包装类的作用 :
将基本引用类型像对象一样操作
| 基本类型 | 对应的包装类 |
|---|---|
| byte | Byte |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| double | Double |
| char | Character |
| boolean | Boolean |
装箱与拆箱
装箱 : 从基本类型转换为对应的包装类对象
拆箱 : 从包装类对象转换为对应的基本类型
装箱
构造方法 :
Integer(int value)构造一个新分配的Integer对象, 它表示指定的int值Integer (String s)构造一个新分配的Integer对象, 它表示String参数所指示的int值

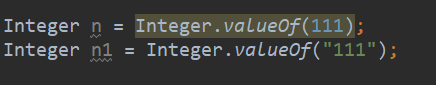
静态方法 :
static Integer valueOf(int i)static Integer valueOf(String s)
拆箱
成员方法 :
int intValue()以 int 类型返回该Integer值
Integer n1 = Integer.valueOf("111");
int m = n1.intValue(); // 拆箱 ( Integer -> int )
自动装箱和自动拆箱
JDK1.5之后基本类型数据和包装类之间可以自动的相互转换
e.g.
Integer n = 123; // 自动装箱 等价于 Integer n = Integer.valueOf(123)
注意 : 包装类无法直接参与运算 , 可以自动转换为基本类型的数据再参与计算 --- 自动拆箱
e.g.
Integer n = 123;
int x = n + 1;
sout(x); // 124
基本类型与字符串之间的转换
基本类型 --> 字符串
-
直接基本类型 + "" , 比如 34 + "" --- 最简单方式
-
static String toString(int i ) -
static String valueOf(int i)
字符串-->基本类型
使用包装类的静态方法parseXXX
e.g.
String s1 = "100000";
int s2 = Integer.parseInt(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
// s2 = 100000