Computer Network --- Others
A stub area is a special area because it cannot receive other OSPF AS routes through the ABR in this area like other areas. The internal routers in the Stub area only need to configure a default route (0.0.0.0.0.0.0.0) to reach the ABR in this area to implement routes between different areas in the same AS, so that the routing tables of the internal routers in these areas The size of the network and the number of routing information transfers will be greatly reduced.
computer network
A problem with the RIP protocol is that when the network fails, it takes a long time to transmit information to all routers. In this intermediate process, it is actually the problem of routing loops: when a routing loop occurs, the routing table will change frequently, resulting in one or several routing tables being unable to converge. As a result, the network will be in a state of Paralyzed or semi-paralyzed state.
Solutions for routing loops:
- Define the maximum value and stop accumulating after reaching the value
- Horizontal split method:
-
- Simple split horizon: Route entries received from the local interface are no longer sent from this interface.
- Split horizon with poison reverse: the routing entry sent from this interface will be sent from this interface, but marked as unreachable
- Suppression timer: The router delays possible failures in the network, confirms and then updates

computer network:
Multimode fibers generally use LED light sources, while single-mode fibers use extremely expensive lasers as light sources.
Computer Network---Network Planning and Design
Logical network design document: use the results of requirements analysis and existing network system analysis to design the logical network structure, and finally get a logical network design document, the output content includes the following points:
- Logical Network Design Diagram
- IP address scheme
- security plan
- Specific hardware and software, WAN connectivity equipment and basic services
- Specific instructions for recruiting and training network staff
- Initial cost estimates for software, hardware, services, staff and training
Physical design document: It is the physical realization of the logical network design. By determining the specific physical distribution of equipment and the operating environment, it is ensured that the physical connection of the network meets the requirements of the logical connection.
- Network physical structure diagram and wiring scheme
- Detailed list of equipment and parts
- Estimation of software, hardware and installation costs
- According to the schedule, detail the time and duration of the service
- Follow the test plan after
- User Training Program
Information Security---Firewall Technology
Firewall technology can be divided into two types: network-level firewall and application-level firewall.
- Network-level firewalls are used to prevent illegal intrusions from outside the entire network. For example, packet filtering and authorization servers fall into this category. The former checks all information flowing into the network, and then rejects data that does not meet a set of pre-established criteria, while the latter checks whether the user's login is legal;
- Application-level firewalls implement access control from applications, and usually use application-level gateways or proxy servers to distinguish various applications.
For example, you can allow only www applications and block all ftp applications
Information Security---Information Digest and Digital Signature
In the field of security, the use of digital signature technology can prevent message tampering, prevent message forgery, and prevent message errors during transmission, but it cannot prevent message leakage. Because the digital signature is essentially encrypted with the private key and verified with the public key, which means that everyone can unlock the content of the digital signature, so there is no confidentiality.
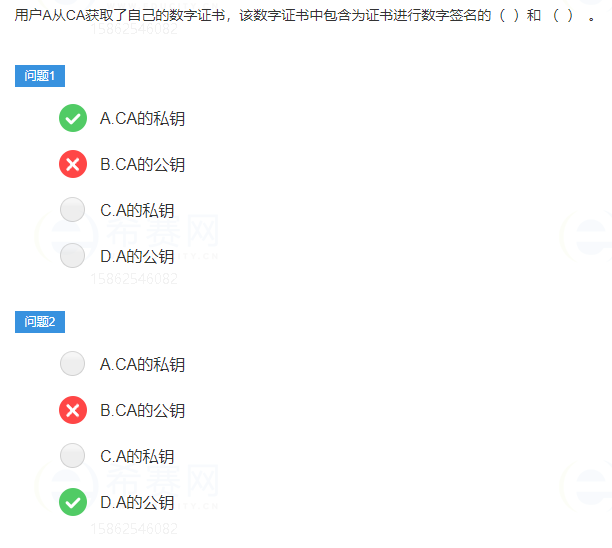
Information Security---Digital Certificate
The digital certificate of user A contains the private key of user A, and then the CA center signs with its own private key
Information Security --- Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption
Common symmetric encryption algorithms include: DES, 3DES, RC-5\IDEA, AES
Common asymmetric encryption algorithms include: RSA, ECC, Elgamal, knapsack algorithm, Rabin, DH
Common information digest algorithms include: SHA, MD5, HMAC
When using an asymmetric encryption system for encryption, A uses the existing public key to encrypt, and then uses the matching private key to decrypt;
Information Security---Others
Database disaster recovery should belong to system security and application security, because on the one hand, the database management system belongs to the system software, and on the other hand, the database stores application-level data;
Information Security---Network Security Protocol
- SSL is from the transport layer to the application layer
- PGP works at the application layer
- IPSec works at the network layer
Information Security --- Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption
In the symmetric encryption algorithm, since the same secret key is used for encryption and decryption, the secret key needs to be shared, so it is also called the shared secret key algorithm;
Triple DES encryption is done using 2 DES keys and performing multiple operations, so the length of the key is 56*2-112
Information Security---Information Digest and Digital Signature
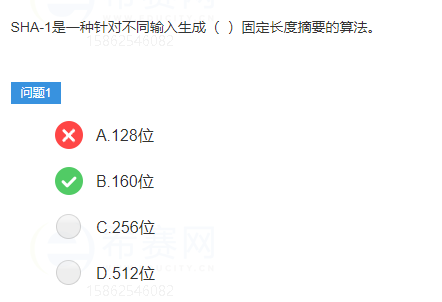
Commonly used message digest algorithms include MD5, SHA, etc. The hash values of MD5 and SHA algorithms widely used in the market are 128 and 160 bits respectively. Since SHA usually uses a longer secret key, the security of SHA is higher than that of MD5;
Information Security---Digital Certificate
In the public key system, the exchange of private keys is absolutely not allowed under any circumstances. The premise of mutual trust is based on CA, if only exchanging AB's public key will not solve the trust problem.

Information Security --- Symmetric Encryption and Asymmetric Encryption
RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm; both SHA-1 and MD5 are information digest algorithms; RC-5 is a symmetric encryption algorithm; among these algorithms, SHA-1 and MD5 cannot encrypt data, and RSA asymmetric encryption is generally not used due to efficiency issues. It will be used for plaintext encryption, and only RC-5 is suitable for plaintext encryption.

Information Security---Digital Certificate
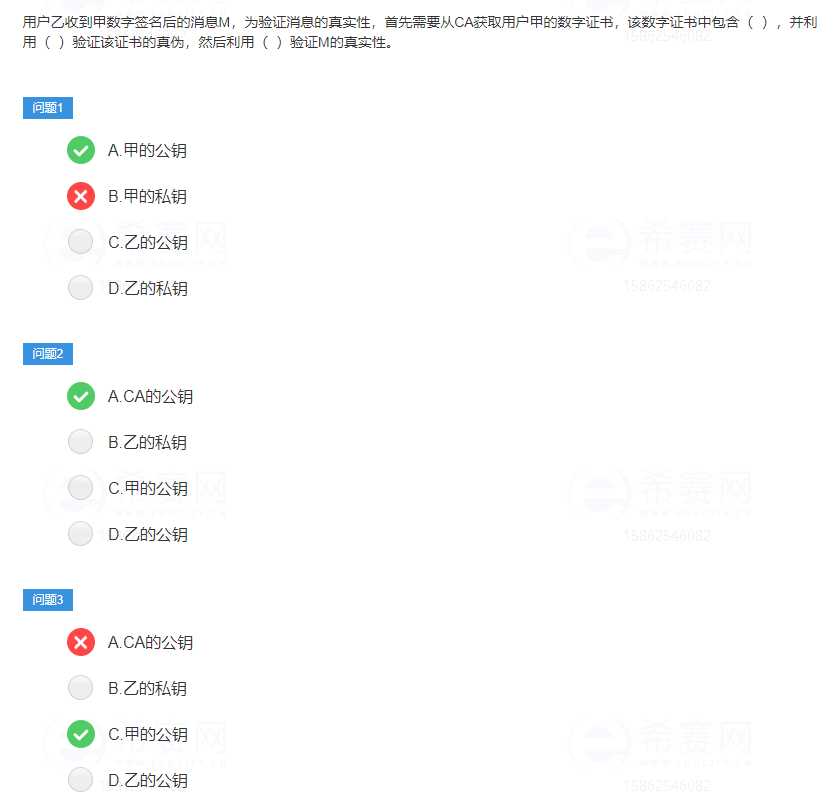
CA is the abbreviation of Certification Center. In order to authenticate the identities of both communication parties on the Internet, you can apply for your own digital certificate in the corresponding cognitive center.
The digital certificate issued by the CA to the user includes the user's public key information, the certification information of the authority, and the validity period. After receiving the digitally signed message, the user must first verify the authenticity of the certificate, that is, use the public key of the certificate to verify, and then use the public key of the other party to verify the authenticity of the message.
Information Security---Others
As an all-round system, the overall system security protection system is also divided into layers. Different layers reflect different security issues. According to the current application status and structure of the network, the layers of the security protection system can be divided into physical layer security, system layer security, Network layer security, application layer security and security management.
- The security of the physical environment, the security of the physical layer includes communication lines. Physical equipment and computer room security, etc. The security of the physical layer is mainly reflected in the reliability of communication lines (line backup, gateway software and transmission media), the security of software and hardware equipment (replacing equipment, dismantling equipment, adding equipment), equipment backup, disaster prevention capabilities, and anti-interference capacity, equipment operating environment (temperature, humidity, smoke) and uninterruptible power supply protection, etc.
- The security of the operating system, the security of the system layer comes from the security of the operating system used in the computer network, for example, Window Server and UNIX, etc., mainly in three aspects:
-
- The insecure factors brought about by the defects of the operating system itself mainly include identity authentication, access control and system vulnerabilities, etc.
- Security configuration issues for the operating system
- Viruses Threat to Operating System
- network security. The security issues at the network layer are mainly reflected in the security of the computer network, including network layer identity authentication, access control of network resources, confidentiality and integrity of data transmission, security of remote access, domain name system security, and routing system security. , means of intrusion detection and anti-virus of network facilities, etc.;
- App security. The security issues at the application layer are mainly generated by the security of application software and data used to provide services, including Web services, electronic point systems, and DNS. In addition, threats to the system by viruses are also included.
- Managed security. Safety management includes management of safety technology and equipment, safety management system, organizational rules of departments and personnel, etc. Management institutionalization greatly affects the security of the entire computer network. Strict security management systems, clear division of departmental security responsibilities, and reasonable personnel role allocation can greatly reduce security vulnerabilities at other levels.

Information Security---Others
WPA is a standards-based, interoperable WLAN security enhancement solution that can greatly enhance the data protection and access control levels of existing and future wireless LAN systems. WPA is derived from the IEEE802.11 standard under development and will remain forward compatible with it. Properly deployed, WPA ensures that WLAN users' data is protected and that only authorized network users can access the WLAN network.
Due to the insecurity of WEP, WPA is used to provide users with a temporary solution before the 802.11 protocol is perfected. The standard data encryption uses the temporary key integrity protocol TKIP that can dynamically change the key

Information Security---Network Security Protocol
In the DNS system, there are only 13 servers in the world based on the main directory that the server is mainly used to manage the Internet. 1 is the main root server, placed in the United States. The remaining 12 are auxiliary root servers. Nine of them are placed in the United States, two in Europe, located in the UK and Sweden, and one in Asia, located in Japan. All root servers are managed by ICANN, the Internet domain name and number assignment agency authorized by the US government, and are responsible for the management of global Internet domain name root servers, domain name system and IP addresses.
When the root domain name server is attacked and cannot be used normally, the problem is that the domain name cannot be resolved to the correct server when accessing the website. Naturally, the corresponding website cannot be accessed. At this time, the domain name of the normal website may be resolved to the wrong one. the address of.

Information Security---Intrusion Detection
Intrusion Detection (Intrusion Detection), as the name suggests, is the detection of intrusion performance. By collecting and analyzing information on several key points in a computer network or computer system, it is found whether there are signs of violations of security policies and attacks in the network or system.
The collected information about the status and behavior of the system, network, data, and user activities are generally analyzed through three technical means:
- pattern matching
- Statistical Analysis
- Integrity analysis
The first two methods are used for real-time intrusion detection, while integrity analysis is used for post-mortem analysis.

Information Security---Firewall Technology
The working level of the firewall is the main factor that determines the efficiency and security of the firewall. Generally speaking, the lower the working level of the firewall, the higher the working efficiency, but the lower the security; on the contrary, the higher the working level, the lower the working efficiency. The security will be higher.

Information Security---Network Security Protocol
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) is an open standard framework that uses encrypted security services to ensure confidential and secure communications over Internet Protocol IP networks.
- IPSec (Internet Protocol Security) is the long-term direction of secure Internet. It provides proactive protection against private network and Internet attacks through end-to-end security. In communication, only the sender and receiver are the only ones who must understand IPsec to protect computers. The IPsec protocol notarizes at layer 3 of the OSI model, making it suitable for protecting TCP or UDP based protocols when used alone. (Secure Socket Layer SSL cannot protect the communication flow of UDP layer)
- The AH protocol is used to provide data integrity and authentication to IP communications, and can provide anti-replay services;
- ESP provides IP-layer encryption assurance and authenticates the source of data for monitoring on the network. Although AH can protect the communication from tampering, it does not transform the data, and the data is still clear to hackers. In order to effectively protect the security of data transmission, there is another packet header ESP in IPv6 to further provide data confidentiality and prevent tamper.
- IPSec supports two encapsulation modes
-
- Tunnel mode (tunnel): The entire IP data packet of the user is used to calculate the AH or ESP header, and the user data encrypted by the AH or ESP header and ESP is encapsulated in a new IP data packet. Usually, tunnel mode is applied to the communication between two security gateways.
- Transport mode (transport): Only the transport layer data is used to calculate the AH or ESP header, and the AH or ESP header and ESP-encrypted user data are placed behind the original IP header. Usually, the transport mode is applied to the communication between two hosts, or the communication between a host and a security gateway. A common format is defined.

Information Security---Information Digest and Digital Signature
The message digest is a fixed output calculated by using a one-way hash function algorithm to calculate a message of any length. The so-called one-way means that the algorithm is irreversible, and it is very difficult to find two different messages with the same message digest. It is precisely because the message summary has this feature, so we will generate a message summary in the process of transmitting the message, and transmit the summary to the other party in different ways. After receiving the message and the message summary, the other party can compare the message with the summary. The text is verified to determine whether the message has been tampered with. Therefore, the message digest is a means to protect data integrity, which can prevent the sent message from being tampered with.

Information Security---Information Digest and Digital Signature
Digital Signature (Digital Signature) technology is a typical application of asymmetric encryption algorithm: the sender of the data source uses its own private key to encrypt the data verification and other variables related to the data content to complete the legal signature of the data, and the data receiver Then use the public key of the other party to interpret the received digital signature, and use the interpretation result to verify the integrity of the data to confirm the validity of the signature. The main functions of digital signatures are: ensuring the integrity of information transmission, authenticating the identity of the sender, and preventing repudiation in transactions.
