
下面是我自己画的,关系画得没上面好,但我自己看着清楚些
还有一张下载来的: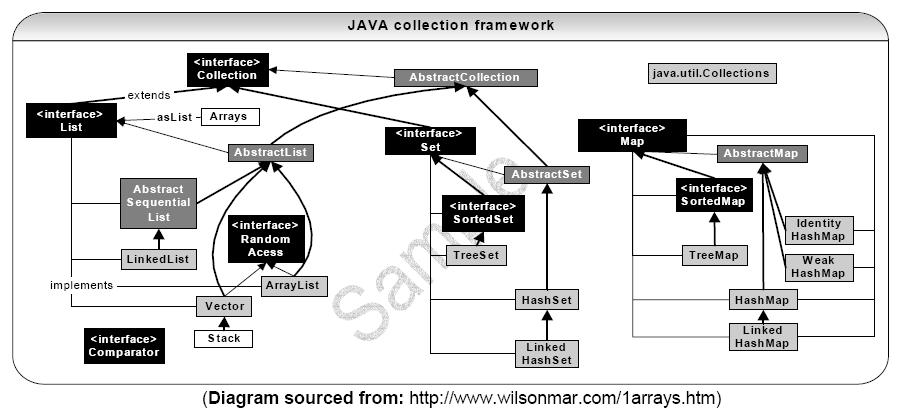
| 有序否 |
允许元素重复否 |
||
| Collection |
否 |
是 |
|
| List |
是 |
是 |
|
| Set |
AbstractSet |
否 |
否 |
| HashSet |
|||
| TreeSet |
是(用二叉树排序) |
||
| Map |
AbstractMap |
否 |
使用key-value来映射和存储数据,Key必须惟一,value可以重复 |
| HashMap |
|||
| TreeMap |
是(用二叉树排序) |
几个面试常见问题:
1.Q:ArrayList和Vector有什么区别?HashMap和HashTable有什么区别?
A:Vector和HashTable是线程同步的(synchronized)。性能上,ArrayList和HashMap分别比Vector和Hashtable要好。
2.Q:大致讲解java集合的体系结构
A:List、Set、Map是这个集合体系中最主要的三个接口。
其中List和Set继承自Collection接口。
Set不允许元素重复。HashSet和TreeSet是两个主要的实现类。
List有序且允许元素重复。ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector是三个主要的实现类。
Map也属于集合系统,但和Collection接口不同。Map是key对value的映射集合,其中key列就是一个集合。key不能重复,但是value可以重复。HashMap、TreeMap和Hashtable是三个主要的实现类。
SortedSet和SortedMap接口对元素按指定规则排序,SortedMap是对key列进行排序。
3.Q:Comparable和Comparator区别
A:调用java.util.Collections.sort(List list)方法来进行排序的时候,List内的Object都必须实现了Comparable接口。
java.util.Collections.sort(List list,Comparator c),可以临时声明一个Comparator 来实现排序。
Collections.sort(imageList, new Comparator() {
public int compare(Object a, Object b) {
int orderA = Integer.parseInt( ( (Image) a).getSequence());
int orderB = Integer.parseInt( ( (Image) b).getSequence());
return orderA - orderB;
}
});
如果需要改变排列顺序
改成return orderb - orderA 即可。
4.Q:简述equals()和hashCode()
A:...不知道。下回分解
public interface
Collection
extends Iterable
public interface
List
extends Collection
public abstract class
AbstractList
extends AbstractCollection
implements List
public class
Vector
extends AbstractList
implements List,
RandomAccess,
java.lang.Cloneable,
java.io.Serializable
基于Array
是“sychronized”的
public class
ArrayList
extends AbstractList
implements List,
RandomAccess,
Cloneable,
java.io.Serializable
基于Array
ArrayList是非同步的。所以在性能上要比Vector优越一些
public class
LinkedList
extends AbstractSequentialList
implements List,
Queue,
Cloneable,
java.io.Serializable
不基于Array
基于Array的List(Vector,ArrayList)适合查询,而LinkedList(链表)适合添加,删除操作
List基本上都是以Array为基础。但是Set则是在HashMap的基础上来实现的,这个就是Set和List的根本区别
public abstract class AbstractSet
extends AbstractCollection
implements Set
public class HashSet
extends AbstractSet
implements Set, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
HashSet的存储方式是把HashMap中的Key作为Set的对应存储项
public class LinkedHashSet
extends HashSet
implements Set, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
public class TreeSet
extends AbstractSet
implements SortedSet, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
它是通过SortedMap来实现的
public interface Map<K,V>
public abstract class AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, Serializable
public class TreeMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements SortedMap<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
HashMap通过hashcode对其内容进行快速查找,而TreeMap中所有的元素都保持着某种固定的顺序,如果你需要得到一个有序的结果你就应该使用TreeMap(HashMap中元素的排列顺序是不固定的)
更详细的可以看:
http://www.frontfree.net/view/article_695.html
http://blog.csdn.net/happyzhm5/archive/2007/03/17/1532101.aspx
http://blog.csdn.net/Java_apprentice/archive/2007/07/20/1700351.aspx
