str[s] == 'L')
{
add(st, s, 0);
}
else if (str[s] == 'R')
{
add(st, s + n, 0);
}
else
{
add(st, s, 0);
add(st, s + n, 0);
}
//加末尾点ed
if (str[t] == 'L')
{
add(t, ed, 0);
}
else if (str[t] == 'R')
{
add(t + n, ed, 0);
}
else
{
add(t, ed, 0);
add(t + n, ed, 0);
}
while (m--)
{
int a, b;
LL c;
sc2(a, b);
scl(c);
//拆点建立双向边,左右方向不同,边权需要额外加x,换手时间,如果方向是M,那么左右手都要建边
if (str[a] == 'L')
{
if (str[b] == 'L')
{
add(a, b, c);
}
else if (str[b] == 'R')
{
add(a, b + n, c + x);
}
else
{
add(a, b, c);
add(a, b + n, c + x);
}
}
else if (str[a] == 'R')
{
if (str[b] == 'L')
{
add(a + n, b, c + x);
}
else if (str[b] == 'R')
{
add(a + n, b + n, c);
}
else
{
add(a + n, b, c + x);
add(a + n, b + n, c);
}
}
else
{
if (str[b] == 'L')
{
add(a, b, c);
add(a + n, b, c + x);
}
else if (str[b] == 'R')
{
add(a, b + n, c + x);
add(a + n, b + n, c);
}
else
{
add(a, b, c);
add(a, b + n, c + x);
add(a + n, b, c + x);
add(a + n, b + n, c);
}
}
}
cout << dijkstra() << endl; //最后跑一边dijkstra
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}1005 Equal Sentences
题意
给定n个字符串,相邻的字符串可以交换,也可以不交换,问最终形成的序列最多有几种。
解题思路
- dp。dp[i]表示从 1 到 i 这几个字符串不同组合最多几个,
- 当a[i]==a[i-1]时,交换之后组合数是一样的,所以直接继承。
- 当a[i]!=a[i-1]时,交换之后变成了新的组合,所以可以继承前两个状态。
- 状态转移方程:
- 初始化dp[0]=dp[1]=1
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define sc(a) scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc2(a, b) scanf("%d%d", &a, &b)
#define sc3(a, b, c) scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c)
#define scl(a) scanf("%lld", &a)
#define scl2(a, b) scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b)
#define ss(a) scanf("%s", a)
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define PII pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
string str[N];
int dp[N];
int main()
{
int t;
sc(t);
while (t--)
{
int n;
sc(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> str[i];
//mem(dp, inf);
dp[1] = dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (str[i] == str[i - 1])
dp[i] = dp[i - 1];
else
dp[i] = (dp[i - 1] + dp[i - 2]) % mod;
}
cout << dp[n] << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}1007-Go Running
持续更新中
1011-Kindergarten Physics
水题。万有引力对两个物体的影响小之又小,直接输出距离即可。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define sc(a) scanf("%d", &a)
#define sc2(a, b) scanf("%d%d", &a, &b)
#define sc3(a, b, c) scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c)
#define scl(a) scanf("%lld", &a)
#define scl2(a, b) scanf("%lld%lld", &a, &b)
#define ss(a) scanf("%s", a)
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
#define PII pair<int, int>
using namespace std;
const LL N = 1e5 + 7;
const LL inf = 1e18;
const int mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int base = 5e4;
int main()
{
int t;
sc(t);
while (t--)
{
int a, b, c, d;
sc2(a, b);
sc2(c, d);
cout << c << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}1012-Last Problem
持续更新中