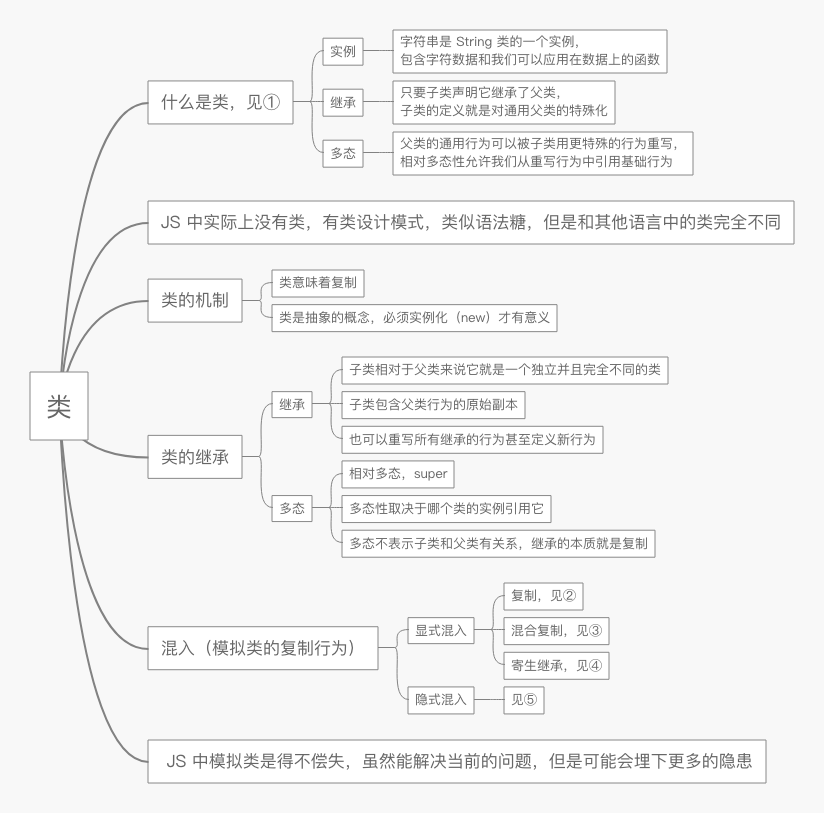
① What is the class, describing the organizational structure of a code, a modeling method in the field of real-world problems in software
②
// very simple a mixin () Examples of function a mixin (sourceObj, targetObj) { for ( var Key in sourceObj) { // only replicate in the absence of IF (! (Key in targetObj)) { targetObj [Key] = sourceObj [Key] } } return targetObj; } var Vehicle = { Engines: . 1 , Ignition: function () { the console.log ( 'Engine My Turning ON.' ); }, Drive: function () { this.ignition(); console.log('Steering and moving forward!'); } } var Car = mixin(Vehicle, { wheel: 4, drive: function(){ Vehicle.drive.call(this); console.log('Rolling on all ' + this.wheel + ' wheels!'); } })
③
// Another mixed function, there may be the risk of overwriting function a mixin (sourceObj, targetObj) { for ( var Key in sourceObj) { targetObj [Key] = sourceObj [Key]; } return targetObj; } var Vehicle = { // ... } // first create an empty object and the content copied into Vehicle var Car = a mixin (Vehicle, {});
// then copy the contents into the new Car in a mixin ({ Wheels: . 4 , Drive: function ( ) { // ... } }, Car)
④
// conventional type JS, Vehicle function Vehicle () { the this .engines =. 1 ; } Vehicle.prototype.ignition = function () { the console.log ( 'Engine My Turning ON.' ); } Vehicle.prototype.drive = function () { the this .ignition (); the console.log ( 'Steering and Moving Forward!' ); } // parasitized Car function Car () { // first, Car is a Vehicle var CAR = new new Vehicle (); // then we customize for Car =. 4 car.wheels ; // save the Vehicle :: drive () special reference var vehDrive = car.drive; // override Vehicle :: drive () car.drive = function () { vehDrive.call ( the this ) ; the console.log ( 'ON All Rolling' + the this .wheels + 'Wheels!' ); } return CAR; } var myCar = new new Car () myCar.drive ();
⑤
var Something = { cool: function () { this.greeting = 'Hello World'; this.count = this.count ? this.count + 1 : 1; } } Something.cool(); Something.greeting; // 'Hello World' Something.count; // 1 var Another = { cool: function() { // 隐式把 Something 混入 Another Something.cool.call(this); } }; Another.cool(); Another.greeting; // 'Hello World' Another.count; // 1