算法上机报告3——地图路由(Map Routing)
目录
四、实验内容(含源代码)
一、实验简介
本实验要求学生能够综合运用排序、搜索、图处理和字符串处理的基础算法和数据结构,
将算法理论、算法工程和编程实践相结合开发相应的软件,解决科学、工程和应用环境下的
实际问题。使学生能充分运用并掌握算法设计与分析的方法以及算法工程技术,为从事计算
机工程和软件开发等相关工作打下坚实的基础。
二、实验目的
通过本课程的学习使学生系统掌握算法设计与分析的基本概念和基本原理,理解排序、
搜索、图处理和字符串处理的算法设计理论及性能分析方法,掌握排序、搜索、图处理和字符串处理的数据结构与算法实现技术。课程强调算法的开发及 Java 实现,理解相应算法的性能特征,评估算法在应用程序中的潜在性能。
三、实验环境
1.安装Windows操作系统的计算机
2.Java的IDE——eclipse
3.安装 Java 编程环境。 引入stdlib.jar and algs4.jar。
四、实验内容
1.问题重述
实现经典的 Dijkstra 最短路径算法,并对其进行优化。 这种算法广泛应用于地理信息系统(GIS),包括 MapQuest 和基于 GPS 的汽车导航系统。
本次实验对象是图 maps 或 graphs,其中顶点为平面上的点,这些点由权值为欧氏距离的边相连成图。 可将顶点视为城市,将边视为相连的道路。 为了在文件中表示地图,我们列出了顶点数和边数,然后列出顶点(索引后跟其 x 和 y 坐标),然后列出边(顶点对),
最后列出源点和汇点。
目标: 优化 Dijkstra 算法,使其可以处理给定图的数千条最短路径查询。 一旦你读取图(并可选地预处理),你的程序应该在亚线性时间内解决最短路径问题。 一种方法是预先计算出所有顶点对的最短路径;然而,你无法承受存储所有这些信息所需的二次空间。 你的目标是减少每次最短路径计算所涉及的工作量,而不会占用过多的空间。 建议你选择下面的一些潜在想法来实现, 或者你可以开发和实现自己的想法。
想法 1. Dijkstra 算法的朴素实现检查图中的所有 V 个顶点。 减少检查的顶点数量的一种策略是一旦发现目的地的最短路径就停止搜索。 通过这种方法,可以使每个最短路径查询的运行时间与 E' log V'成比例,其中 E'和 V'是 Dijkstra 算法检查的边和顶点数。 然而,这需要一些小心,因为只是重新初始化所有距离为∞就需要与 V 成正比的时间。由于你在不断执行查询,因而只需重新初始化在先前查询中改变的那些值来大大加速查询。
想法 2. 你可以利用问题的欧式几何来进一步减少搜索时间,这在算法书的第 21.5 节描述过。对于一般图,Dijkstra 通过将 d[w]更新为 d[v] + 从 v 到 w 的距离来松弛边 v-w。 对于地图,则将 d[w]更新为 d[v] + 从 v 到 w 的距离 + 从 w 到 d 的欧式距离 − 从 v 到 d 的欧式距离。
这种方法称之为 A*算法。这种启发式方法会有性能上的影响,但不会影响正确性。
想法 3. 使用更快的优先队列。 在提供的优先队列中有一些优化空间。 你也可以考虑使用Sedgewick 程序 20.10 中的多路堆。
测试: 美国大陆文件 usa.txt 包含 87,575 个交叉口和 121,961 条道路。 图形非常稀疏 - 平均的度为 2.8。 你的主要目标应该是快速回答这个网络上的顶点对的最短路径查询。 你的算法可能会有不同执行时间,这取决于两个顶点是否在附近或相距较远。 我们提供测试这两种情况的输入文件。 你可以假设所有的 x 和 y 坐标都是 0 到 10,000 之间的整数。
注:这个问题的实验由 Bob Sedgewick 和 Kevin Wayne 设计开发(Copyright © 2004)。更多信息可参考 http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/。
2.问题求解
该题算法的核心是Dijkstra算法,Dijkstra算法即是加点法,即从起点出发,遍历测试松弛起点邻接的每一个点,然后将最小的边加入最小生成树。
针对具体应用,可以在本来普适的Dijkstra算法上加入修改,想法1即是针对某次查询,不必生成整张地图的最小生成树,查找到了目的地即可停止搜索;想法2非常有意思,它是基于A*算法对Dijkstra算法中路径长度改进为启发函数,即采用了启发式搜索而非原Dijkstra的盲目搜索(松弛当前顶点周围的所有顶点),这是因为在地图路由中,含有目的地这一先验信息,故可以朝着目的地进行搜索;想法3即是采用其他的数据结构实现松弛,将二路堆改为多路堆,不失为一种尝试。
地图采用usa.txt文件,查询采用usa-100long.txt。
2.1亚线性时间完成初始化
我首先用原Dijkstra算法实现了地图路由,并输出查询路径、时间以及通过可视化输出其查找路径,作为其他想法修改的对比。
对于多条查询,可以设置额外的空间,我采用了队列实现,将搜索过的区域坐上标记,下次查询的时候只需要初始化上次搜索过的区域即可。
2.2想法1
想法1非常简单和朴素,也是有效的,由于已知目的地顶点编号,故只需要在Dijkstra算法中生成最小生成树的循环中加入判定条件,若当前顶点等于目的地,则退出,查找结束。
2.3想法2
想法2采用了启发式搜索算法即A*算法,其正确性这是基于以下命题
命题1
在欧氏平面中,路径长即为欧氏距离,并且存在着三角形不等式
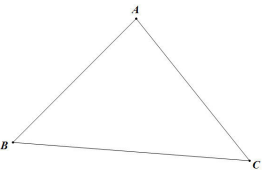
AB+AC>BC
命题2
如果h(B)总是小于(或者等于)从结点B走到目标结点C的代价,那么A*算法是一定可以找到最优路径的。
这里h(B)为启发函数,即当前节点B到目标节点C的估算开销(即上图中的BC),从结点B走到目标结点C的代价,是算法求出的路径长,或是经过A点即AB+AC,或是直接到C点即BC,都有
AB+AC>BC 或 BC=BC
即由命题1可以得到命题2,即在地图路由中,此时的模型为欧氏平面,可以保证采用启发式搜索算法能够得到最优解。
下面推证Dijkstra算法的A*改正的路径长度表达式
此时采用启发式搜索,引入新的度量D[v](即f)代替d[v](即g),加入当前点到终点的欧氏距离
D[v]=d[v]+distance(v,t)
(f(n)=g(n)+h(n))
f(n)为新的起始点到当前点n的路径长度,g(n)为原路径长度
这里启发函数h(n)即为
h(v)=distance(v,t)
即顶点v到终点t的欧氏距离。
则松弛边e为
If(D[w]>D[v]-distance(v,t)+e(v,w)+distance(w,t))
{
D[w]=D[v]-distance(v,t)+e(v,w)+distance(w,t);
将该边加入树;
}
这里解释下为什么D[w]更新为如上式子,由D[w]定义
D[w]=d[w]+distance(w,t) 式1
又d[w]是s->w路径长,此时边e(v,w)的另一个端点为v,松弛该边,则应测试s->v+v->w的路径长,故把d[w]写为
d[w]=d[v]+e(v,w) 式2
此时式1变为
D[w]=d[v]+e(v,w)+distance(w,t) 式3
此时求d[v],由于此时只储存了新度量D,故从D[v]表达式入手
D[v]=d[v]+distance(v,t)
得d[v]
d[v]=D[v]-distance(v,t) 式4
将式(4)代入式(3)即得改进条件
D[w]=D[v]-distance(v,t)+e(v,w)+distance(w,t); 式5
式(5)即是Dijkstra算法的A*改进,或称启发式搜索改进。
此时搜索方向大致朝着终点方向搜索,并且由于三角形不等式,易证明该算法能够得到最优路径。
此时代码的修改也非常简单,只需要修改松弛时的条件表达式以及更新路径长的表达式即可。
2.4想法3
该想法也非常朴实,即将原算法采用的二叉堆数据结构改为多路堆,从而达到改进算法
性能的目的。即改变多路堆IndexMultiwayMinPQ(V,way)中的参数way的值即可。
3.3实验结果
查询usa-100long.txt文件中的查询对,结果为

Improve0是亚线性时间初始化改进
Improve1是想法1改进
Improve2是想法2改进
Improve3是想法3改进,采用的是三路堆
由此知采用亚线性时间初始化以及A*算法对算法性能改善显著。
这是时间性能上的对比,再看看空间搜索上的改进对比,查询对0-2000
1.原算法

原算法搜索了整个地图
2.想法1

由图知,想法1仍需要搜索大部分空间
3.想法2

想法2采用了启发式搜索算法,可以明显的减小搜索空间,在想法2的基础上的想法3结果相同,只是采用了多路堆。
3.4源代码
1.原算法
import java.awt.Color;
public class Dijkstra {
private static double INFINITY = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private static double EPSILON = 0.000001;
private EuclideanGraph G;
private double[] dist;
private int[] pred;
public Dijkstra(EuclideanGraph G) {
this.G = G;
}
// return shortest path distance from s to d
public double distance(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
return dist[d];
}
// print shortest path from s to d (interchange s and d to print in right order)
public void showPath(int d, int s) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
if (pred[d] == -1) {
System.out.println(d + " is unreachable from " + s);
return;
}
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
System.out.print(v + "-");
System.out.println(s);
}
// plot shortest path from s to d
public void drawPath(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,1);
if (pred[d] == -1) return;
Turtle.setColor(Color.red);
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(pred[v]));
Turtle.render();
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm to find shortest path from s to d
public void dijkstra(int s, int d,int draw) {
int V = G.V();
// initialize
dist = new double[V];
pred = new int[V];
//points = new Point[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) dist[v] = INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pred[v] = -1;
// priority queue
IndexPQ pq = new IndexPQ(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pq.insert(v, dist[v]);//这里可以优化
// set distance of source
dist[s] = 0.0;
pred[s] = s;
pq.change(s, dist[s]);
// run Dijkstra's algorithm
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
//// System.out.println("process " + v + " " + dist[v]);
// points[n]=G.point(v);
//n=n+1;
// v not reachable from s so stop
if (pred[v] == -1) break;
// scan through all nodes w adjacent to v
IntIterator i = G.neighbors(v);
while (i.hasNext()) {
int w = i.next();
if(draw == 1)
{
Turtle.setColor(Color.yellow);
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(w));
Turtle.render();
try
{
for(long j=0;j<10000;j++);
}
catch(Exception e){} //每画一条边都延时
}
//n=n+1;
if (dist[v] + G.distance(v, w) < dist[w] - EPSILON) {
dist[w] = dist[v] + G.distance(v, w);
pq.change(w, dist[w]);
pred[w] = v;
//// System.out.println(" lower " + w + " to " + dist[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
- improve0
import java.awt.Color;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.IndexMultiwayMinPQ;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.Queue;
//改进第1问,找到点就停止,并加上第一问没有加上的亚线性初始化
public class Dijkstra_improve {
private static double INFINITY = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private static double EPSILON = 0.000001;
private EuclideanGraph G;
private double[] dist;
private int[] pred;
private Queue<Integer> reindex;
public Dijkstra_improve(EuclideanGraph G) {
this.G = G;
//serched=0;
this.reindex = new Queue();
int V = G.V();
// initialize
this.dist = new double[V];
this.pred = new int[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) this.dist[v] = INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) this.pred[v] = -1;
}
// return shortest path distance from s to d
public double distance(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
return dist[d];
}
// print shortest path from s to d (interchange s and d to print in right order)
public void showPath(int d, int s) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
if (pred[d] == -1) {
System.out.println(d + " is unreachable from " + s);
return;
}
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
System.out.print(v + "-");
System.out.println(s);
}
// plot shortest path from s to d
public void drawPath(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,1);
if (pred[d] == -1) return;
Turtle.setColor(Color.red);
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(pred[v]));
Turtle.render();
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm to find shortest path from s to d
public void dijkstra(int s, int d,int draw) {
int V = G.V();
// initialize
int tempv;
while(!this.reindex.isEmpty()){
tempv = this.reindex.dequeue();
dist[tempv] = INFINITY;
pred[tempv] = -1;
}
// 初始完了被影响的点,sum归零
// set distance of source
dist[s] = 0.0;
pred[s] = s;
IndexMultiwayMinPQ pq =new IndexMultiwayMinPQ<Double>(V,3);
this.reindex.enqueue(s);
pq.insert(s, dist[s]);
// run Dijkstra's algorithm
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
//// System.out.println("process " + v + " " + dist[v]);
if(d == v)
{
//System.out.println("找到d点,终止算法");
//System.out.println(pred[v]);
break;
}
// v not reachable from s so stop
if (pred[v] == -1) break;
// scan through all nodes w adjacent to v
IntIterator i = G.neighbors(v);
while (i.hasNext()) {
int w = i.next();
if(draw==1)
{
Turtle.setColor(Color.yellow);
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(w));
Turtle.render();
}
if (dist[v] + G.distance(v, w) < dist[w] - EPSILON) {
dist[w] = dist[v] + G.distance(v, w);
//pq.insert(w, dist[w]);
pred[w] = v;
//// System.out.println(" lower " + w + " to " + dist[w]);
if (pq.contains(w)) {
pq.changeKey(w, dist[w]);
continue;
}
//pq.decreaseKey(w, dist[w]);
else {
pq.insert(w, dist[w]);
this.reindex.enqueue(w);
}
}
}
}
}
}
3.improve1
import java.awt.Color;
//改进第1问,找到点就停止
public class Dijkstra_improve_1 {
private static double INFINITY = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private static double EPSILON = 0.000001;
private EuclideanGraph G;
private double[] dist;
private int[] pred;
public Dijkstra_improve_1(EuclideanGraph G) {
this.G = G;
}
// return shortest path distance from s to d
public double distance(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
return dist[d];
}
// print shortest path from s to d (interchange s and d to print in right order)
public void showPath(int d, int s) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
if (pred[d] == -1) {
System.out.println(d + " is unreachable from " + s);
return;
}
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
System.out.print(v + "-");
System.out.println(s);
}
// plot shortest path from s to d
public void drawPath(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,1);
if (pred[d] == -1) return;
Turtle.setColor(Color.red);
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(pred[v]));
Turtle.render();
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm to find shortest path from s to d
public void dijkstra(int s, int d,int draw) {
int V = G.V();
// initialize
dist = new double[V];
pred = new int[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) dist[v] = INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pred[v] = -1;
// priority queue
IndexPQ pq = new IndexPQ(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pq.insert(v, dist[v]);//这里可以优化
// set distance of source
dist[s] = 0.0;
pred[s] = s;
pq.change(s, dist[s]);
// run Dijkstra's algorithm
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
//// System.out.println("process " + v + " " + dist[v]);
if(d == v)
{
//System.out.println("找到d点,终止算法");
//System.out.println(pred[v]);
break;
}
// v not reachable from s so stop
if (pred[v] == -1) break;
// scan through all nodes w adjacent to v
IntIterator i = G.neighbors(v);
while (i.hasNext()) {
int w = i.next();
if(draw==1)
{
Turtle.setColor(Color.yellow);
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(w));
Turtle.render();
try
{
for(long j=0;j<10000;j++);
}
catch(Exception e){} //每画一条边都延时
}
if (dist[v] + G.distance(v, w) < dist[w] - EPSILON) {
dist[w] = dist[v] + G.distance(v, w);
pq.change(w, dist[w]);
pred[w] = v;
//// System.out.println(" lower " + w + " to " + dist[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
4.improve2
import java.awt.Color;
//改进第二问,启发式搜索即A*算法
public class Dijkstra_improve_2 {
private static double INFINITY = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private static double EPSILON = 0.000001;
private EuclideanGraph G;
private double[] dist;
private int[] pred;
public Dijkstra_improve_2(EuclideanGraph G) {
this.G = G;
}
// return shortest path distance from s to d
public double distance(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
return dist[d];
}
// print shortest path from s to d (interchange s and d to print in right order)
public void showPath(int d, int s) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
if (pred[d] == -1) {
System.out.println(d + " is unreachable from " + s);
return;
}
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
System.out.print(v + "-");
System.out.println(s);
}
// plot shortest path from s to d
public void drawPath(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,1);
if (pred[d] == -1) return;
Turtle.setColor(Color.red);
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(pred[v]));
Turtle.render();
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm to find shortest path from s to d
public void dijkstra(int s, int d,int draw) {
int V = G.V();
// initialize
dist = new double[V];
pred = new int[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) dist[v] = INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pred[v] = -1;
// priority queue
IndexPQ pq = new IndexPQ(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pq.insert(v, dist[v]);//这里可以优化
// set distance of source
dist[s] = 0.0;
pred[s] = s;
pq.change(s, dist[s]);
// run Dijkstra's algorithm
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
//// System.out.println("process " + v + " " + dist[v]);
if(d == v)
{
//System.out.println("找到d点,终止算法");
//System.out.println(pred[v]);
break;
}
// v not reachable from s so stop
if (pred[v] == -1) break;
// scan through all nodes w adjacent to v
IntIterator i = G.neighbors(v);
while (i.hasNext()) {
int w = i.next();
if(draw==1)
{
Turtle.setColor(Color.yellow);
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(w));
Turtle.render();
try
{
for(long j=0;j<50000;j++);
}
catch(Exception e){} //每画一条边都延时
}
if (dist[v] -G.distance(v, d)+ G.distance(v, w) +G.distance(w, d)< dist[w] - EPSILON) {
dist[w] = dist[v] -G.distance(v, d)+ G.distance(v, w) +G.distance(w, d);
pq.change(w, dist[w]);
pred[w] = v;
//// System.out.println(" lower " + w + " to " + dist[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
5.improve3
//改进第三问。即采用多路堆
import java.awt.Color;
import edu.princeton.cs.algs4.IndexMultiwayMinPQ;
public class Dijkstra_improve_3 {
private static double INFINITY = Double.MAX_VALUE;
private static double EPSILON = 0.000001;
private EuclideanGraph G;
private double[] dist;
private int[] pred;
private int way;
public Dijkstra_improve_3(EuclideanGraph G,int way) {
this.G = G;
this.way=way;
}
// return shortest path distance from s to d
public double distance(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
return dist[d];
}
// print shortest path from s to d (interchange s and d to print in right order)
public void showPath(int d, int s) {
dijkstra(s, d,0);
if (pred[d] == -1) {
System.out.println(d + " is unreachable from " + s);
return;
}
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
System.out.print(v + "-");
System.out.println(s);
}
// plot shortest path from s to d
public void drawPath(int s, int d) {
dijkstra(s, d,1);
if (pred[d] == -1) return;
Turtle.setColor(Color.red);
for (int v = d; v != s; v = pred[v])
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(pred[v]));
Turtle.render();
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm to find shortest path from s to d
public void dijkstra(int s, int d,int draw) {
int V = G.V();
// initialize
dist = new double[V];
pred = new int[V];
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) dist[v] = INFINITY;
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pred[v] = -1;
// priority queue
IndexMultiwayMinPQ pq = new IndexMultiwayMinPQ(V,way);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) pq.insert(v, dist[v]);//这里可以优化
// set distance of source
dist[s] = 0.0;
pred[s] = s;
pq.changeKey(s, dist[s]);
// run Dijkstra's algorithm
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int v = pq.delMin();
//// System.out.println("process " + v + " " + dist[v]);
if(d == v)
{
//System.out.println("找到d点,终止算法");
//System.out.println(pred[v]);
break;
}
// v not reachable from s so stop
if (pred[v] == -1) break;
// scan through all nodes w adjacent to v
IntIterator i = G.neighbors(v);
while (i.hasNext()) {
int w = i.next();
if (draw==1) {
Turtle.setColor(Color.yellow);
G.point(v).drawTo(G.point(w));
Turtle.render();
}
if (dist[v] -G.distance(v, d)+ G.distance(v, w) +G.distance(w, d)< dist[w] - EPSILON) {
dist[w] = dist[v] -G.distance(v, d)+ G.distance(v, w) +G.distance(w, d);
pq.changeKey(w, dist[w]);
pred[w] = v;
//// System.out.println(" lower " + w + " to " + dist[w]);
}
}
}
}
}
6查询
/*************************************************************************
* Compilation: javac ShortestPath.java
* Execution: java ShortestPath file < input.txt
* Dependencies: EuclideanGraph.java Dijkstra.java In.java StdIn.java Turtle.java
*
* Reads in a map from a file, and two integers s and d from standard input,
* and plots the shortest path from s to d using turtle graphics.
*
* % java ShortestPath usa.txt
* 0 5000
*
****************************************************************************/
public class ShortestPath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Turtle.create(1000, 700);
// read in the graph from a file
In graphin = new In(args[0]);
EuclideanGraph G = new EuclideanGraph(graphin);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + args[0]);
//System.err.println("Enter query pair from stdin");
int draw=1;
//draw为0,则不作图,为1则作图
if(draw==1)
{
Turtle.create(1000, 700);
G.draw();
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
//G.draw();
Dijkstra dijkstra = new Dijkstra(G);
Dijkstra_improve dijkstra0 = new Dijkstra_improve(G);
Dijkstra_improve_1 dijkstra1 = new Dijkstra_improve_1(G);
Dijkstra_improve_2 dijkstra2 = new Dijkstra_improve_2(G);
Dijkstra_improve_3 dijkstra3 = new Dijkstra_improve_3(G,3);
edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In inputin;
String file="D:\\Eclipse\\WorkStation\\algos_3_mapping\\src\\usa-1.txt";
//原算法测试
inputin=new edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In(file);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + file+"\toriginal");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
test(inputin,dijkstra,G,draw);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("原算法程序运行时间:"+(endTime-startTime)+"ms");
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
//改进0测试
/*
edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In inputin0=new edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In(file);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + file+"\timprove");
long startTime0 = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
test0(inputin0,dijkstra0,G,draw);
//double time = t1.elapsedTime();
long endTime0 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("improve0程序运行时间:"+(endTime0-startTime0)+"ms");*/
//改进1测试
edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In inputin1=new edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In(file);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + file+"\timprove_1");
long startTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
test1(inputin1,dijkstra1,G,draw);
//double time = t1.elapsedTime();
long endTime1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("improve1程序运行时间:"+(endTime1-startTime1)+"ms");
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(5000);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
//改进2测试
edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In inputin2=new edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In(file);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + file+"\timprove_2");
long startTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
test2(inputin2,dijkstra2,G,draw);
long endTime2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("improve2程序运行时间:"+(endTime2-startTime2)+"ms");
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
//改进3测试
edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In inputin3=new edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In(file);
System.err.println("Done reading the graph " + file+"\timprove_3");
long startTime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
test3(inputin3,dijkstra3,G,draw);
long endTime3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("improve3程序运行时间:"+(endTime3-startTime3)+"ms");
}
private static void test(edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In in,Dijkstra dijkstra,EuclideanGraph G,int draw) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!in.isEmpty())
{
int s = in.readInt();
int d = in.readInt();
if(draw==1) {
G.draw();
dijkstra.drawPath(s,d);
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1000);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
else {
dijkstra.dijkstra(s, d,0);
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("static-access")
private static void test1(edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In in,Dijkstra_improve_1 dijkstra,EuclideanGraph G,int draw) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!in.isEmpty())
{
int s = in.readInt();
int d = in.readInt();
if(draw==1) {
G.draw();
dijkstra.drawPath(s,d);
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1500);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
else {
dijkstra.dijkstra(s, d,0);
}
}
}
private static void test2(edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In in,Dijkstra_improve_2 dijkstra,EuclideanGraph G,int draw) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!in.isEmpty())
{
int s = in.readInt();
int d = in.readInt();
if(draw==1) {
G.draw();
dijkstra.drawPath(s,d);
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1500);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
else {
dijkstra.dijkstra(s, d,0);
}
}
}
private static void test3(edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In in,Dijkstra_improve_3 dijkstra,EuclideanGraph G,int draw) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!in.isEmpty())
{
int s = in.readInt();
int d = in.readInt();
if(draw==1) {
G.draw();
dijkstra.drawPath(s,d);
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1500);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
else {
dijkstra.dijkstra(s, d,0);
}
}
}
private static void test0(edu.princeton.cs.algs4.In in,Dijkstra_improve dijkstra,EuclideanGraph G,int draw) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while(!in.isEmpty())
{
int s = in.readInt();
int d = in.readInt();
if(draw==1) {
G.draw();
dijkstra.drawPath(s,d);
try
{
Thread.currentThread().sleep(1500);//毫秒
}
catch(Exception e){}
}
else {
dijkstra.dijkstra(s, d,0);
}
}
}
}
五、实验感想
这次实验让我认识到在算法的改进上并非是有多么复杂的改动就能够实现性能的飞跃,比如A*算法在Dijkstra算法地图路由上的改进,仅仅改变了两条语句,就大大的减小了搜索空间,或许这就是算法自身的魅力吧!虽然改动很少,但其中蕴含的思想确是非常优雅且有效,这里A*算法的改进就是启发式搜索,大大减少了搜索空间,其理论基础是地图路由算法中面对的是欧式空间,我从中认识到了哪怕是相通的算法,面对不同的应用场景时会有不同的改进方法以大幅度提高性能。
