主启动类Application.class
1 package com.vegeta.spring_boot; 2 3 import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; 4 import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; 5 6 @SpringBootApplication 7 public class Application { 8 9 public static void main(String[] args) { 10 SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args); 11 } 12 13 }
进入注解@SpringBootApplication之中
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @SpringBootConfiguration 6 @EnableAutoConfiguration 7 @ComponentScan( 8 excludeFilters = {@Filter( 9 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, 10 classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class} 11 ), @Filter( 12 type = FilterType.CUSTOM, 13 classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class} 14 )} 15 ) 16 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan 17 public @interface SpringBootApplication { 18 ......... 19 }
可以看到SpringBootApplication上有个注解@EnableAutoConfiguration开启自动配置,进入该注解
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @AutoConfigurationPackage 6 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) 7 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration { 8 String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration"; 9 10 Class<?>[] exclude() default {}; 11 12 String[] excludeName() default {}; 13 }
可以看到该注解上有@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}),进入AutoConfigurationImportSelect.class,主要步骤看下面注解的代码
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector
implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered { private static final AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry EMPTY_ENTRY =
new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(); private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = new String[0]; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class); private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE = "spring.autoconfigure.exclude"; private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory; private Environment environment; private ClassLoader beanClassLoader; private ResourceLoader resourceLoader; public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return NO_IMPORTS; } else { AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
// 获取自动配置 AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = this.getAutoConfigurationEntry(autoConfigurationMetadata, annotationMetadata); return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()); } } protected AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata, AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { if (!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { return EMPTY_ENTRY; } else { AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
// 自动配置的候选的配置 List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations); Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); configurations.removeAll(exclusions); configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); return new AutoConfigurationImportSelector.AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions); } } protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
// 配置信息是从spring工厂加载器中加载获得 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }
}
进入SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames的方法中,具体细节继续看注解的代码
public final class SpringFactoriesLoader { public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class); private static final Map<ClassLoader, MultiValueMap<String, String>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap();
// 获取加载集合,调用了下面的方法 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
//内部调用了loadSpringFactories方法 return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList()); }
// 这个到了真正能看懂的方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); if (result != null) { return result; } else { try {
// 获取META-INF/spring.factories的资源文件,并映射到urls这个中 Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories") : ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); // 遍历urls并将值封装到result中,并返回,那么核心就是这个META-INF/spring.factories文件 while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); while(var6.hasNext()) { Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); String factoryTypeName = ((String)entry.getKey()).trim(); String[] var9 = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue()); int var10 = var9.length; for(int var11 = 0; var11 < var10; ++var11) { String factoryImplementationName = var9[var11]; result.add(factoryTypeName, factoryImplementationName.trim()); } } } cache.put(classLoader, result); return result; } catch (IOException var13) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var13); } } } }
这个META-INF/spring.factories文件在哪里呢?就在你maven引入的org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-autoconfigure的jar包中
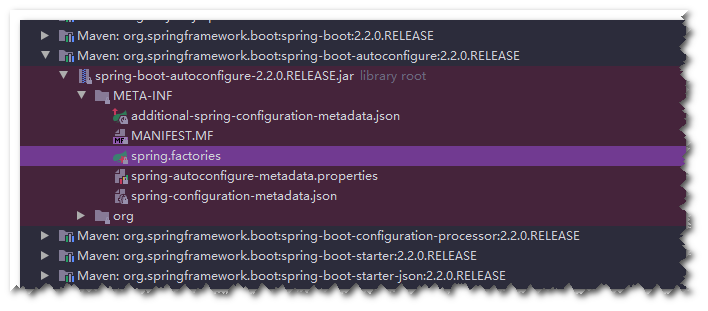
打开这个spring.factories文件如下(只是一部分,全部很多),全是xxxAutoConfiguration自动配置类
1 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.validation.ValidationAutoConfiguration,\ 2 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.client.RestTemplateAutoConfiguration,\ 3 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.embedded.EmbeddedWebServerFactoryCustomizerAutoConfiguration,\ 4 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.HttpHandlerAutoConfiguration,\ 5 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.ReactiveWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ 6 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.WebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ 7 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.error.ErrorWebFluxAutoConfiguration,\ 8 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnectorAutoConfiguration,\ 9 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.reactive.function.client.WebClientAutoConfiguration,\ 10 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration,\ 11 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration,\ 12 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.error.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration,\ 13 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\ 14 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.MultipartAutoConfiguration,\ 15 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.WebMvcAutoConfiguration,\ 16 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.reactive.WebSocketReactiveAutoConfiguration,\ 17 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketServletAutoConfiguration,\ 18 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.websocket.servlet.WebSocketMessagingAutoConfiguration,\ 19 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.WebServicesAutoConfiguration,\ 20 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.webservices.client.WebServiceTemplateAutoConfiguration
为了演示方便,我们打开一个简单的HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) @EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class}) @ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET ) @ConditionalOnClass({CharacterEncodingFilter.class}) @ConditionalOnProperty( prefix = "spring.http.encoding", value = {"enabled"}, matchIfMissing = true ) public class HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration { ...... }
其中最关键的注解为@EnableConfigurationProperties({HttpProperties.class}),我们进入HttpProperties类
// 这里可以到配置该设置的前缀为spring.http
@ConfigurationProperties( prefix = "spring.http" ) public class HttpProperties { private boolean logRequestDetails;
// 其中属性名称为encoding,这是一个对象 private final HttpProperties.Encoding encoding = new HttpProperties.Encoding(); public HttpProperties() { } public boolean isLogRequestDetails() { return this.logRequestDetails; } public void setLogRequestDetails(boolean logRequestDetails) { this.logRequestDetails = logRequestDetails; } public HttpProperties.Encoding getEncoding() { return this.encoding; } public static class Encoding {
// 这个对象一共有过5个属性 public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET; private Charset charset; private Boolean force; private Boolean forceRequest; private Boolean forceResponse; private Map<Locale, Charset> mapping; public Encoding() { this.charset = DEFAULT_CHARSET; } public Charset getCharset() { return this.charset; } public void setCharset(Charset charset) { this.charset = charset; } public boolean isForce() { return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.force); } public void setForce(boolean force) { this.force = force; } public boolean isForceRequest() { return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceRequest); } public void setForceRequest(boolean forceRequest) { this.forceRequest = forceRequest; } public boolean isForceResponse() { return Boolean.TRUE.equals(this.forceResponse); } public void setForceResponse(boolean forceResponse) { this.forceResponse = forceResponse; } public Map<Locale, Charset> getMapping() { return this.mapping; } public void setMapping(Map<Locale, Charset> mapping) { this.mapping = mapping; } public boolean shouldForce(HttpProperties.Encoding.Type type) { Boolean force = type != HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST ? this.forceResponse : this.forceRequest; if (force == null) { force = this.force; } if (force == null) { force = type == HttpProperties.Encoding.Type.REQUEST; } return force; } static { DEFAULT_CHARSET = StandardCharsets.UTF_8; } public static enum Type { REQUEST, RESPONSE; private Type() { } } } }
这里可以到配置该设置的前缀为spring.http;其中属性名称为encoding,这是一个对象;这个对象一共有过5个属性charset, force, forceRequest, forceResponse, mapping;
所以application.properties中可以指定这个配置
spring.http.encoding.charset=utf-8 spring.http.encoding.force=true spring.http.encoding.force-request=true spring.http.encoding.force-response=true spring.http.encoding.mapping.zh_CN=GBK spring.http.encoding.mapping.en_US-=UTF-8
当然这是我们指定配置的,如果我们没有配置,那么springboot一样会根据这一套流程加载配置,只不过是默认配置
自动配置过程中涉及的一些注解
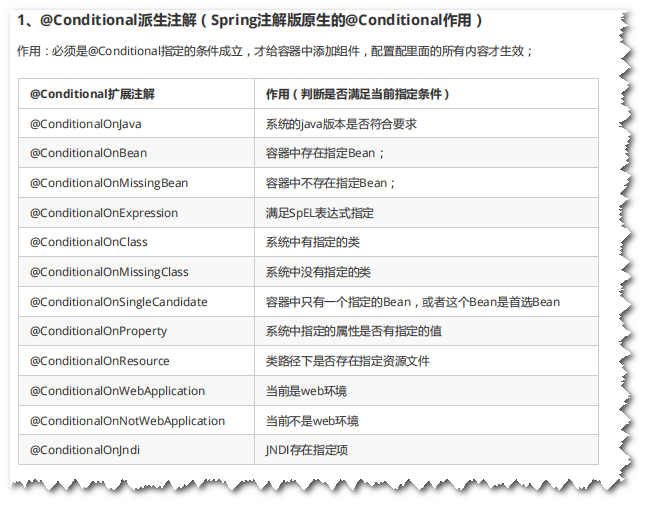
我们怎么知道哪些自动配置类生效;我们可以通过在配置文件中启用 debug=true属性;来让控制台打印自动配置报告