Article directory
foreword
Everything is growth, including tears, constant farewells, and constant encounters.
Introduction to DHCP Service
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) was developed and designed by the IETF (Internet Task Force), and became a standard protocol in October 1993. Its predecessor was the BOOTP protocol. The current definition of DHCP can be found in RFC 2131, and the proposed standard over IPv6 (DHCPv6) can be found in RFC 3315.
DHCP refers to a range of IP addresses controlled by the server. When the client logs in to the server, it can automatically obtain the IP address and subnet mask assigned by the server.
In the working principle of DHCP, the DHCP server provides three IP allocation methods: automatic allocation (Automatic allocation), manual allocation and dynamic allocation (Dynamic Allocation).
1. Automatic allocation means that when the DHCP client successfully obtains an IP address from the DHCP server for the first time, it will use this IP address permanently.
2. Manual allocation is an IP address specially designated by the administrator of the DHCP server.
3. Dynamic allocation means that when the client obtains the IP address from the DHCP server for the first time, it does not use the address permanently. After each use, the DHCP client You need to release this IP for use by other clients.
DHCP lease process
The process in which the client obtains an IP address from the DHCP server is called the DHCP lease process. The lease process is divided into four steps, namely:
the client requests IP (the client sends a DHCP Discover broadcast packet) the
server responds (the server sends a DHCP Offer broadcast packet)
the client selects an IP (the client sends a DHCP Request broadcast packet)
the server confirms the lease (The server sends a DHCP ACK broadcast packet)
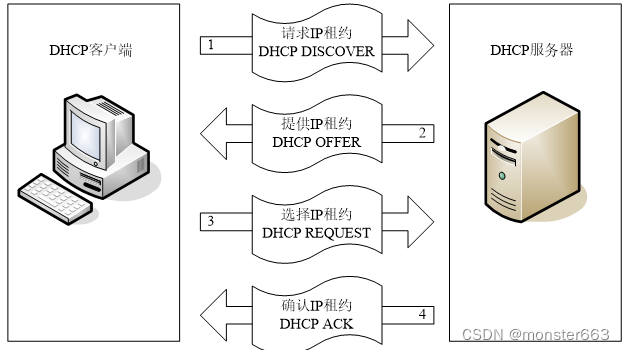
As for the lease term of IP, it is very particular. It is not as simple as renting a house. Take NT as an example: the default lease time of IP address is 8 days. In addition to sending a DHCPrequest request every time the DHCP client is turned on, it will also send a DHCPrequest when the lease period is halfway. If the DHCP server does not get confirmation at this time, the workstation can continue to use the IP; when the lease period expires 87.5% of the time, if the client still cannot contact the original DHCP server, it will try to communicate with other DHCP servers. If there is no any DHCP protocol server running on the network, the client computer must stop using the IP address, and start from sending a Dhcpdiscover data packet, and the silent DHCP server responds. If there is a server response, repeat the whole process again.
Experimental procedure
lab environment
In this experiment, I choose a Windows Server 2003 as the DHCP server, a Windows Server 2000 as the client, and connect the two virtual machines to the same LAN to avoid interference from other factors. Installation and configuration experiments.
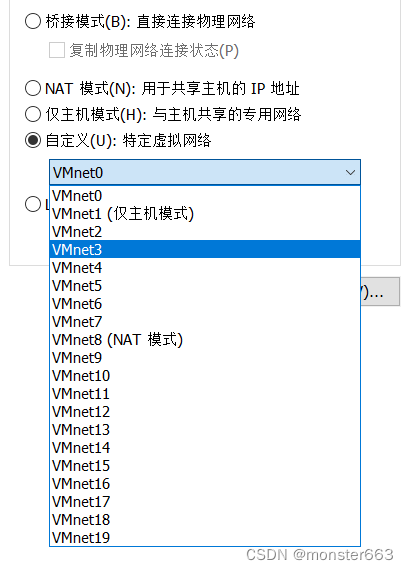
Choose an unused LAN, but don't choose LAN0 (bridge to real environment), host-only mode and NAT mode
Installation of DHCP service
First find the control panel in Windows Server 2003, select "Add Windows Components" in the "Add or Remove Programs" option and check "Network Services", and at the same time check "Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)" in the detailed information And complete the DHCP installation.
Configuration of DHCP service
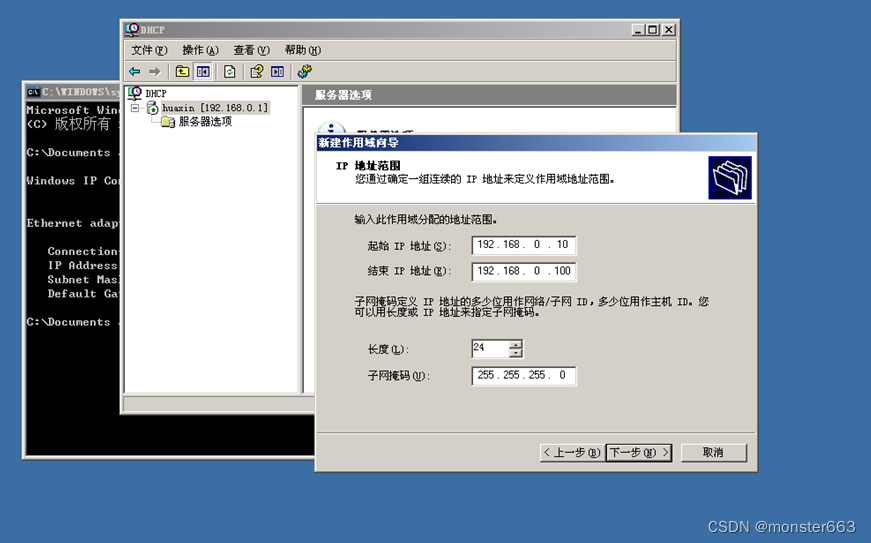
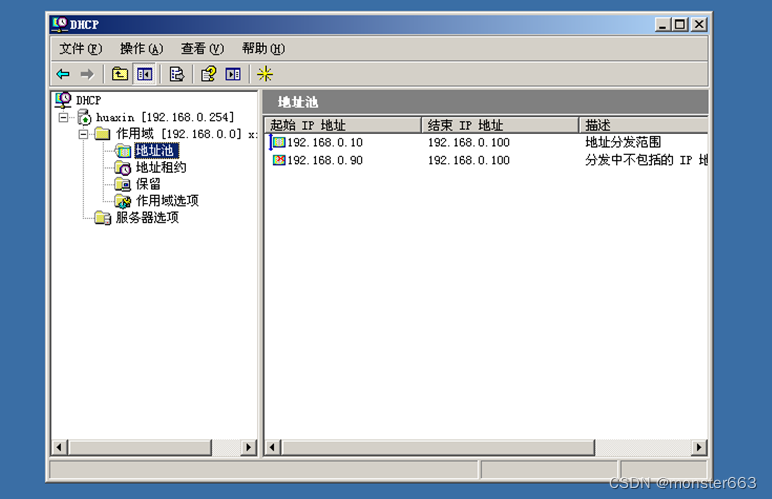
Open the DHCP console window, configure the IP address of the DHCP server network card to 192.168.0.254, and add a new scope, and set the IP address range to 192.168.0.10~192.168.0.100 to add an
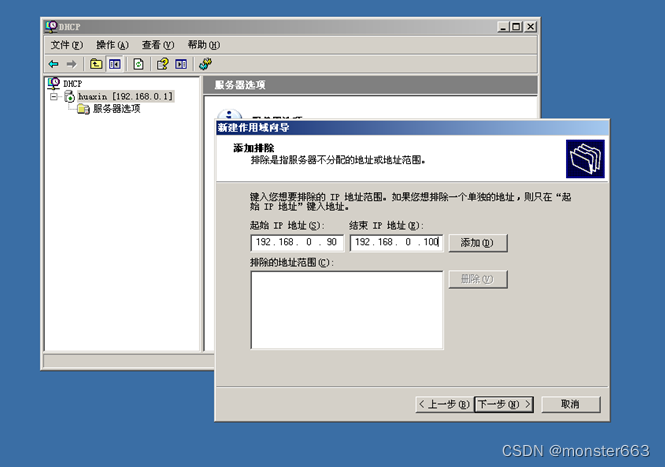
excluded IP address range to 192.168.0.90~ 192.168.0.100
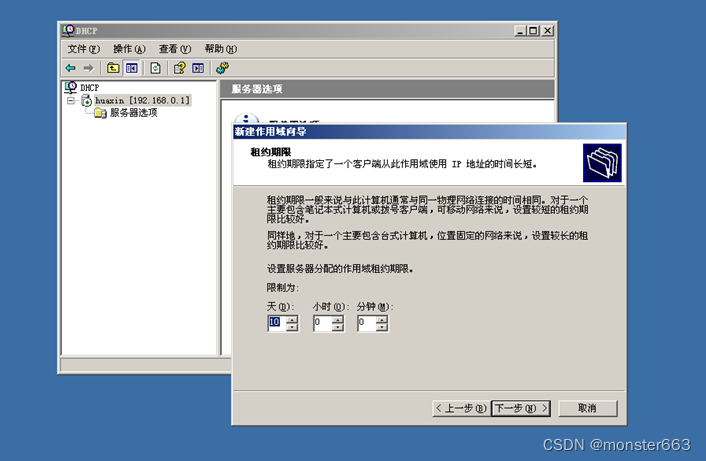
Set the lease period to 10 days:
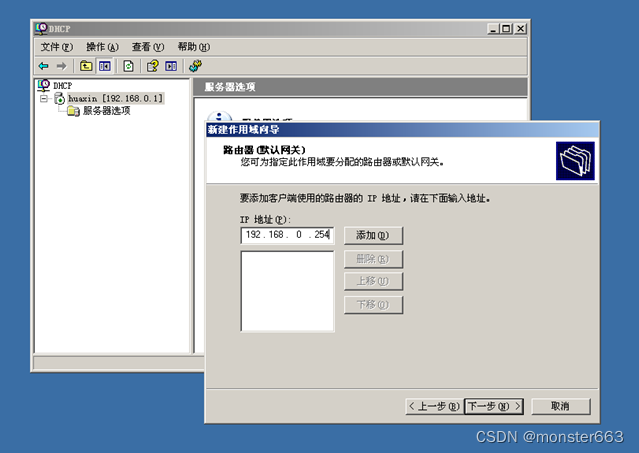
Configure the default gateway to 192.168.0.254:
The final configured interface is as follows:
Verification of experimental results
After the above configuration, the range of the IP address pool of the DHCP server we configured is:
192.168.0.10 ~ 192.168.0.100
The range of excluded IP addresses is 192.168.0.90 ~ 192.168.0.100
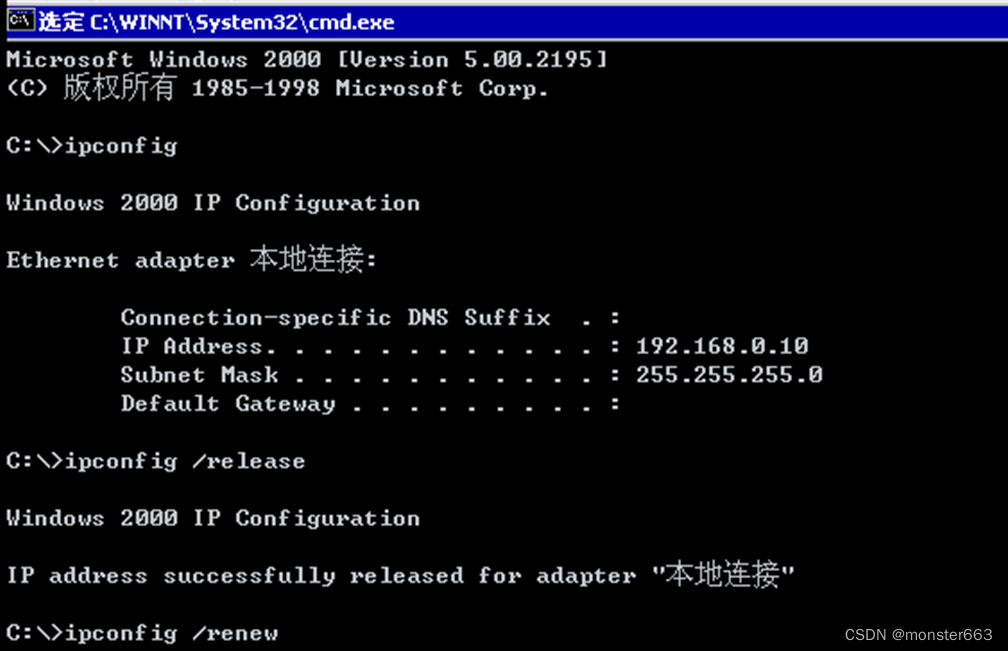
We turn on another Windows Server 2000, make sure that the two virtual machines are connected to the same LAN, and configure the Windows Server 2000 to automatically obtain an IP address. In the command line interface, we can see that the IP address obtained by Windows Server 2000 through DHCP is 192.168. 0.10, which meets the experimental expectations:
At the same time, we further experimented and configured the range of excluded IP addresses as 192.168.0.10 ~ 192.168.0.20.
In Windows Server 2000, use the "ipconfig /relesase" and "ipconfig /renew" commands to reacquire the IP address , you can see that the IP address in Windows Server 2000 has been changed to: 192.168.0.21, which also meets the experimental expectations. The
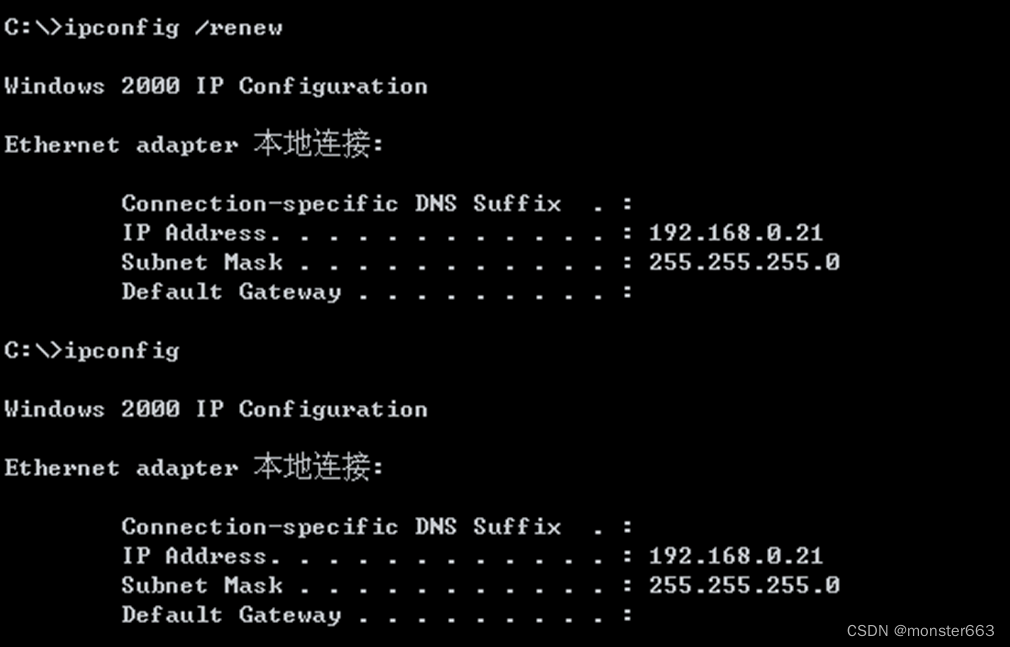
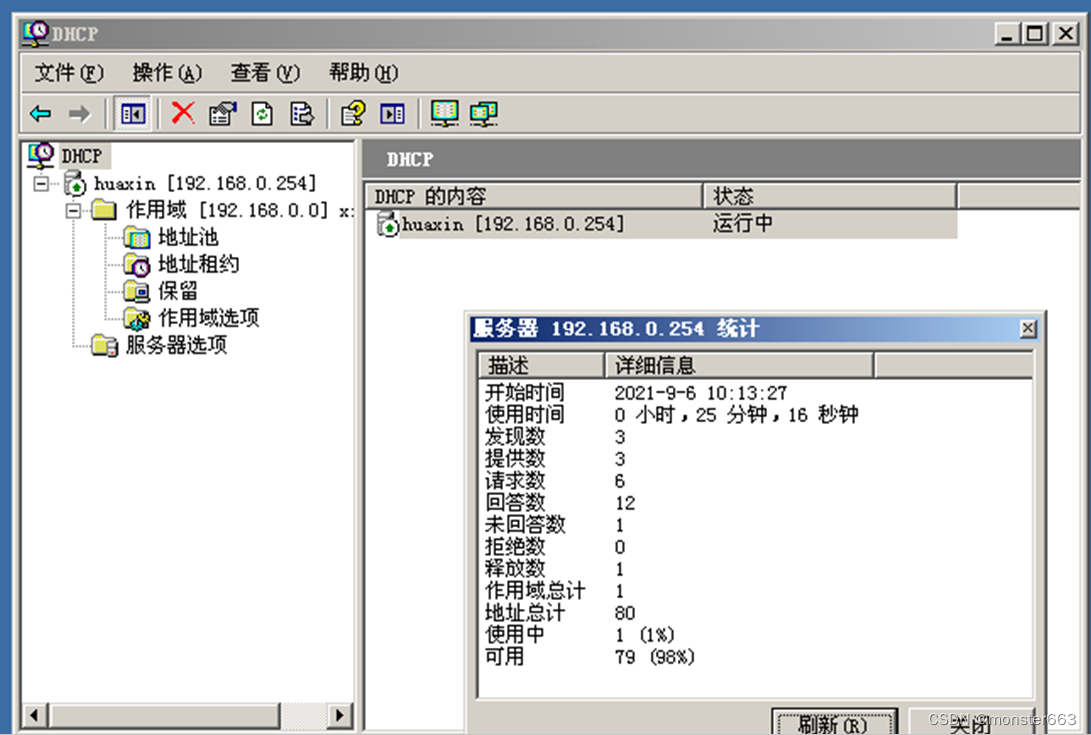
statistical information of the DHCP server is as follows:
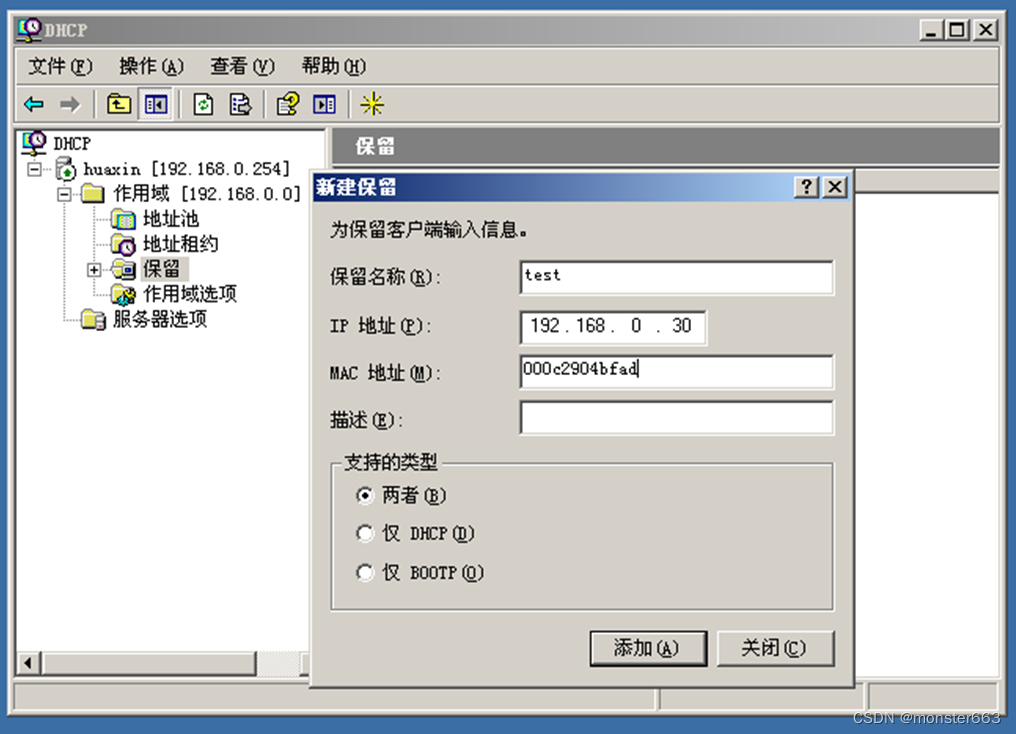
DHCP reserved address
Let’s continue to explore and configure the reservation function of DHCP. Let’s create a new reservation named test with an IP address of 192.168.0.30 and bind it to the MAC address of the client.
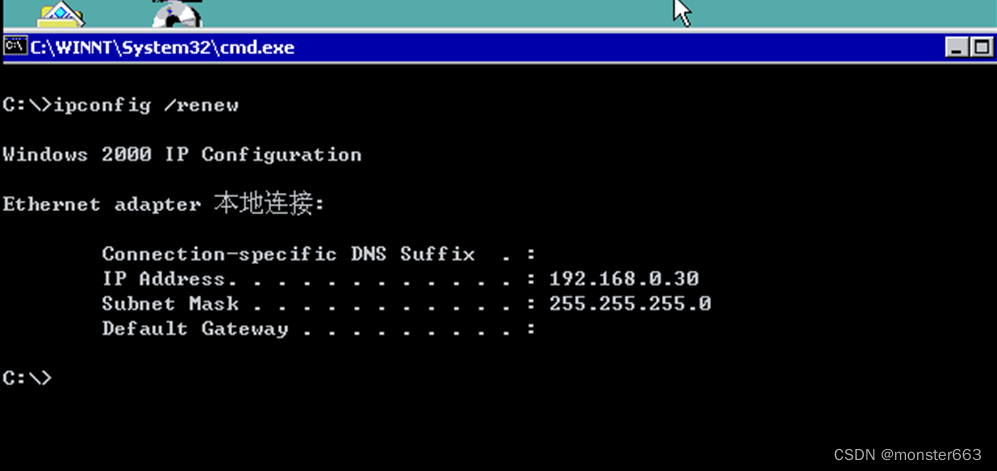
After the configuration is complete, the client uses ipconfig /renew to obtain the IP address again, and you can see that the client's IP address has changed to 192.168.0.30 bound in the reserved configuration
postscript
If you have any other questions, please leave a comment