(一)Java Swing概述
通过图形用户界面(GUI),用户和程序之间可以方便的进行交互。Java的java.awt包,即java抽象窗口工具包(AWT)提供了许多用来设计GUI的组件类。java早期进行用户界面设计时,主要使用java.awt包提供的类,比如button(按钮)、textfield(文本框)、list(列表)等。
(二)窗口
(1)JFrame常用方法
i.JFrame(String a) 创建一个窗体对象,并指定标题
setSize(int width,int height) 设置窗体大小
setBackgorund(color.red) 设置窗体背景颜色
setLocation(int x,int y) 设置组件的显示位置
setLocation(point p) 通过point来设置组件的显示位置
setVisible(true/false) 显示或隐藏组件
add(Component comp) 向容器中增加组件
setLay·out(LayoutManager mgr) 设置局部管理器,设置为null表示不使用
pack() 调整窗口大小,以适合其子组件的首选大小和局部
getContentpane() 返回此窗口的容器对象
ii.Component类的子类及间接子类创建的对象称为一个组件;Container类的子类及间接子类创建的对象称为一个容器;可以通过add方法向容器中添加组件;可以通过removeAll方法移除容器中的所有组件;remove(Component c)方法移除指定的组件;容器本身也是一个组件,可以把一个容器嵌套在另一个容器中;当容器中添加或移除组件时,应让容器调用validate方法,保证容器中的组件能正确显示出来。
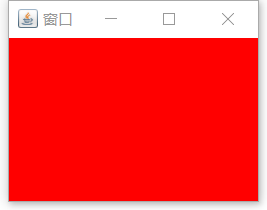
public class text1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jFrame=new JFrame("窗口");//创建一个标题为窗口的窗口
Container container=jFrame.getContentPane();
container.setBackground(Color.red);//设置背景为红色
jFrame.setVisible(true);//设置窗口可见
jFrame.setBounds(200,200,200,200);//设置窗口的位置和长,宽
jFrame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);//退出程序
}
}效果
(2)菜单、菜单条、菜单项
菜单条、菜单、菜单项是窗口常用的组件,菜单放在菜单条里,菜单项放在菜单里。JComponent的子类JMenuBar负责创建菜单条,JMenuBar的一个实例就是一个菜单条;子类JMenu负责创建菜单,JMenu的一个实例就是一个菜单;子类JMenuItem负责创建菜单项,JMenuItem的一个实例就是一个菜单项。菜单本身也是一个菜单项,可以将菜单看作菜单项添加到某个菜单中。菜单项通过setIcon方法为菜单项设置图标。
public class text1 extends JFrame{
JMenuBar jMenuBar;
JMenu jMenu1,jMenu2;
JMenuItem item1,item2;
text1(){
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
jMenuBar=new JMenuBar();//菜单条
jMenu1=new JMenu("菜单");//菜单
jMenu2=new JMenu("软件");//菜单里的菜单
item1=new JMenuItem("计算机");//菜单项
item2=new JMenuItem("物流");
jMenu2.add(new JMenuItem("汽车"));
jMenu2.add(new JMenuItem("飞机"));
setJMenuBar(jMenuBar);
jMenuBar.add(jMenu1);
jMenu1.add(jMenu2);
jMenu1.add(item1);
jMenu1.add(item2);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(200,200,200,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
text1 text1=new text1();
}
}
(三)常用组件与布局
(1)常用组件
常用组件都是JComponent的子类
JTextField:文本框:允许用户输入单行文本
JTextArea:文本区:允许用户输入多行文本
JButton:按钮:单击 按钮
JLabel:标签:为用户提供提示信息
JCheckBox:复选框:为用户提供多项选择,有选中与未选中两种状态
JRadioButton:单选按钮:为用户提供单项选择
JComboBox:下拉列表:单项选择
JPasswordField:密码框,默认显字符是*,可通过setEchoChar(char c)重新设置显字符
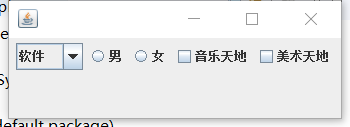
public class text1 extends JFrame{
JComboBox<String> comboBox;
JRadioButton radioButton1,radioButton2;
ButtonGroup group;
JCheckBox checkBox1,checkBox2;
text1(){
setLayout(new FlowLayout());
checkBox1=new JCheckBox("音乐天地");
checkBox2=new JCheckBox("美术天地");
radioButton1=new JRadioButton("男");
radioButton2=new JRadioButton("女");
group=new ButtonGroup();
group.add(radioButton1);
group.add(radioButton2);
comboBox=new JComboBox<>();
comboBox.addItem("软件");
comboBox.addItem("计算机");
dd(comboBox);
add(radioButton1);
add(radioButton2);
add(checkBox1);
add(checkBox2);
setVisible(true);
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100,100,400,200);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
text1 text3=new text1();
}
}
效果如下:
(2)常用容器
JPanel面板:默认是FlowLayout布局,可以向面板中添加组件,再把面板添加到其他容器中
JTabbedPane:选项卡容器,当向选项卡容器添加组件时,会为这个组件设置选项卡,这样点击这个选项卡就会显示这个组件,选项卡默认在顶部从左向右排列。也可以通过JTabbedPane.TOP等设置位置
JScrollPane:滚动窗格,可以将文本区放在滚动窗格中
JScrollPane jScrollPane=new JScrollPane(new TextArea())
JSplitPane:拆分窗格,可分为左右或上下两部分,有两个构造方法:
JSplitPane(int a,Component b,Component c)
//参数a决定时水平还是垂直:HORIZONTAL_SPLIT,VERTICAL_SPLIT
//如
JSplitPane jSplitPane=new JSplitPane(JSplitPane.VERTICAL_SPLIT,new JButton(),new JButton())
JSplitPane(int a,boolean d,Component b,Component c)
//参数d是决定拆分线移动时,组件是否连续变化,true是连续
(3)常用布局
1.FlowLayout布局(流式布局)
2.BorderLayout布局(边界布局)
3.CardLayout布局(卡片布局)
4.GridLayout布局(网格布局)
5.null布局(空布局)
6.BoxLaYout布局(盒子布局)
流式布局
import java.awt.FlowLayout ;
import javax.swing.JFrame ;
import javax.swing.JButton ;
class text1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("流式布局") ;
frame.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.CENTER,3,3)) ;
JButton button = null ;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
button = new JButton("按钮"+i) ;
frame.add(button) ;
}
frame.setSize(300,300) ;
frame.setVisible(true) ;
}
}

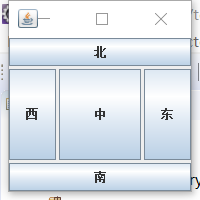
边界布局
import java.awt.BorderLayout ;
import javax.swing.JButton ;
import javax.swing.JFrame ;
class text1
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
JFrame frame = new JFrame("边界布局") ;
frame.setLayout(new BorderLayout(3,3)) ;
frame.add(new JButton("东"),BorderLayout.EAST) ;
frame.add(new JButton("西"),BorderLayout.WEST) ;
frame.add(new JButton("南"),BorderLayout.SOUTH) ;
frame.add(new JButton("北"),BorderLayout.NORTH) ;
frame.add(new JButton("中"),BorderLayout.CENTER) ;
frame.setSize(200,200) ;
frame.setVisible(true) ;
}
}