1. Virtualization
1.1 Concept
The various physical resources of the computer (CPU, memory, disk space, network adapter, etc.) are abstracted, converted and presented, and can be partitioned and combined into one or more computer configuration environments.
1.2 Reasons for Application Dataization
1) The same physical machine runs multiple different versions of application software
2) Low hardware dependency
3) Facilitate data migration
1.3 Advantages of Virtualization
1) Improve app compatibility
2) Reduce operating costs
3) Accelerate application deployment
4) Improve server availability
5) Improve resource utilization
6) Dynamic scheduling of resources
7) Reduce energy consumption
2.KVM
2.1KVM
1) KVM is open source software
2) It is a Linux full virtualization solution with x86 architecture and hardware supports virtualization technology (such as intel VT or AMD-V)
3) Contains the core module kvm.ko (kvm-intel.ko or kvm-AMD.ko) that provides the low-level virtualization loadable for the processor
4) The modified QEMU software (qemu-kvm) is required as the upper layer control and interface of the virtual machine
5) Can run multiple virtual machines at the same time without changing the linux or windows image, (it means that multiple virtual machines use the same image) and configure personalized hardware environment (network card, disk, graphics) for each virtual machine adapter...) and KVM can also use ksm technology to help the host server save memory.
2.2Virtual Machine Manager
1) Virtual machine administrator, which allows users to manage multiple virtual machines
2) Create, edit, boot or stop virtual machines
3) View and control the console of each virtual machine
4) View the performance and usage of each virtual machine
5) View the real-time and usage information of each running virtual machine and the host
6) KVM, Xen, QEMU can be used whether locally or remotely
3. KVM deployment
3.1 Environment Preparation
[root@KVM ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.4.1708 (Core)
[root@KVM ~]# uname -r
3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64
[root@KVM ~]# ifconfig
eth0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 10.0.0.101 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.0.0.255
inet6 fe80::af24:1fe3:9292:9747 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether 00:0c:29:2c:94:03 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 714 bytes 132837 (129.7 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 247 bytes 35367 (34.5 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
eth1: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether 00:0c:29:2c:94:0d txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
[root@KVM ~]# getenforce
Disabled
[root@KVM ~]# systemctl status firewalld.service
● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: inactive (dead)
Docs: man:firewalld(1)
3.2安装相关软件包
[root@KVM ~]# yum install qemu-kvm libvirt virt-install virt-manager bridge-utils
说明:qemu-kvm ----模拟计算机的工具,为KVM虚拟机提供IO设备
libvirt ----管理虚拟机
virt-install ----命令行的虚拟机创建安装工具
bridge-utils ----网桥工具
3.4启动
[root@KVM ~]# systemctl start libvirtd
方法一:使用命令行安装部署
3.4创建网桥
[root@KVM ~]# nmcli c add type bridge autoconnect yes con-name br0 ifname br0
Connection 'br0' (f8cd2a6d-1683-4174-825a-76d79b8cefcd) successfully added.
[root@KVM ~]# nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.addresses 10.0.0.101/24 ipv4.method manual
[root@KVM ~]# nmcli c modify br0 ipv4.gateway 10.0.0.254
[root@KVM ~]# nmcli c delete eth0
[root@KVM ~]# nmcli c add type bridge-slave autoconnect yes con-name eth0 ifname eth0 master br0
3.5重启
[root@KVM ~]# reboot
3.6创建安装磁盘
[root@KVM ~]# mkdir -p /var/linux/images
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /var/linux/images/centos74.img 20G
Formatting '/var/linux/images/centos71.img', fmt=qcow2 size=21474836480 encryption=off cluster_size=65536 lazy_refcounts=off
3.7安装虚拟机
[root@KVM ~]# virt-install --name centos71 --ram 512 --vcpus 2 --disk path=/var/linux43/images/centos71.img,size=10 --os-type linux --os-variant rhel7 --graphics none --console pty,target_type=serial --location=/var/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1708.iso --extra-args 'console=ttyS0,115200n8 serial'
方法二:VNC
3.4下载VNC(官网:http://www.tightvnc.com)
3.5创建安装磁盘
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /var/linux/images/centos742.img 20G
3.6安装虚拟机(NAT模式)
virt-install --virt-type=kvm --name=c72 --vcpus=1 -r 1024 -c /var/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1503-01.iso --network bridge=br0 --graphics vnc,listen=0.0.0.0 --noautoconsole --os-type=linux --os-variant=rhel7 --disk path=/var/linux/images/centos742.img,size=20,format=qcow2
3.7Windows下VNC连接
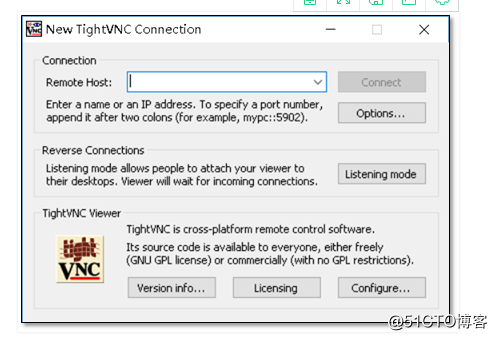
4.KVM的相关命令
4.1退出虚拟机
ctrl + ]
4.2进入虚拟机
virsh console centos74
4.3查看虚拟机的及状态
virsh list
virsh list --all
4.4启动虚拟机
virsh start centos74
4.5关闭虚拟机
virsh shutdown centos74
4.6强制关闭虚拟机
virsh destroy centos74
4.7删除虚拟机
virsh shutdown centos74
virsh undefine centos74
5.磁盘管理
5.1查看当前虚拟机硬盘信息
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img info /var/linux/images/centos74.img
image: /var/linux/images/centos74.img
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 20G (21474836480 bytes)
disk size: 1.2G
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
lazy refcounts: false
refcount bits: 16
corrupt: false
5.2转换磁盘格式(qcow2转换为raw)
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img convert -f qcow2 -O raw /var/linux/images/centos74.img /var/linux/images/centos74.img
5.3KVM虚拟机添加硬盘
5.3.1创建一块新的硬盘
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img create -f qcow2 /var/linux/images/centos74-add.qcow2 2G
5.3.2查看创建的硬盘信息
[root@KVM ~]# qemu-img info /var/linux/images/centos74-add.qcow2
image: /var/linux/images/centos74-add.qcow2
file format: qcow2
virtual size: 2.0G (2147483648 bytes)
disk size: 196K
cluster_size: 65536
Format specific information:
compat: 1.1
lazy refcounts: false
refcount bits: 16
corrupt: false
5.3.3为虚拟机添加硬盘
[root@KVM ~]# virsh attach-disk centos74 /var/linux/images/centos74-add.qcow2 vdb --live --cache=none --subdriver=qcow2
Disk attached successfully
说明:vdb 第二块硬盘
--live 热添加
--sudbriver 驱动类型
detach-disk 分离磁盘设备
attach-disk 附加磁盘设备
5.4格式化磁盘(在KVM虚拟机中操作)
[root@centos74 ~]# mkfs.xfs /dev/vdb
6.快照管理
6.1创建快照
[root@KVM ~]# virsh snapshot-create cnetos74
6.2查看主机快照列表
[root@KVM ~]# virsh snapshot-list centos74
6.3查看快照信息
[root@KVM ~]# virsh snapshot-info centos74 --spanshotname 1516607756
6.4还原快照
[root@KVM ~]# virsh snapshot-revert centos74 --spanshotname 1516607756
6.5删除快照
[root@KVM ~]# virsh snapshot-delete centos74 --spanshotname 1516607756
7.KVM虚拟机克隆
[root@KVM ~]# virsh-clone --auto-clone -o centos74
8.KVM虚拟机冷迁移
8.1在KVM02中安装kvm组件
[root@KVM02 ~]# yum install -y libvirt* virt-* qemu-kvm*
8.2配置桥接网络
[root@KVM 02~]# virsh iface-bridge eth0 br0
8.3KVM主机将虚拟机关闭,导出配置文件
[root@KVM ~]# virsh shutdown centos74
[root@KVM ~]# virsh dumpxml centos74 > centos74.xml
8.4将虚拟文件传输到KVM02上
[root@KVM ~]# scp -rp centos74.xml 10.0.0.102:/data
8.5KVM02主机导入文件
[root@KVM02 ~]# virsh define centos74.xml
8.6启动虚拟机
[root@KVM02 ~]# virsh start centos74
9.KVM虚拟机热迁移
9.1KVM虚拟机热迁移的核心
共享存储。这里使用NFS共享存储(详情参考:http://blog.51cto.com/13520761/2087720)
9.1安装virt-manager所需桌面及vnc-server
[root@KVM ~]# yum groupinstall "GNOME Desktop" -y
[root@KVM ~]# yum install -y tigervnc-server
[root@KVM ~]# yum install -y opnssh-askpass
9.2复制vnc配置文件
[root@KVM ~]# cp /usr/lib/systemd/system/[email protected] /usr/lib/systemd/system/vncserver@\:1.server
9.3修改配置文件
[root@KVM ~]#
egrep -v "^#|^$" /usr/lib/systemd/system/vncserver@\:1.service
[Unit]
Description=Remote desktop service (VNC)
After=syslog.target network.target
[Service]
Type=forking
User=root
ExecStartPre=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i
ExecStart=/usr/bin/vncserver %i
PIDFile=/root/.vnc/%H%i.pid
ExecStop=-/usr/bin/vncserver -kill %i
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
9.4设置vnc连接时的密码
[root@KVM ~]# vncpasswd
9.5启动vnc服务
[root@KVM ~]# systemctl start vncserver@\:1.services
9.6在KVM主机上部署NFS服务
9.7在KVM02主机上挂载目录
[root@KVM02 ~]# mount -t nfs 172.16.1.101:/var/linux/images /var/linux/images
9.8vnc连接KVM宿主机
9.9添加KVM02宿主机
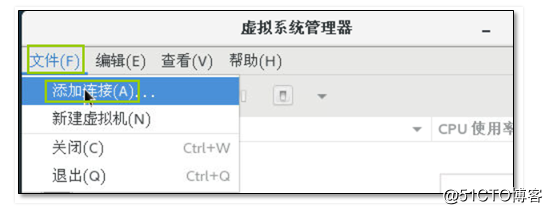
9.10主机热迁移
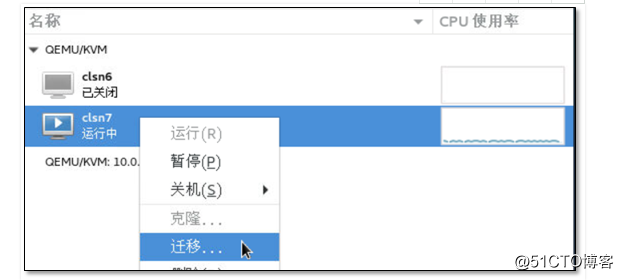
9.11在KVM02上查看虚拟主机
[root@KVM02 ~]# virsh list --all