Spring Cloud Config Server能够统一管理配置,我们绝大多数情况都是基于git或者svn作为其配置仓库,其实SpringCloud还可以把数据库作为配置仓库,今天我们就来了解一下。顺便分析一下其实现原理。
一、PropertySourceLocator接口
1.1、代码分析
这个接口的作用用于定制化引导配置,通过这个接口我们可以通过代码动态的向Environment中添加PropertySource,该接口定义如下:

/* * Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; /** * Strategy for locating (possibly remote) property sources for the Environment. * Implementations should not fail unless they intend to prevent the application from * starting. * * @author Dave Syer * */ public interface PropertySourceLocator { /** * @param environment the current Environment * @return a PropertySource or null if there is none * * @throws IllegalStateException if there is a fail fast condition */ PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment); }
那么此接口在SpringCloud类引导类PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration里有处理,核心代码如下:
@Configuration @EnableConfigurationProperties(PropertySourceBootstrapProperties.class) public class PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext>, Ordered { @Override public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) { CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource( BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.propertySourceLocators); boolean empty = true; ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment(); for (PropertySourceLocator locator : this.propertySourceLocators) { PropertySource<?> source = null; source = locator.locate(environment); if (source == null) { continue; } logger.info("Located property source: " + source); composite.addPropertySource(source); empty = false; } if (!empty) { MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources(); String logConfig = environment.resolvePlaceholders("${logging.config:}"); LogFile logFile = LogFile.get(environment); if (propertySources.contains(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) { propertySources.remove(BOOTSTRAP_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME); } insertPropertySources(propertySources, composite); reinitializeLoggingSystem(environment, logConfig, logFile); setLogLevels(applicationContext, environment); handleIncludedProfiles(environment); } } //..... private void insertPropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources, CompositePropertySource composite) { MutablePropertySources incoming = new MutablePropertySources(); incoming.addFirst(composite); PropertySourceBootstrapProperties remoteProperties = new PropertySourceBootstrapProperties(); new RelaxedDataBinder(remoteProperties, "spring.cloud.config") .bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(incoming)); if (!remoteProperties.isAllowOverride() || (!remoteProperties.isOverrideNone() && remoteProperties.isOverrideSystemProperties())) { propertySources.addFirst(composite); return; } if (remoteProperties.isOverrideNone()) { propertySources.addLast(composite); return; } if (propertySources .contains(StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME)) { if (!remoteProperties.isOverrideSystemProperties()) { propertySources.addAfter( StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, composite); } else { propertySources.addBefore( StandardEnvironment.SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, composite); } } else { propertySources.addLast(composite); } } }
在这里我们可以清楚的看到,首先会获取所有的PropertySourceLocator,并调用其locate方法,只有当propertySouceLocator有实现类时,它才会获取当前引导上下文的Environment,并在 insertPropertySources方法里,把PropertySourceLocator的自定义属性值添加到引导上下文的环境当中。
1.2、代码示例
代码目录结构如下:
在这里注意,自定义实现的PropertySourceLocator是我们的引导程序,因此一定不能被主程序componentScan到
MyTestPropertySourceLocator代码如下:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.config.bootstrap; import org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; @Configuration public class MyTestPropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator { @Override public PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment) { Map<String, Object> propertySource = new HashMap<>(); propertySource.put("student.name", "admin"); MapPropertySource mapPropertySource = new MapPropertySource("customer", propertySource); return mapPropertySource; } }
spring.factories文件:

org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\
com.bdqn.lyrk.config.bootstrap.MyTestPropertySourceLocator
ConfigServer:

package com.bdqn.lyrk.config.server; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.EnableConfigServer; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; @SpringBootApplication @EnableConfigServer public class ConfigServer { public static void main(String[] args) { ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(ConfigServer.class, args); Environment environment = applicationContext.getBean(Environment.class); System.out.println(environment); System.out.println(environment.getProperty("student.name")); } }
运行结果如下:
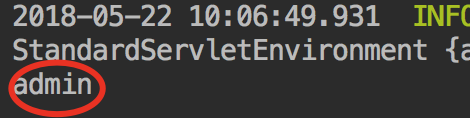
我们可以看到,当我们把自定义的PropertySourceLocator作为引导程序配置时,该接口的locate方法返回值会添加到Environment当中
二、ConfigServer
ConfigServer是配置中心的服务端,它负责统一管理配置,当我们以http://地址:端口号/{application}-{profile}.properties发送请求时会被EnvironmentController处理,我们来看一下EnvironmentController的源码:
@RestController @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, path = "${spring.cloud.config.server.prefix:}") public class EnvironmentController { public EnvironmentController(EnvironmentRepository repository) { this(repository, new ObjectMapper()); } public EnvironmentController(EnvironmentRepository repository, ObjectMapper objectMapper) { this.repository = repository; this.objectMapper = objectMapper; } @RequestMapping("/{name}/{profiles}/{label:.*}") public Environment labelled(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles, @PathVariable String label) { if (name != null && name.contains("(_)")) { // "(_)" is uncommon in a git repo name, but "/" cannot be matched // by Spring MVC name = name.replace("(_)", "/"); } if (label != null && label.contains("(_)")) { // "(_)" is uncommon in a git branch name, but "/" cannot be matched // by Spring MVC label = label.replace("(_)", "/"); } Environment environment = this.repository.findOne(name, profiles, label); return environment; } @RequestMapping("/{name}-{profiles}.properties") public ResponseEntity<String> properties(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "true") boolean resolvePlaceholders) throws IOException { return labelledProperties(name, profiles, null, resolvePlaceholders); } @RequestMapping("/{label}/{name}-{profiles}.properties") public ResponseEntity<String> labelledProperties(@PathVariable String name, @PathVariable String profiles, @PathVariable String label, @RequestParam(defaultValue = "true") boolean resolvePlaceholders) throws IOException { validateProfiles(profiles); Environment environment = labelled(name, profiles, label); Map<String, Object> properties = convertToProperties(environment); String propertiesString = getPropertiesString(properties); if (resolvePlaceholders) { propertiesString = resolvePlaceholders(prepareEnvironment(environment), propertiesString); } return getSuccess(propertiesString); } // .....省略其他代码 }
在这里的核心代码是labelled,该方法首先会解析(_)将其替换为/ ,然后调用的EnvironmentRepository的findOne方法。

/* * Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment; /** * @author Dave Syer * @author Roy Clarkson */ public interface EnvironmentRepository { Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label); }
此接口主要是根据application profiles label这三个参数拿到对应的Environment 注意这里的Environment不是Springframework下的Environment接口:

/* * Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.config.environment; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonCreator; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonProperty; /** * Simple plain text serializable encapsulation of a list of property sources. Basically a * DTO for {@link org.springframework.core.env.Environment}, but also applicable outside * the domain of a Spring application. * * @author Dave Syer * @author Spencer Gibb * */ public class Environment { private String name; private String[] profiles = new String[0]; private String label; private List<PropertySource> propertySources = new ArrayList<>(); private String version; private String state; public Environment(String name, String... profiles) { this(name, profiles, "master", null, null); } /** * Copies all fields except propertySources * @param env */ public Environment(Environment env) { this(env.getName(), env.getProfiles(), env.getLabel(), env.getVersion(), env.getState()); } @JsonCreator public Environment(@JsonProperty("name") String name, @JsonProperty("profiles") String[] profiles, @JsonProperty("label") String label, @JsonProperty("version") String version, @JsonProperty("state") String state) { super(); this.name = name; this.profiles = profiles; this.label = label; this.version = version; this.state = state; } public void add(PropertySource propertySource) { this.propertySources.add(propertySource); } public void addAll(List<PropertySource> propertySources) { this.propertySources.addAll(propertySources); } public void addFirst(PropertySource propertySource) { this.propertySources.add(0, propertySource); } public List<PropertySource> getPropertySources() { return propertySources; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getLabel() { return label; } public void setLabel(String label) { this.label = label; } public String[] getProfiles() { return profiles; } public void setProfiles(String[] profiles) { this.profiles = profiles; } public String getVersion() { return version; } public void setVersion(String version) { this.version = version; } public String getState() { return state; } public void setState(String state) { this.state = state; } @Override public String toString() { return "Environment [name=" + name + ", profiles=" + Arrays.asList(profiles) + ", label=" + label + ", propertySources=" + propertySources + ", version=" + version + ", state=" + state + "]"; } }
SpringCloud中的Environment类与Springframework的Environment接口相仿,前者中的属性终将会添加至后者当中,下面我们可以看一下它是怎么实现的
首先我们下找到spring-cloud-config-server-xxx.jar下的spring.factories文件:

# Bootstrap components org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap.ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EncryptionAutoConfiguration # Application listeners org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\ org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap.ConfigServerBootstrapApplicationListener # Autoconfiguration org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.ConfigServerAutoConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EncryptionAutoConfiguration
我们可以看到,此处配置了引导类有一个叫:ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration,我们不妨看看这个引导类:

/*
* Copyright 2013-2015 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.bootstrap;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigClientProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.ConfigServerProperties;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.config.TransportConfiguration;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment.EnvironmentRepository;
import org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment.EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* Bootstrap configuration to fetch external configuration from a (possibly
* remote) {@link EnvironmentRepository}. Off by default because it can delay
* startup, but can be enabled with
* <code>spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap=true</code>. This would be useful,
* for example, if the config server were embedded in another app that wanted to
* be configured from the same repository as all the other clients.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Roy Clarkson
*/
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnProperty("spring.cloud.config.server.bootstrap")
public class ConfigServerBootstrapConfiguration {
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ConfigServerProperties.class)
@Import({ EnvironmentRepositoryConfiguration.class, TransportConfiguration.class })
protected static class LocalPropertySourceLocatorConfiguration {
@Autowired
private EnvironmentRepository repository;
@Autowired
private ConfigClientProperties client;
@Autowired
private ConfigServerProperties server;
@Bean
public EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator environmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator() {
return new EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator(this.repository, this.client.getName(),
this.client.getProfile(), getDefaultLabel());
}
private String getDefaultLabel() {
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.client.getLabel())) {
return this.client.getLabel();
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.server.getDefaultLabel())) {
return this.server.getDefaultLabel();
}
return null;
}
}
}
该引导中装配了一个EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator的类,我们继续看看这个类:

/* * Copyright 2013-2014 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import java.util.Map; import org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.CompositePropertySource; import org.springframework.core.env.Environment; import org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource; /** * A PropertySourceLocator that reads from an EnvironmentRepository. * * @author Dave Syer * */ public class EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator { private EnvironmentRepository repository; private String name; private String profiles; private String label; public EnvironmentRepositoryPropertySourceLocator(EnvironmentRepository repository, String name, String profiles, String label) { this.repository = repository; this.name = name; this.profiles = profiles; this.label = label; } @Override public org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> locate(Environment environment) { CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource("configService"); for (PropertySource source : repository.findOne(name, profiles, label) .getPropertySources()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) source.getSource(); composite.addPropertySource(new MapPropertySource(source.getName(), map)); } return composite; } }
这个类很明显实现了PropertySourceLocator接口,在locate方法里会调用EnvironmentRepository的findOne方法,此时会将SpringCloud的Environment类和Spring中的Environment相关联
三、config-client
当我们添加config-client时,启动时会去服务端请求远程的配置进而加载至当前的Environment当中。我们先看一看它的spring.factories文件:

# Auto Configure org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigClientAutoConfiguration # Bootstrap components org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapConfiguration=\ org.springframework.cloud.config.client.ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration,\ org.springframework.cloud.config.client.DiscoveryClientConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration
根据引导配置,我们去追溯一下ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration的源代码:

/*
* Copyright 2013-2017 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.cloud.config.client;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.EnableRetry;
import org.springframework.retry.annotation.Retryable;
import org.springframework.retry.interceptor.RetryInterceptorBuilder;
import org.springframework.retry.interceptor.RetryOperationsInterceptor;
/**
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Tristan Hanson
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
public class ConfigServiceBootstrapConfiguration {
@Autowired
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
@Bean
public ConfigClientProperties configClientProperties() {
ConfigClientProperties client = new ConfigClientProperties(this.environment);
return client;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.config.enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator configServicePropertySource(ConfigClientProperties properties) {
ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator locator = new ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(
properties);
return locator;
}
@ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.cloud.config.failFast", matchIfMissing=false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Retryable.class, Aspect.class, AopAutoConfiguration.class })
@Configuration
@EnableRetry(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Import(AopAutoConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RetryProperties.class)
protected static class RetryConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "configServerRetryInterceptor")
public RetryOperationsInterceptor configServerRetryInterceptor(
RetryProperties properties) {
return RetryInterceptorBuilder
.stateless()
.backOffOptions(properties.getInitialInterval(),
properties.getMultiplier(), properties.getMaxInterval())
.maxAttempts(properties.getMaxAttempts()).build();
}
}
}
与config-server端类似,我们可以发现其装配了一个ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator的Bean,这里我贴出关键代码部分:
@Order(0) public class ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator implements PropertySourceLocator { private static Log logger = LogFactory .getLog(ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator.class); private RestTemplate restTemplate; private ConfigClientProperties defaultProperties; public ConfigServicePropertySourceLocator(ConfigClientProperties defaultProperties) { this.defaultProperties = defaultProperties; } @Override @Retryable(interceptor = "configServerRetryInterceptor") public org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource<?> locate( org.springframework.core.env.Environment environment) { ConfigClientProperties properties = this.defaultProperties.override(environment); CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource("configService"); RestTemplate restTemplate = this.restTemplate == null ? getSecureRestTemplate(properties) : this.restTemplate; Exception error = null; String errorBody = null; logger.info("Fetching config from server at: " + properties.getRawUri()); try { String[] labels = new String[] { "" }; if (StringUtils.hasText(properties.getLabel())) { labels = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(properties.getLabel()); } String state = ConfigClientStateHolder.getState(); // Try all the labels until one works for (String label : labels) { Environment result = getRemoteEnvironment(restTemplate, properties, label.trim(), state); if (result != null) { logger.info(String.format("Located environment: name=%s, profiles=%s, label=%s, version=%s, state=%s", result.getName(), result.getProfiles() == null ? "" : Arrays.asList(result.getProfiles()), result.getLabel(), result.getVersion(), result.getState())); if (result.getPropertySources() != null) { // result.getPropertySources() can be null if using xml for (PropertySource source : result.getPropertySources()) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") Map<String, Object> map = (Map<String, Object>) source .getSource(); composite.addPropertySource(new MapPropertySource(source .getName(), map)); } } if (StringUtils.hasText(result.getState()) || StringUtils.hasText(result.getVersion())) { HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); putValue(map, "config.client.state", result.getState()); putValue(map, "config.client.version", result.getVersion()); composite.addFirstPropertySource(new MapPropertySource("configClient", map)); } return composite; } } } catch (HttpServerErrorException e) { error = e; if (MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON.includes(e.getResponseHeaders() .getContentType())) { errorBody = e.getResponseBodyAsString(); } } catch (Exception e) { error = e; } if (properties.isFailFast()) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Could not locate PropertySource and the fail fast property is set, failing", error); } logger.warn("Could not locate PropertySource: " + (errorBody == null ? error==null ? "label not found" : error.getMessage() : errorBody)); return null; } private Environment getRemoteEnvironment(RestTemplate restTemplate, ConfigClientProperties properties, String label, String state) { String path = "/{name}/{profile}"; String name = properties.getName(); String profile = properties.getProfile(); String token = properties.getToken(); String uri = properties.getRawUri(); Object[] args = new String[] { name, profile }; if (StringUtils.hasText(label)) { args = new String[] { name, profile, label }; path = path + "/{label}"; } ResponseEntity<Environment> response = null; try { HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders(); if (StringUtils.hasText(token)) { headers.add(TOKEN_HEADER, token); } if (StringUtils.hasText(state)) { //TODO: opt in to sending state? headers.add(STATE_HEADER, state); } final HttpEntity<Void> entity = new HttpEntity<>((Void) null, headers); response = restTemplate.exchange(uri + path, HttpMethod.GET, entity, Environment.class, args); } catch (HttpClientErrorException e) { if (e.getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND) { throw e; } } if (response == null || response.getStatusCode() != HttpStatus.OK) { return null; } Environment result = response.getBody(); return result; } //。。。省略其他代码 }
在这里我们可以发现,当client端启动时,通过RestTemplate请求服务端的EnvironmentController进而添加至当前的Environment
三、使用数据库作为配置中心的仓库
我们先看一下自动装配类:
@Configuration @Profile("jdbc") class JdbcRepositoryConfiguration { @Bean public JdbcEnvironmentRepository jdbcEnvironmentRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbc) { return new JdbcEnvironmentRepository(jdbc); } }
这里面创建了JdbcEnvironmentRepostiory,紧接着我们在看一下这个类的源码:

/* * Copyright 2016-2017 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.cloud.config.server.environment; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.LinkedHashMap; import java.util.LinkedHashSet; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Properties; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.Environment; import org.springframework.cloud.config.environment.PropertySource; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.ResultSetExtractor; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; /** * An {@link EnvironmentRepository} that picks up data from a relational database. The * database should have a table called "PROPERTIES" with columns "APPLICATION", "PROFILE", * "LABEL" (with the usual {@link Environment} meaning), plus "KEY" and "VALUE" for the * key and value pairs in {@link Properties} style. Property values behave in the same way * as they would if they came from Spring Boot properties files named * <code>{application}-{profile}.properties</code>, including all the encryption and * decryption, which will be applied as post-processing steps (i.e. not in this repository * directly). * * @author Dave Syer * */ @ConfigurationProperties("spring.cloud.config.server.jdbc") public class JdbcEnvironmentRepository implements EnvironmentRepository, Ordered { private static final String DEFAULT_SQL = "SELECT KEY, VALUE from PROPERTIES where APPLICATION=? and PROFILE=? and LABEL=?"; private int order = Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 10; private final JdbcTemplate jdbc; private String sql = DEFAULT_SQL; private final PropertiesResultSetExtractor extractor = new PropertiesResultSetExtractor(); public JdbcEnvironmentRepository(JdbcTemplate jdbc) { this.jdbc = jdbc; } public void setSql(String sql) { this.sql = sql; } public String getSql() { return this.sql; } @Override public Environment findOne(String application, String profile, String label) { String config = application; if (StringUtils.isEmpty(label)) { label = "master"; } if (StringUtils.isEmpty(profile)) { profile = "default"; } if (!profile.startsWith("default")) { profile = "default," + profile; } String[] profiles = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(profile); Environment environment = new Environment(application, profiles, label, null, null); if (!config.startsWith("application")) { config = "application," + config; } List<String> applications = new ArrayList<String>(new LinkedHashSet<>( Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(config)))); List<String> envs = new ArrayList<String>(new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(profiles))); Collections.reverse(applications); Collections.reverse(envs); for (String app : applications) { for (String env : envs) { Map<String, String> next = (Map<String, String>) jdbc.query(this.sql, new Object[] { app, env, label }, this.extractor); if (!next.isEmpty()) { environment.add(new PropertySource(app + "-" + env, next)); } } } return environment; } @Override public int getOrder() { return order; } public void setOrder(int order) { this.order = order; } } class PropertiesResultSetExtractor implements ResultSetExtractor<Map<String, String>> { @Override public Map<String, String> extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException, DataAccessException { Map<String, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<>(); while (rs.next()) { map.put(rs.getString(1), rs.getString(2)); } return map; } }
我们可以看到该类实现了EnvironmentRepository接口,在findone方法里通过JDBCTemplate来获取数据库中的配置信息。
下面我们来修改config-server端代码
4.1、gradle配置
dependencies { compile('org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-config-server') compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-jdbc') compile group: 'mysql', name: 'mysql-connector-java' }
4.2、bootstrap.yml
spring: profiles: active: jdbc application: name: config-server cloud: config: server: jdbc: sql: SELECT `KEY`,`VALUE` FROM PROPERTIES where APPLICATION=? and PROFILE=? and LABEL=? profile: local label: master datasource: url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/MySchool?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false username: root password: root server: port: 8888
3、DDL脚本
create table PROPERTIES ( ID int auto_increment primary key, `KEY` varchar(32) null, VALUE varchar(32) null, APPLICATION varchar(64) null, PROFILE varchar(32) null, LABEL varchar(16) null, CREATE_DATE datetime null ) CHARSET='utf8' ;
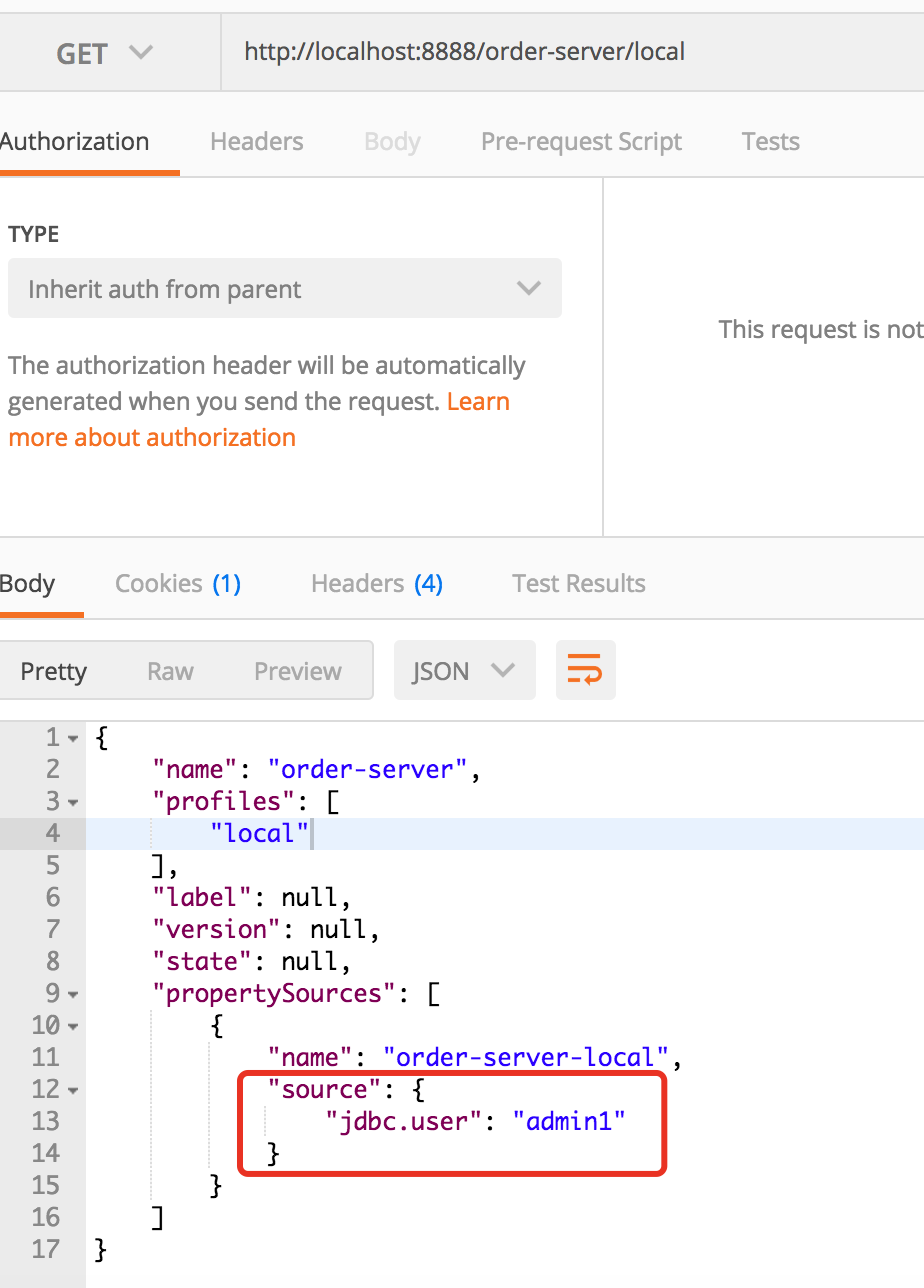
4、验证结果
四、总结
1.ConfigServer利用了SpringCloud引导机制,当主程序启动时,通过PropertySourceLocator的方法把相关配置读到当前的Environment中,同时提供了EnvironmentController使外界能够根据不同的请求获取不同格式的配置结果,由于是引导程序是核心,因此务必使用bootstrap.yml(properties)进行配置操作。
2.SpringCloud的客户端同样利用引导,通过实现PropertySourceLocator接口在程序启动前利用RestTemplate访问ConfigServer获取到配置并加载到当前Environment中
