First, the principle of routing
data packets from A reach B there are many paths to choose from, but since it is a multi-path, a path is bound to be the best choice. Accordingly, in order to enhance the network speed as much as possible, we need a method to determine an optimal path from the source host to the destination host through so as to perform data forwarding, which is routing technology.
1, the working principle of the router
to different network segments connected to the host, then the transmission of data you need a router to play. The source host sends packets to the target host, but not in the two hosts on the same network segment, the source host will send packets to the network segment gateway router, gateway router receives a packet, the destination IP address and then see their own routing table lookup, find the path to the next router forwarding to forward, until you find and forward the data to the target host.
2, forming a routing table
to go somewhere to a man, his mind there will be a map, there are also a map inside each router, this map is the routing table, routing table, containing All of the network address of the master router and the best path through this router to reach these networks. The best path refers to the address of an interface or next-hop router router. It is because the routing table, the router can be forwarded router efficiently. The router is how did this happen? This requires us in two ways directly connected network segments and network segments to understand the non-straight.
Directly connected network segment: segment simply is directly connected to the router, because it is directly connected to the router IP router network can directly record them in the routing table. Direct Connect IP address on the router is like our human arm, while the segment's what we like hands, his hands something we certainly clear.
Non-directly connected network segment: But there are some IP is not directly connected to the router, so this requires the use of static routing or dynamic routing to these segments and how to forward written into the routing table.
Second, the static routing and default route
1, static routing
static route is manually configured by an administrator fixed route in the router. Configure a static route, you need the following points.
(1) requires a certain IP
(2) requires a local interface IP address or a static route to the next router directly connected with static routing interface.
(3) Static routing is set manually by the administrator, unless the administrator intervention, or static route will not change.
Static Routing Features
(1) allows for accurate routing behavior of control.
(2) static routing is unidirectional.
Shortcoming (3) a static router is the lack of flexibility.
2, the default route
default route is a static routing, the router is selected to make the routing table when the destination address of the packet between the no matching IP. If there is no default route, then the destination address does not match the IP routing table data will be discarded. The default route will greatly simplify the configuration of the router, to reduce the workload of administrators.
3, the router forwards the encapsulated packet process 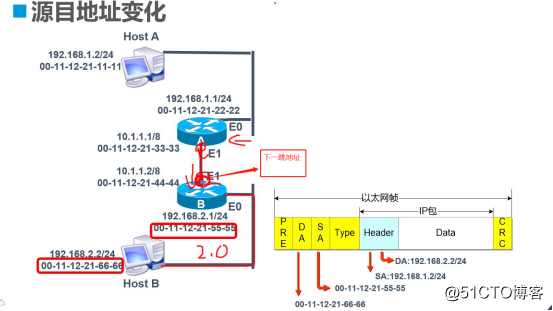
(. 1) HostA to HostB data packets should, but after HostA view he does not find the gateway router A HostA forwarding destination host on the same network segment, the data packets need to go through.
(2) HostA address resolution obtained by the MAC address of the router interface E0 connected with their A, in the data link layer HostA encapsulating the packets into a data frame, the data frame in the source MAC address as header 00-11-12-21 -11-11, the destination address is 00-11-12-21-22-22.
(3) router a receives the data frame, the data frame encapsulation removed. Then consider the packet is forwarded to their own, so the router A will find its own routing table, find the IP routing table entry that matches the target, then a next hop routing table to forward the packet to E1 interface.
(4) A re-E1 on the router encapsulated into a data frame, the data frame to sleep at this time can not be the source MAC address 00-11-12-21-33, -33, destination MAC address 00-11-12-21-44 -44.
(5) router B receives the data frame encapsulating the data of the same frame are released, to the destination IP checked and matched against the routing table, and routing table information according to the next hop to forward the packet to the interface E0.
(6) In this case that the destination router B with its own network interfaces E0 is connected, the router B geocoded the MAC address of HostB. Router B then by encapsulating the packets into a data frame, the source MAC address is 00-11-12-21-55-55, the destination address is 00-11-12-21-66-66 ,. Package is completed, the data frame transmitted from the interface E0 to HostB.
Third, the two different segments of the PC interoperability experiments
we need to open GNS3 and added to the list two routers and two PC operating area.
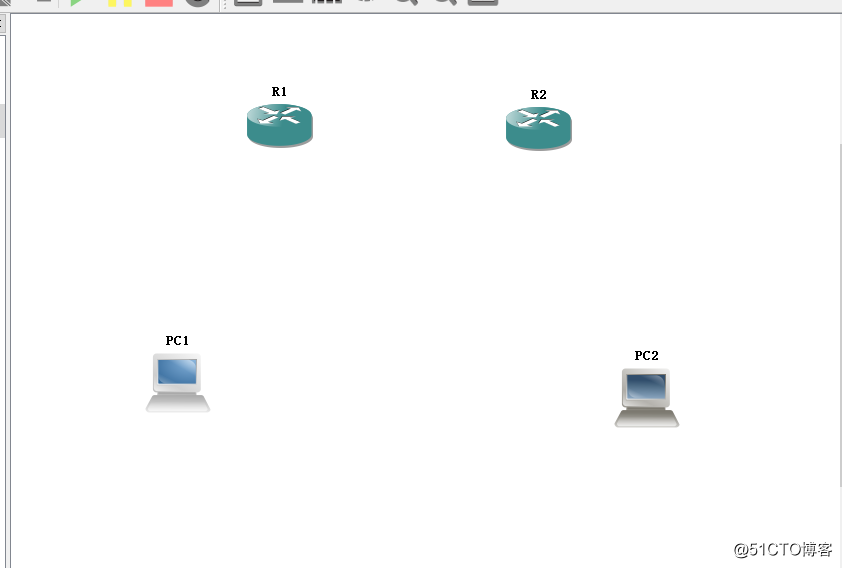
Next, connect the device to the network cable in turn, and then on the IP address of each interface device planning, important to note that two different devices connected to the interface IP to the same network segment, two different interfaces to the same device IP points at different network segments.
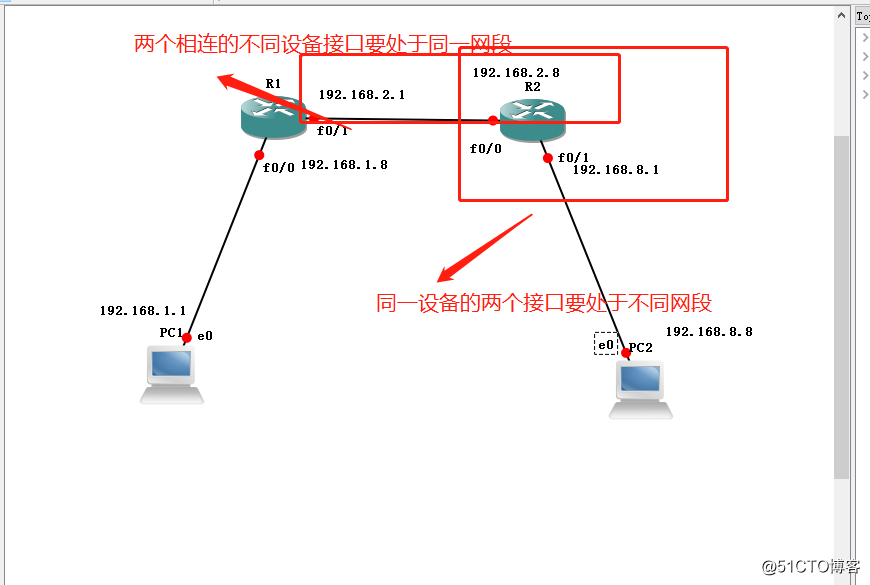
The next step is we need to be configured for each IP interface device address planning. First, the configuration of the 0/0 and 0/1 R1 interface IP addresses.
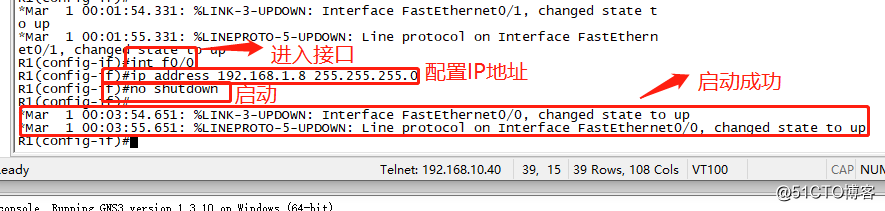
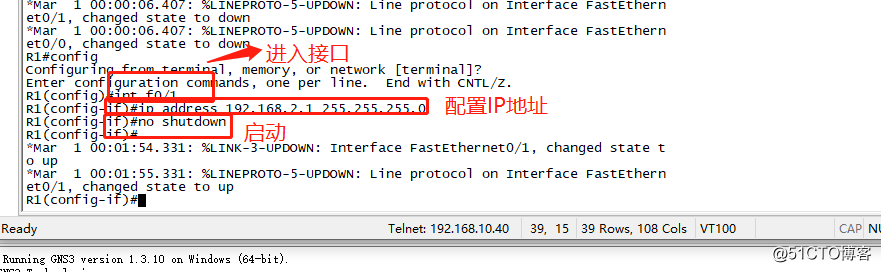
Because it is the interconnection of two different segments of the pc, so we also need to R1 static routing configuration.
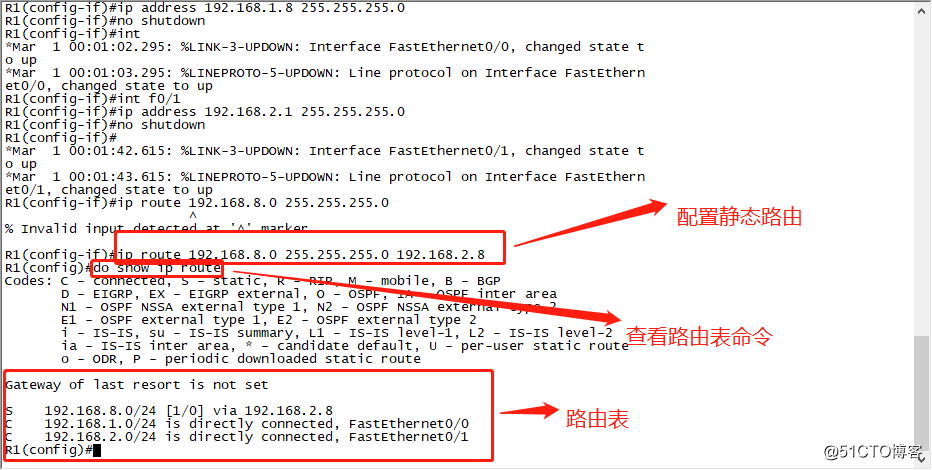
After you configure a static route we open the routing table for viewing.
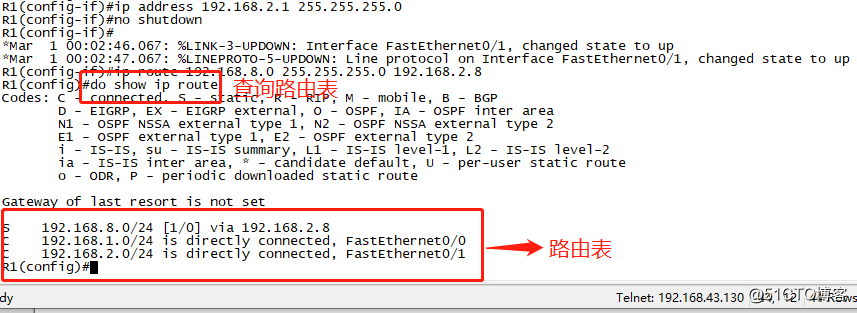
Next, we configured on R2 in the same step.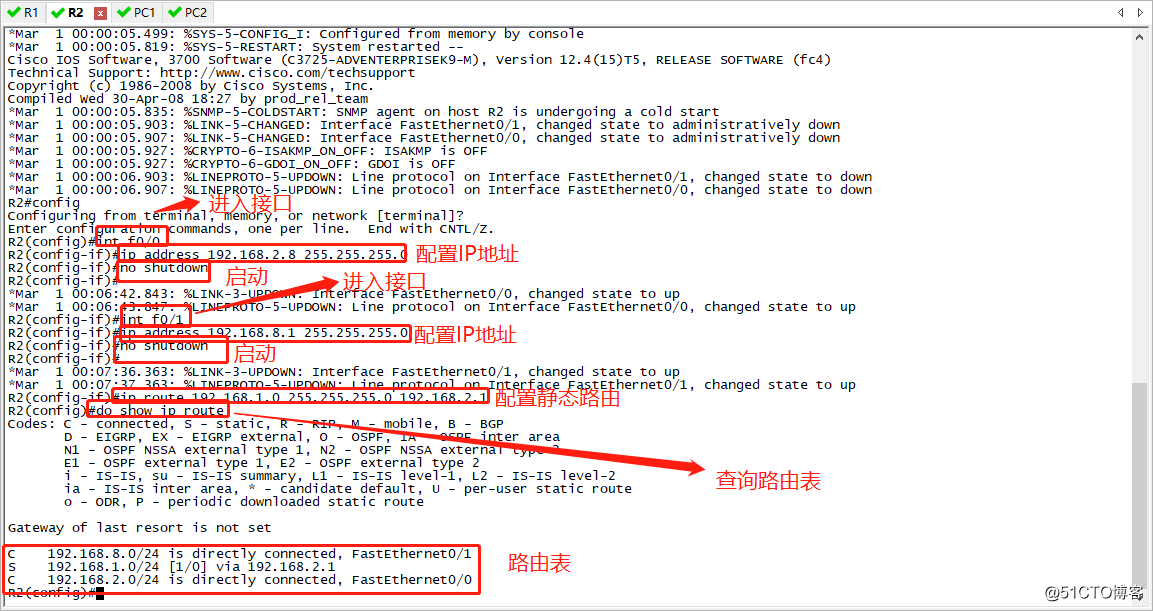
After configuring the router, we also need two PC IP address configuration.
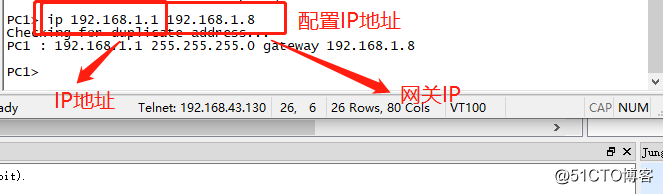
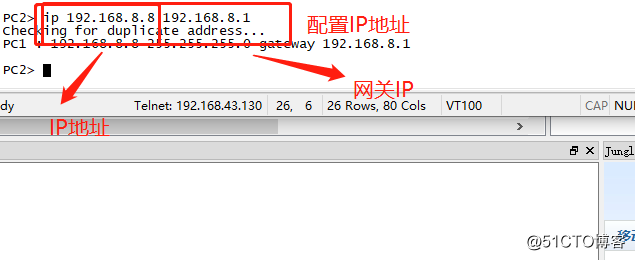
When all conditions are ready ready, we can carry out interoperability test between the two PC.
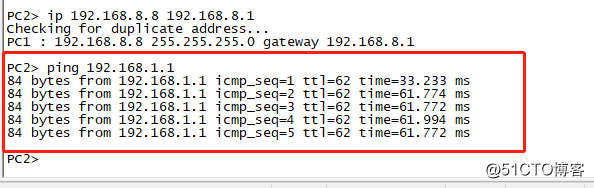
The results described above can successfully tested FIG.