归档的创建:
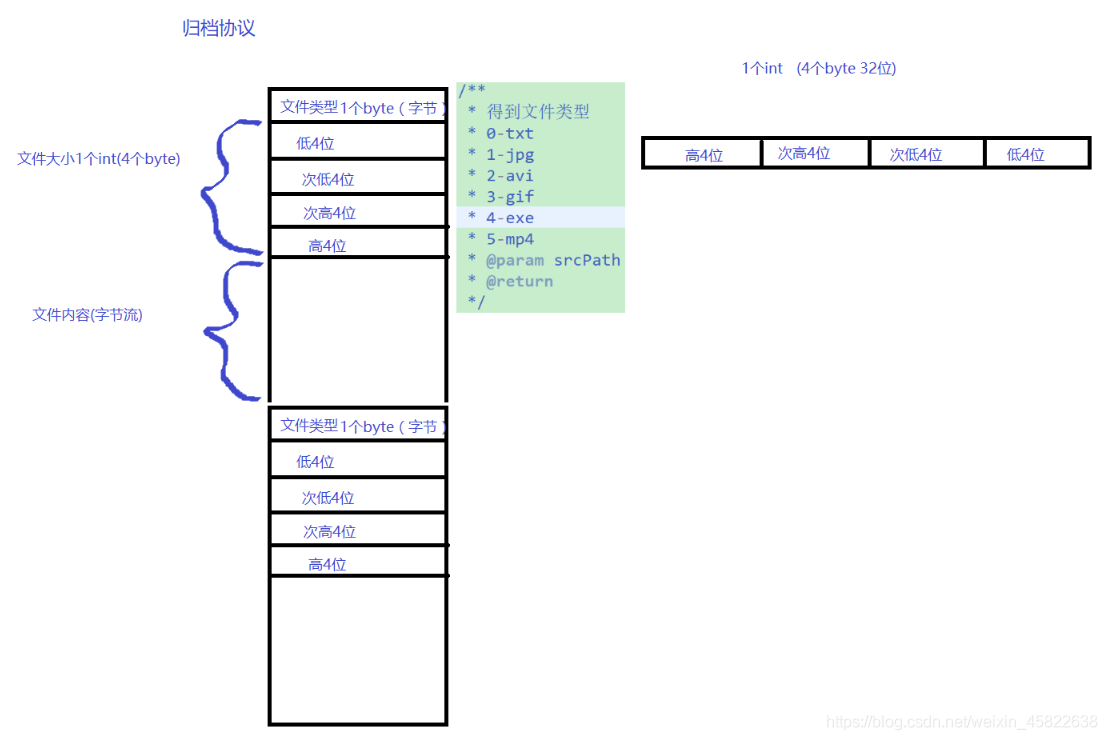
归档的创建:
public class Archiver {
/**
* 创建归档文件
* @throws Exception
*/
public void newArchiveFile(String [] srcPaths,String yarPath) throws Exception {
//srcPaths数组,yarPath文件路径
FileOutputStream fout=null;
try {
//创建归档文件的输出流
fout=new FileOutputStream(yarPath);
//Object srcPaths;
//一个个添加文件
for(String srcPath : srcPaths) {
addFile(srcPath,fout);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(fout!=null) {
fout.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 向yar归档文件按中添加文件
* @param srcPath
* @param fout
* @throws IOException
*/
private void addFile(String srcPath, FileOutputStream fout) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fin =null;
try {
//1.取出srcPath文件的类型和长度
int fType = getFileType(srcPath);
//2.取出文件 的长度
fin =new FileInputStream(srcPath);
int length=fin.available();
//3.将ftype类型写入fout
byte bFtype=(byte)fType;
fout.write(new byte[] {bFtype});
//4.将长度写入yar中
byte [] bytes=Int2ByteArr(length);
fout.write(bytes);
//5.写入文件的内容
int len=-1;
byte[]buffer=new byte[1024];
while((len=fin.read(buffer))!=-1) {
fout.write(buffer,0,len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
finally {
if(fin!=null) {
fin.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 将整数转换成字节数组
* ---------------
*
* @param length
* @return
*/
private byte[] Int2ByteArr(int i) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
byte [] bytes=new byte[4];
bytes[0]=(byte)i;
bytes[1]=(byte)(i>>8);
bytes[2]=(byte)(i>>16);
bytes[3]=(byte)(i>>24);
return bytes;
}
/**
* 得到文件类型
* 0-txt
* 1-jpg
* 2-avi
* 3-gif
* 4-exe
* @param srcPath
* @return
*/
private int getFileType(String srcPath) {
//得到文件的扩展名
String exr= srcPath.substring(srcPath.lastIndexOf(".")).toLowerCase();
int type=-1;
if(".txt".equals(exr)) {
type =0;
}
else if(".jpg".equals(exr))
{
type =1;
}
else if(".jpg".equals(exr))
{
type =1;
}
else if(".avi".equals(exr))
{
type =2;
}
else if(".gif".equals(exr))
{
type =3;
}
else if(".exe".equals(exr))
{
type =4;
}
return type;
}
/**
* 添加新文件到yar归档文件中
* @param srcPath
* @param yarPath
* @throws Exception
*/
public void addFile(String srcPath,String yarPath) throws Exception {
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(yarPath,true);
addFile(srcPath,fos);
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
解档:
/解档文件
public void unarchive(String yarPath,String destDir) {
try {
FileInputStream fin=new FileInputStream(yarPath);
//循环读取下一个文件
int i=1;
while(readNextFile(destDir,i+" ",fin)) {
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 读取下一个文件
* @param fin
* @return
*/
private boolean readNextFile(String destDir,String fname,FileInputStream fin) {
int type;
try {
//文件类型
type = fin.read();
//获取文件扩展名
String ext=getFile2Ext(type);
if(type==-1) {
return false;
}
/**
* 开始读取文件,写入到新文件中
*/
//0:构造文件输出流
FileOutputStream fout=new FileOutputStream(destDir+"/"+fname+ext);
//1:读取文件长度
byte[] bytes=new byte[4];
fin.read(bytes);
//2:转换成字节数组成为int
int fileLength=byteArr2Int(bytes);
//读取文件并写入到新文件中
byte[]buffer=new byte[1024];
//计算读取的循环次数
int cout=0;
if(fileLength%buffer.length==0) {
cout=fileLength/buffer.length;
}
else {
cout=fileLength/buffer.length+1;
}
//开始循环次数
for(int i=0;i<cout;i++) {
//不是最后一次
if(i!=(cout-1)) {
fin.read(buffer);
fout.write(buffer);
}
else {
byte[]buf0=new byte[fileLength % buffer.length];
fin.read(buf0);
fout.write(buf0);
}
}
fout.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return true;
}
/**
* 得到文件的扩展名
* @param type
* @return
*/
private String getFile2Ext(int type) {
String ext=".tmp";
switch( type) {
case 0:
ext=".txt";
break ;
case 1:
ext=".jpg";
break ;
case 2:
ext=".avi";
break ;
case 3:
ext=".gif";
break ;
case 4:
ext=".exe";
break ;
default:
ext= ".tmp";
break;
}
return ext;
}
/**
* 将长度为4的字节数组转换为int
* @param bytes
* @return
*/
private int byteArr2Int(byte[] bytes) {
int i0=bytes[3]<<24;
int i1=(bytes[2]&0xff)<<16;
int i2=(bytes[1]&0xff)<<8;
int i3=(bytes[0]&0xff);
return i0|i1|i2|i3;
}
}
然后新建class处理归档解档案:
public class App {
/**
* 新建归档文件
* @throws Exception
*
*/
@Test
public void newArchiveFile() throws Exception{
Archiver ar=new Archiver();
String []srcPaths= {
"D:/ar/hi.txt",
"D:/ar/beijing2.jpg"
};
String yarPath="d:/ar/myyar.yar";
ar.newArchiveFile(srcPaths, yarPath);
System.out.println("over");
}
结果:
hi.txt和beijing2.jpg会被归档到myyar.yar中一份
向原有归档文件中添加新文件
/**
* 向原有归档文件中添加新文件
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void addFile() throws Exception {
Archiver ar=new Archiver();
ar.addFile("D:/ar/beijing2.jpg" ,"D:/ar/myyar.yar");
}
结果:
在myyar.yar中会多一份beijing2.jpg,字节数会变大
解档
*/
@Test
public void unarchiveFile() {
Archiver ar=new Archiver();
ar.unarchive("D:/ar/myyar.yar" ,"D:/ar/unarch");
}
结果:
myyar.yar中的文件会被解档到unarch中
使用文本文件储存jpg
/**
* 使用文本文件存储jpg
* 1:将媒体文件的字节数组写入文本中,每个字节转换成了0-255之间的字符
* 2:使用BufferedReader读行,读取的每行转换成int,再换换成字节数byte
* 3:将转换成的bute数据写入到文件中
* 4:检验是否ok?
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void readMp3() throws Exception {
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:/ar/a.txt");
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:/beijing.jpg");
int b=-1;
while((b=fis.read())!=-1) {
fos.write((b +"" ).getBytes());
fos.write(new byte[] {'\r','\n'});
}
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
结果:
图片会被转换成一堆数字储存在文本中
上述文本还原为照片
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(newFileReader(此处填想还原的文件的路径));
BufferedOutputStream bos=new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream());
String str=null;
while((str.br.readLine())!=null){
byte c=(byte)Integer.parseInt(str);
bos.write(c);
}
br.close();
bos.close();
}
使用文本文件储存jpg2
@Test
public void readMp32() throws Exception {
FileWriter writer=new FileWriter("d:/a.txt");
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:/beijing.jpg");
int len=-1;
byte []buffer=new byte[1024];
while((len=fis.read(buffer))!=-1) {
writeByteArrToFile(buffer,0,len,writer);
}
writer.close();
fis.close();
}
/***
* 将字节数组中的字节数写入到fos中
* @param arr
* @param fos
*/
private void writeByteArrToFile(byte[]arr,int startIndex,int length,FileWriter writer) {
try {
for(int j=startIndex;j<length;j++) {
writer.write(arr[j]+"\r\n");
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
读取文本文件的内容,写入到jpg文件中,恢复图像2
/**
* 读取文本文件的内容,写入到jpg文件中,恢复图像
*
*/
@Test
public void readTxt2JPG() {
try {
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("d:/a.txt"));
FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("d:/ar/1.jpg");
String line=null;
//循环读行
while((line=reader.readLine())!=null) {
//把每行数字换成字节byte
byte b=(byte)Integer.parseInt(line);
//fos.write(b);或者其他方法
fos.write(new byte[] {b});
}
fos.close();
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
显示文件(文件+文件夹)路径名
private static void showFile(String path) {
//通过路径构造File对象
File f=new File(path);
if(f.exists()) {
//输出文件的绝对路径
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
//是否是目录
if(f.isDirectory()) {
File []children= f.listFiles();
if( children==null||children.length==0)
{
System.out.println(f.getName()+"是空文件夹");
return;
}//不加if会出现空指针
for(File ff:children) {
String p0=ff.getAbsolutePath();
showFile(p0);
}
}
}
}
创建文件夹
public class FileTest {
@Test
public void file1() {
File f=new File("d:\\ar");
System.out.println(f.exists());
System.out.println(f.isDirectory());
String dir="d:/ar/a/b/c";
f=new File(dir);
if(!f.exists()) {
f.mkdirs();
//mkdir只能创建一个
}
f=new File("d:/ar");
if(f.isDirectory()) {
File[] files=f.listFiles();
for(File f0:files) {
// System.out.println(f0.getName());//打印文件名
System.out.println(f0.getAbsolutePath());//打印绝对路径
}
}
}
}
得到子目录的文件长度
File [] fs=new File("D:\\ar\\unarch").listFiles();
System.out.println(fs.length);
重命名
f.renameTo(new File(f.getParent(),"b.txt"));
判断是否存在不存在就创建
f=new File("d:\\ccc.txt");
if(!f.exists()) {
try {
//如果没有就创建此新文件
f.createNewFile();
}
catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
列出文件系统的root
File[] fa=File.listRoots();
for(File f0:fs) {
System.out.println(f0.getAbsolutePath());
}
得到文件长度
File f=new File("D:\\ar\\unarch\\1.txt");
//文件长度
long len=f.length();
System.out.println(len);
得到上级目录
//得到上级目录
String str=f.getParent();
System.out.println(str);
