Expanded configuration of static routing:
1. Load balancing
When a router accesses the same target with multiple paths with similar costs (the number of routers passed), the traffic can be split and transmitted along multiple paths at the same time, which can achieve the effect of superimposed bandwidth . (When the overhead is not similar, load balancing will reduce the efficiency of data flow reaching the target network segment. It will only take effect when all data flow reaches the target network segment. It is similar to the short-board effect of wooden barrels.) 2. Manual aggregation as
a
router When multiple consecutive subnets can be accessed, if they all pass the same next hop, these network segments can be summarized and calculated, and then only the static route to the summarized network segment can be edited, so as to reduce the number of routing entries and improve the performance of the router. The purpose of forwarding efficiency.
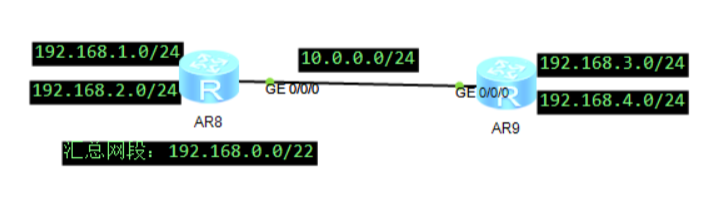
192.168.1.0 24
192.168.2.0 24
Summary: 192.168.0.0 22
[r2]ip route-static 192.168.0.0 22
3. Routing black holes
are included in the summary, if the network segments that do not actually exist in the network are included, the traffic may go to nothing back, wasting link resources. (For example, the 192.168.0.0/22 network segment contains 4 /24 network segments, 192.168.0.0/24, 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, 192.168.3.0/24, but there are only two network segments At this time, if there is traffic that wants to send information to a non-existing network segment, the traffic will never return, resulting in a waste of link resources.)
Reasonable subnet division and summarization can reduce the occurrence of routing black holes.
4. Default route
If the route black hole meets the default route, 100% will be out of the ring.
Default Route—A route entry that does not specify a destination. When looking up the table, if all the local routes are not matched, the default route will be matched.
5. Empty interface routing
Prevent routing black holes and default routes from forming loops. On the blackhole router, configure a route to the summary network segment pointing to the empty interface.
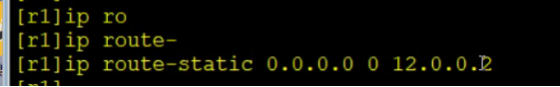
[R1]ip route-static 192.168.0.0 22 NULL 0
1. The matching principle of the routing table: the longest matching principle (accurate matching principle) (the longest mask)
2. The role of the empty interface: NULL0 port, the outgoing port of a route If the interface is an empty interface, the data packets matching the route will be discarded directly. (The received network segment information belonging to this summary network segment that does not exist will be discarded directly)
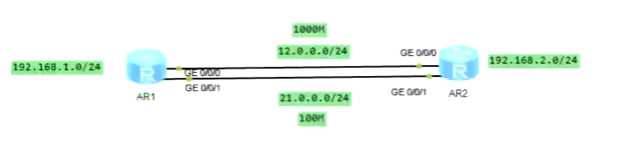
6. Floating static routing
By modifying the default priority of static routing, the backup effect of static routing can be realized.
Command configuration: 
For two routes with the same target network segment, the route with lower priority will not be loaded into the routing table. Only when the route with higher priority fails, the route with lower priority will be loaded into the routing table. table, so as to achieve the effect of backup.
(The higher the priority number, the lower the priority)
Extended configuration of static routing
Guess you like
Origin blog.csdn.net/xiaoxiaoxyxz/article/details/128541107
Recommended
Ranking