1.Use of labelme
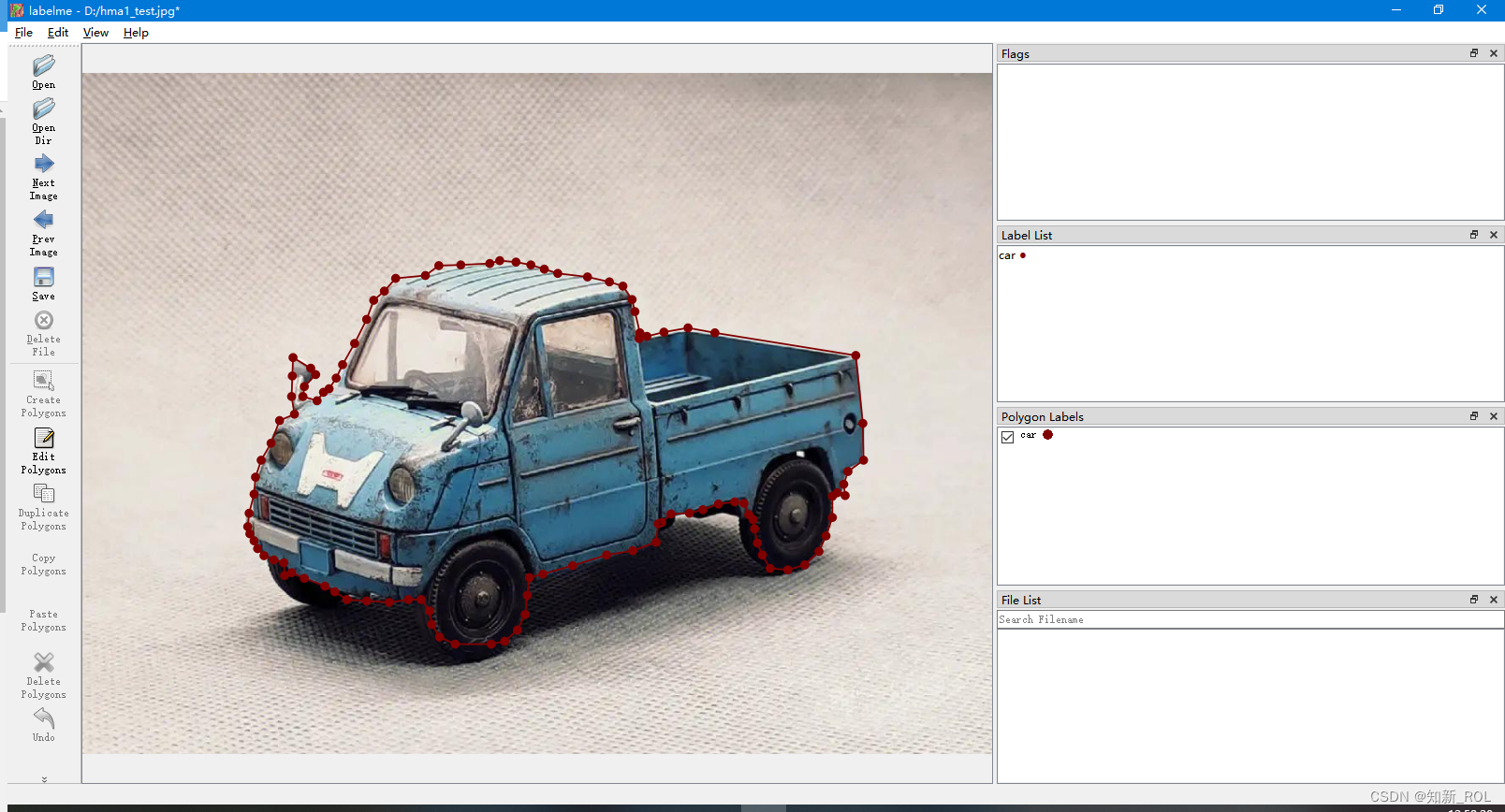
Each picture will generate a corresponding one:
![]()
All the data sets have been drawn above (!!)
2. Here is an introduction to how to batch generate this data set if they are all unchanged data sets and the positions of the labels are the same.
We first copy the first data set 2275 times,
import shutil
# 设置源文件和目标文件夹路径
source_file = 'E:\\data_seg\\quanjingCameraPicture\\segdata0001.json'
target_folder = 'E:\\data_seg\\quanjingCameraPicture\\'
# 循环从2到2275
for i in range(2, 2276):
# 创建目标文件名
target_file = target_folder + 'segdata' + str(i).zfill(4) + '.json'
# 复制源文件到目标文件
shutil.copyfile(source_file, target_file)
Modify the corresponding path to generate the following data set
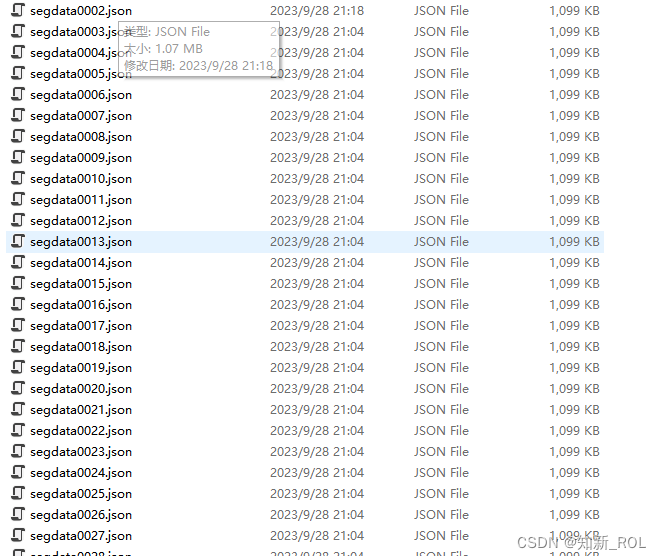
Open the generated data set and you will find:

Since the json generated by directly copying the first picture, the dictionary value
imagePath and imageData need to be replaced accordingly.
Here is the replaced code:
1. Modify the corresponding image name of imagePath ---
import json
import os
# 设置文件夹路径
folder_path = 'E:\\data_seg\\quanjingCameraPicture\\'
# 循环从2到2275
for i in range(2, 2276):
# 创建文件名
file_name = 'segdata' + str(i).zfill(4) + '.json'
file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file_name)
# 读取文件
with open(file_path, 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# 修改参数
data['imagePath'] = 'segdata' + str(i).zfill(4) + '.jpg'
# 重新写入文件
with open(file_path, 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4) 2. Modify the information when modifying imageData --- the byte stream of the corresponding image,
import json
import os
import base64
from PIL import Image
import io
# 设置文件夹路径
folder_path = 'E:\\data_seg\\quanjingCameraPicture\\'
# 循环从2到2275
for i in range(2, 2276):
# 创建文件名
json_file_name = 'segdata' + str(i).zfill(4) + '.json'
img_file_name = 'segdata' + str(i).zfill(4) + '.jpg'
json_file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, json_file_name)
img_file_path = os.path.join(folder_path, img_file_name)
# 将图像转换为Base64编码的字节流
with Image.open(img_file_path) as img:
buf = io.BytesIO()
img.save(buf, format='JPEG')
base64_data = base64.b64encode(buf.getvalue()).decode()
# 读取JSON文件
with open(json_file_path, 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# 修改参数
data['imageData'] = base64_data
# 重新写入文件
with open(json_file_path, 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4) 
The above completes all the generation. We create a new folder and put it in it, and then convert the data type.
3. Convert Labelme format data to COCO format
In this part, you first need to convert Labelme-labeled data (Json format data) into COCO format data (merge all Labelme-labeled Json data into a COCO json file). Without further ado, let’s go directly to the code labelme2coco.py:
# Labelme格式数据转为COCO格式
# !/usr/bin/env python
import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import uuid
import imgviz
import numpy as np
import labelme
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print("Please install pycocotools:\n\n pip install pycocotools\n")
sys.exit(1)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
# --input_dir为存放labelme标注json文件所在的文件夹
parser.add_argument("--input_dir", type=str, default="E:/data_seg/quanjingCameraPicture",
help="input annotated directory")
# --output_dir为输出COCO格式的json文件的文件夹
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str,
default="E:/data_seg/quanjingCameraPicture/coco_json",
help="output dataset directory")
# --labels参数为一个txt文本文件,其中包含标注的所有类别,按行分开
parser.add_argument("--labels", type=str, default="E:/data_seg/quanjingCameraPicture/labels.txt", help="labels file")
parser.add_argument(
"--noviz", help="no visualization", action="store_true"
)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print("Output directory already exists:", args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages"))
if not args.noviz:
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, "Visualization"))
print("Creating dataset:", args.output_dir)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
url=None,
version=None,
year=now.year,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f"),
),
licenses=[
dict(
url=None,
id=0,
name=None,
)
],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type="instances",
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
errcnt = 0
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == "__ignore__"
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data["categories"].append(
dict(
supercategory=None,
id=class_id,
name=class_name,
)
)
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "annotations.json")
label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, "*.json"))
# label_files = label_files1[1500:]
# print(type(label_files))
# print(label_files)
for image_id, filename in enumerate(label_files):
print("Generating dataset from:", filename)
try:
label_file = labelme.LabelFile(filename=filename)
except:
errcnt += 1
print("出现异常")
continue
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(filename))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, "JPEGImages", base + ".jpg")
img = labelme.utils.img_data_to_arr(label_file.imageData)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_img_file, img)
data["images"].append(
dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
)
)
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_file.shapes:
points = shape["points"]
label = shape["label"]
group_id = shape.get("group_id")
shape_type = shape.get("shape_type", "polygon")
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if group_id is None:
group_id = uuid.uuid1()
instance = (label, group_id)
if instance in masks:
masks[instance] = masks[instance] | mask
else:
masks[instance] = mask
if shape_type == "rectangle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
x1, x2 = sorted([x1, x2])
y1, y2 = sorted([y1, y2])
points = [x1, y1, x2, y1, x2, y2, x1, y2]
if shape_type == "circle":
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
r = np.linalg.norm([x2 - x1, y2 - y1])
# r(1-cos(a/2))<x, a=2*pi/N => N>pi/arccos(1-x/r)
# x: tolerance of the gap between the arc and the line segment
n_points_circle = max(int(np.pi / np.arccos(1 - 1 / r)), 12)
i = np.arange(n_points_circle)
x = x1 + r * np.sin(2 * np.pi / n_points_circle * i)
y = y1 + r * np.cos(2 * np.pi / n_points_circle * i)
points = np.stack((x, y), axis=1).flatten().tolist()
else:
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[instance].append(points)
segmentations = dict(segmentations)
for instance, mask in masks.items():
cls_name, group_id = instance
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data["annotations"].append(
dict(
id=len(data["annotations"]),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[instance],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
)
)
if not args.noviz:
viz = img
if masks:
labels, captions, masks = zip(
*[
(class_name_to_id[cnm], cnm, msk)
for (cnm, gid), msk in masks.items()
if cnm in class_name_to_id
]
)
viz = imgviz.instances2rgb(
image=img,
labels=labels,
masks=masks,
captions=captions,
font_size=15,
line_width=2,
)
out_viz_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, "Visualization", base + ".jpg"
)
imgviz.io.imsave(out_viz_file, viz)
with open(out_ann_file, "w") as f:
json.dump(data, f)
print(errcnt)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()The generated data set is as follows:

The divided data set is as shown above. We also need to convert the COCO data set into the format of the yolo data set:
4. Convert COCO data set to the format of yolo data set:
【1】Modify the folder path where the COCO format json file in general_json2yolo.py is located (note: it is the folder path, do not write the file path directly).
https://github.com/ultralytics/JSON2YOLO
The first modification of general_json2yolo.py
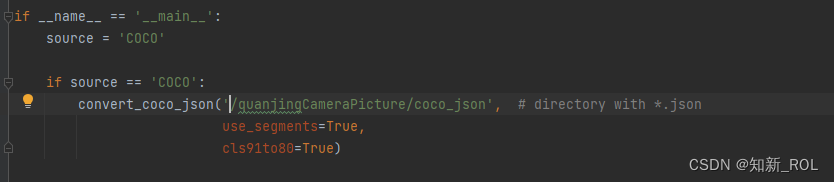
general_json2yolo.py second modification
The original:

after edited:
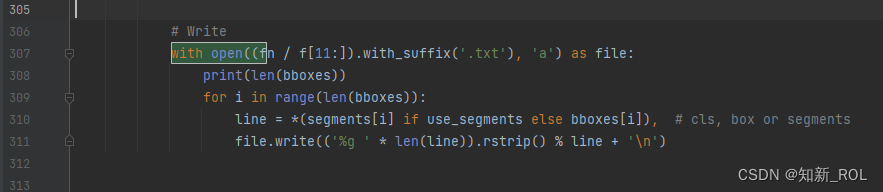
What still needs to be modified is the utils.py that needs to be modified.
There are several categories here, just replace them with your own categories
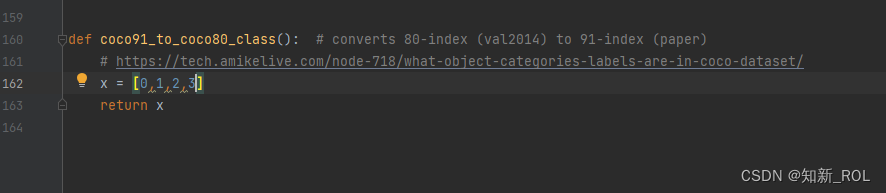
After modifying these, you can run the code general_json2yolo,.py
The corresponding txt tag is generated: