首先我们了解一下树:
每个结点有零个或多个子结点;没有父结点的结点称为根结点;每一个非根结点有且只有一个父结点;除了根结点外,每个子结点可以分为多个不相交的子树
那我们再树之前来看看数组的底层
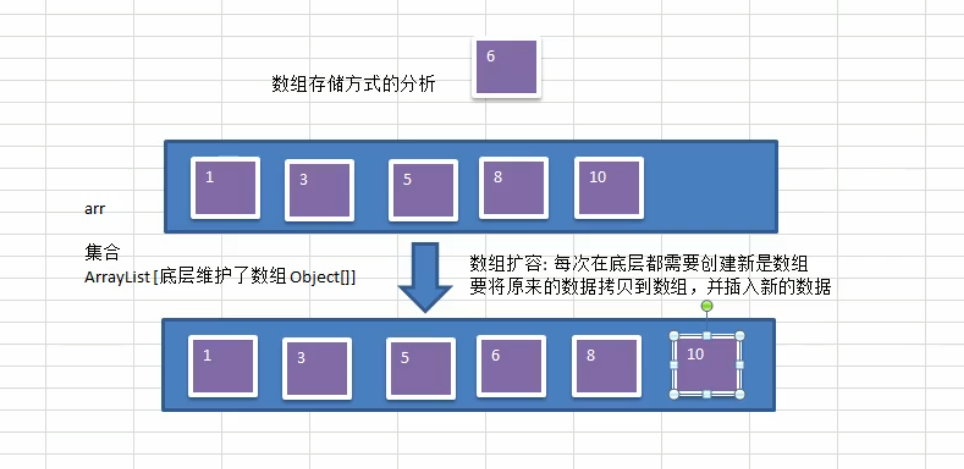
数组如果不够需要扩容,比较麻烦需要创建新的数组,拷贝,插入新数据等,
集合的话也是,因为集合ArrayList底层也是一个Object[]数组,一样的需要扩容麻烦。
那么链式存储呢?,并且还插入删除都方便快速。但是!链式储蓄检索效率太低,想一想一百万个数在链表
而我们要查找80万。是不是害的从头结点开始一个一个遍历!
所以出现树插入删除方便检索也方便!以二叉树为第一个例子

那么这里面比较难理解就是权,那什么是权呢 :二叉树中的权值就是对叶子结点赋予的一个有意义的数量值。就是本身数值。
二叉树的遍历:

思路:如下

看代码的顺序是先class HeroNode创建节点结构 再class BinaryTree创建树结构最后main
package tree;
//c创建节点
class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public HeroNode left;
public HeroNode right;
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public HeroNode getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(HeroNode left) {
this.left = left;
}
public HeroNode getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(HeroNode right) {
this.right = right;
}
public HeroNode(int no, String name) {
this.no = no;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
//前序
public void preOrder(){
System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点
if(this.left!=null){
//递归向左子树前序遍历
this.left.preOrder();
}
if(this.right!=null){
this.right.preOrder();
}
}
//中序
public void infixOrder(){
if(this.left!=null){
//递归向左子树中序遍历
this.left.infixOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点
//递归向右子树中序遍历
if(this.right!=null){
this.right.infixOrder();
}
}
//后序
public void postOrder(){
if(this.right!=null){
//递归向左子树后序遍历
this.right.postOrder();
}
System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点
//递归向左子树后序遍历
if(this.left!=null){
this.left.postOrder();
}
}
}
//创建二叉树
class BinaryTree{
private HeroNode root;
public void setRoot(HeroNode root)
{
this.root=root;
}
//前序遍历实现
public void TreeProOrder(){
if(this.root!=null)
{
this.root.preOrder();
}
else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//中序遍历实现
public void TreeInfixOrder(){
if(this.root!=null)
{
this.root.infixOrder();
}
else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
//后序遍历实现
public void TreePostOrder(){
if(this.root!=null)
{
this.root.postOrder();
}
else {
System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历");
}
}
}
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一刻二叉树
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
//创建需要的节点
HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1,"宋江");
HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2,"吴用");
HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3,"卢俊义");
HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4,"林冲");
//手动创建二叉树
root.setLeft(heroNode2);
root.setRight(heroNode3);
heroNode3.setRight(heroNode4);
binaryTree.setRoot(root);
//测试
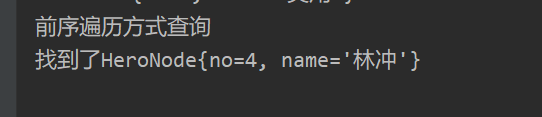
System.out.println("前序遍历");
binaryTree.TreeProOrder();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
binaryTree.TreeInfixOrder();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
binaryTree.TreePostOrder();
}
}



那么了解了二叉树的建立,遍历之后,来看看二叉树的查找

那么还是思路分析一下

在前面代码的搭建树的基础上写查询方法
package tree; import java.util.HashMap; //c创建节点 class HeroNode { public int no; public String name; public HeroNode left; public HeroNode right; public int getNo() { return no; } public void setNo(int no) { this.no = no; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public HeroNode getLeft() { return left; } public void setLeft(HeroNode left) { this.left = left; } public HeroNode getRight() { return right; } public void setRight(HeroNode right) { this.right = right; } public HeroNode(int no, String name) { this.no = no; this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "HeroNode{" + "no=" + no + ", name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } //前序 public void preOrder() { System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点 if (this.left != null) { //递归向左子树前序遍历 this.left.preOrder(); } if (this.right != null) { this.right.preOrder(); } } //中序 public void infixOrder() { if (this.left != null) { //递归向左子树中序遍历 this.left.infixOrder(); } System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点 //递归向右子树中序遍历 if (this.right != null) { this.right.infixOrder(); } } //后序 public void postOrder() { if (this.right != null) { //递归向左子树后序遍历 this.right.postOrder(); } System.out.println(this);//先输出父子节点 //递归向左子树后序遍历 if (this.left != null) { this.left.postOrder(); } } //前序遍历查找 public HeroNode preOrderSearch(int no) { //比较当前节点是不是,就是则返回 if (this.no == no) { return this; } //定义一个返回值 HeroNode resultNode = null; //判断左子节点是否为空,不为空就递归前序查找 //递归前序查找,找到节点,则返回 if (this.left != null) { resultNode = this.left.preOrderSearch(no); //这里其实有点像以前写的链表的temp=temp.next即下一位 } //在左子树找到了这里就返回了resultNode没有后面的事了 if (resultNode != null) { return resultNode; } if(this.right!=null) { resultNode = this.right.preOrderSearch(no); } //如果都没找到就为空,在右子节点找到了就在这里返回 return resultNode; } //中序遍历查找 public HeroNode infixOrderSearch(int no) { HeroNode resNode = null; //判断当前节点的左子节点是否为空 if (this.left != null) { resNode = this.left.infixOrderSearch(no); } if (resNode != null) { //找到就直接返回了 return resNode; } if(this.no ==no) { return this; } if(this.right!=null) { resNode =this.right.infixOrderSearch(no); } return resNode; } } //创建二叉树 class BinaryTree{ private HeroNode root; public void setRoot(HeroNode root) { this.root=root; } //前序遍历实现 public void TreeProOrder(){ if(this.root!=null) { this.root.preOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } } //中序遍历实现 public void TreeInfixOrder(){ if(this.root!=null) { this.root.infixOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } } //后序遍历实现 public void TreePostOrder(){ if(this.root!=null) { this.root.postOrder(); } else { System.out.println("二叉树为空,无法遍历"); } } //前序遍历查找 public HeroNode TreePreOrderSearch(int no){ if(root!=null){ return root.preOrderSearch(no); } else { return null; } } //中序遍历查找 public HeroNode TreeInfixOrderSearch(int no){ if(root!=null){ return root.infixOrderSearch(no); } else { return null; } } } public class BinaryTreeDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建一刻二叉树 BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); //创建需要的节点 HeroNode root = new HeroNode(1,"宋江"); HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2,"吴用"); HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3,"卢俊义"); HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4,"林冲"); //手动创建二叉树 root.setLeft(heroNode2); root.setRight(heroNode3); heroNode3.setRight(heroNode4); binaryTree.setRoot(root); //测试 System.out.println("前序遍历"); binaryTree.TreeProOrder(); System.out.println("中序遍历"); binaryTree.TreeInfixOrder(); System.out.println("后序遍历"); binaryTree.TreePostOrder(); //前序遍历 System.out.println("前序遍历方式查询"); HeroNode res=binaryTree.TreePreOrderSearch(4); if(res!=null) { System.out.println("找到了"+res); } else { System.out.println("没找到"); } } }