软件测试过程与方法_第4章 4.3单元JUnit的单元测试
简单测试
创建JUnit的过程



代码
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/25 21:38
*/
public class BMITest {
BMI testObj;//被测类
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
//创建被测对象
testObj = new BMI(45.0, 1.6);
//调用测试方法
String actual = testObj.getBMIType();
//校验测试结果
String expect = "偏瘦";
assertTrue(expect == actual);
}
}
独立的测试
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.*;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/25 21:38
*/
public class BMITest {
BMI testObj;//被测类
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
testObj = new BMI();
System.out.println("Run @Before method");
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
testObj = null;
System.out.println("Run @After method");
}
@BeforeClass
public static void prepareEnvironment(){
System.out.println("Run @BeforeClass method");
}
@AfterClass
public static void RestoreEnvironment(){
System.out.println("RUn @AfterClass method");
}
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
//创建被测对象
// testObj = new BMI(45.0, 1.6);
testObj.setParams(45.0, 1.6);
//调用测试方法
String actual = testObj.getBMIType();
//校验测试结果
String expect = "偏瘦";
assertTrue(expect == actual);
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_Normal() {
System.out.println("Run getBMIType_Normal");
testObj.setParams(55.0, 1.6);
assertTrue(testObj.getBMIType() == "正常");
}
@Test
public void getBMIType_SlightlyFat() {
System.out.println("Run getBMIType_SlightlyFat");
testObj.setParams(68.0, 1.6);
assertTrue(testObj.getBMIType() == "偏胖");
}
}
4.3.4参数化运行器
参数化运行器
org.junit.runners.Parameterized
测试数据准备构造器注入: 用带参数的构造函数获取数据集
属性注入: 用属性指定获取数据集
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/26 9:15
*/
// 1.指定参数化运行器
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class BMITestParam {
BMI testObj;
//1.定义属性,作为参数
private double weight;//体重
private double height;//身高
private String expected;//预期输出
//2.定义嗲参数的构造方法,传输数据
public BMITestParam(double w, double h, String exp){
this.weight = w;
this.height = h;
this.expected = exp;
}
//3.准备测试数据集
@Parameterized.Parameters(name = "{index}:getBMIType[{0},{1}] = [{2}]")
public static Collection testDataset(){
return Arrays.asList(
new Object[][]{
{45.0,1.6,"偏瘦"},
{55.0,1.6,"正常"},
{68.0,1.6, "偏胖"},
{80.0,1.6, "肥胖"}
}
);
}
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
testObj = new BMI(weight, height);
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
testObj = null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
assertTrue(testObj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
}
输出结果

4.3.5 测试参数化_属性注入
1.指定参数化运行器
2.准备测试数据(属性注入)2.1. 定义参数:定义公有变量,用于保存输入和预期输出
2.2.引入参数: 指定每个属性为参数
2.3.准备测试数据:定义一个特殊方法
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/26 9:52
*/
//指定参数化运行器\
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class BMITestParam2 {
//定义属性
@Parameterized.Parameter(0)
public double weight;//体重
@Parameterized.Parameter(1)
public double height; //身高
@Parameterized.Parameter(2)
public String expected;//预期分类
//准备测试数据集
@Parameterized.Parameters
public static Collection testDataset(){
return Arrays.asList(
new Object[][]{
{45.0,1.6,"偏瘦"},
{55.0,1.6,"正常"},
{68.0,1.6,"偏胖"},
{80.0,1.6,"肥胖"}
}
);
}
//定义被测类
BMI testObj;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
testObj = new BMI(weight, height);
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
testObj = null;
}
@Test
public void getBMIType() {
assertTrue(testObj.getBMIType() == expected);
}
}
属性注入输出结果

4.3.6 测试集
实例:血压计算(BloodPressure)

测试套包运行器
org.junit.runners.Suite

实现代码
package sample.ut;
/**
* @description:根据血压值判断血压分级
* @Author :wuzhichun
* @date :2020年3月26日10:58:59
*/
public class BloodPressure {
int systolicPressure;// 收缩压
int diatolicPressure;// 舒张压
// Getter and Setter
public int getSystolicPressure() {
return systolicPressure;
}
public void setSystolicPressure(int systolicPressure) {
this.systolicPressure = systolicPressure;
}
public int getDiatolicPressure() {
return diatolicPressure;
}
public void setDiatolicPressure(int diatolicPressure) {
this.diatolicPressure = diatolicPressure;
}
// 设置收缩压和舒张压
public void setParams(int sysPressure, int diaPressure){
systolicPressure = sysPressure;
diatolicPressure = diaPressure;
}
// Construction
public BloodPressure(){
systolicPressure = 0;
diatolicPressure = 0;
}
public BloodPressure(int sysPressure, int diaPressure){
systolicPressure = sysPressure;
diatolicPressure = diaPressure;
}
// 根据血压值判断所属血压分级
public String getPressureLevel(){
String level = "";
if(systolicPressure<120 && diatolicPressure<80){
level = "正常";
}else if( (systolicPressure>=120 && systolicPressure<=139) && (diatolicPressure>=80 && diatolicPressure<=89)){
level = "正常高值";
}else if( (systolicPressure>=140 && systolicPressure<=159) || (diatolicPressure>=90 && diatolicPressure<=99)){
level = "1级高血压";
}else if( (systolicPressure>=160 && systolicPressure<=179) || (diatolicPressure>=100 && diatolicPressure<=109)){
level = "2级高血压";
}else if( (systolicPressure>=180) || (diatolicPressure>=110)){
level = "3级高血压";
}else{
level = "异常值";
}
return level;
}
}
测试代码
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/26 10:59
*/
public class BloodPressureTest {
//定义被测类
BloodPressure testObj;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
testObj = new BloodPressure();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
testObj = null;
}
@Test
public void getPressureLevel() {
testObj.setParams(100,70);
assertTrue(testObj.getPressureLevel() == "正常");
}
@Test
public void getPressureLevel_NormalHigher() {
testObj.setParams(130,85);
assertTrue(testObj.getPressureLevel() == "正常高值");
}
@Test
public void getPressureLevel_FirstLevel() {
testObj.setParams(150,95);
assertTrue(testObj.getPressureLevel() == "1级高血压");
}
@Test
public void getPressureLevel_SecondLevel() {
testObj.setParams(170,105);
assertTrue(testObj.getPressureLevel() == "2级高血压");
}
@Test
public void getPressureLevel_ThirdLevel() {
testObj.setParams(190,120);
assertTrue(testObj.getPressureLevel() == "3级高血压");
}
}
测试结果

两个用例公用测试代码(套包测试)
package sample.ut;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Suite;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/26 11:06
*/
//指定运行器,指定要加入的测试类
@RunWith(Suite.class)
@Suite.SuiteClasses({BMITest.class, BloodPressureTest.class})
public class testSuiteWIthBMIAndBP {
}
测试结果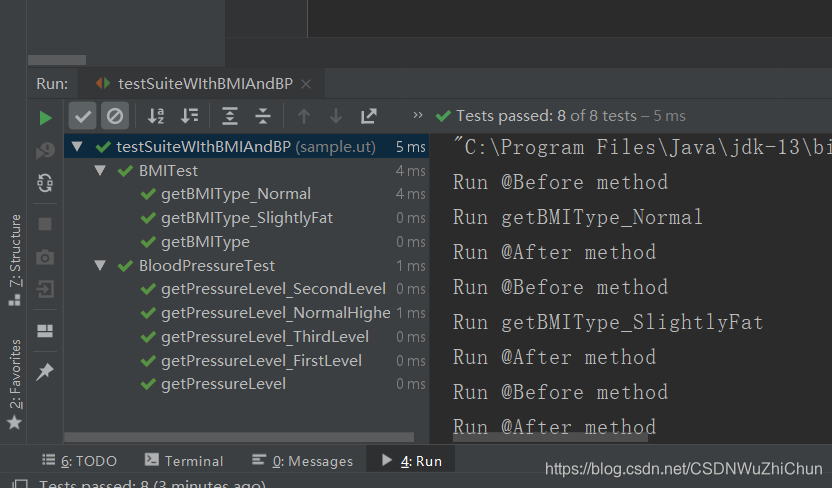
分类测试
基本步骤
1.创建新的测试类,并配置该测试类
2.修改已有测试类,定义具有特定分类的方法

import org.junit.experimental.categories.Categories;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Suite;
import sample.ut.BMITest;
import sample.ut.BVTTest;
import sample.ut.BloodPressureTest;
import sample.ut.EPTest;
/**
* @description
* @Author wuzhichun
* @date 2020/3/26 11:56
*/
//指定运行器
//设置要执行的测试特性
//设置候选测试集
@RunWith(Categories.class)
@Categories.IncludeCategory({BVTTest.class})
@Suite.SuiteClasses({BMITest.class, BloodPressureTest.class})
public class CategoryTest {
}
