0.PTA得分截图

1.本周学习总结
1.1 总结线性表内容
顺序表结构体定义
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize]; //存放顺序表元素
int length ; //存放顺序表的长度
} List;
typedef List *SqList;顺序表插入
void InsertSq(SqList& L, int x)
{
int i;
for (i = L->length; i > 0; i--)
{
if (L->data[i - 1] > x)
L->data[i] = L->data[i - 1];
else
{
L->data[i] = x;
break;
}
}
if (i == 0)
{
L->data[0] = x;
}
L->length++;
}在知道顺序表长度的条件下,从后往前重构顺序表,直至插入位置。
顺序表删除
void DelSameNode(List& L)
{
int i, j=0,k=0;
static int h[100];
for (i = 0; i < L->length; i++)
{
if (h[L->data[i]] == 0)
{
h[L->data[i]]++;
L->data[j++] = L->data[i];
}
else
{
k++;
}
}
L->length -= k;
}使用静态数组标记已出现的数据,重构顺序表。
链表结构体定义
typedef struct LNode //定义单链表结点类型
{
ElemType data; //数据项
struct LNode *next; //指向后继结点
} LNode,*LinkList;头插法
void CreateListF(LinkList& L, int n)//头插法建链表,L表示带头结点链表,n表示数据元素个数
{
int i,j;
ElemType date;
L = new LNode;
L->next = NULL;
LinkList ptr;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ptr = new LNode;
cin >> j;
ptr->data = (ElemType)j;
ptr->next = L->next;
L->next = ptr;
}
}尾插法
void CreateListR(LinkList& L, int n)//尾插法建链表,L表示带头结点链表,n表示数据元素个数
{
int i, j;
LinkList ptr, railPtr;
railPtr = new LNode;
L = new LNode;
L->next = NULL;
L = railPtr;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
ptr = new LNode;
cin >> j;
ptr->data = (ElemType)j;
railPtr->next = ptr;
railPtr = ptr;
ptr->next = NULL;
}
}有序链表插入删除
void ListInsert(LinkList& L, ElemType e)//插入
{
LinkList pre, q,head;
head = L->next;
q = new LNode;
q->data = e;
while (head->next)
{
if (head->next->data > e)
{
q->next = head->next;
head->next = q;
return;
}
head = head->next;
}
head->next = q;
q->next = NULL;
}
void ListDelete(LinkList& L, ElemType e)//删除
{
LinkList q, head;
if (L->next==NULL)
{
return;
} head = L;
while (head->next)
{
if (head->next->data == e)
{
q = new LNode;
q = head->next;
head->next = q->next;
delete(q);
return;
}
if (head->next->data > e)
{
cout << e << "找不到!"<<endl;
return;
}
head = head->next;
}
if (head->data == e)
{
head = NULL;
}
else
{
cout << e << "找不到!" << endl;
}
}循环链表
循环链表是一种头尾相接的链表。其特点是最后一个结点的指针域指向链表的头结点,整个链表的指针域链接成一个环。
特点是从循环链表的任意一个结点出发都可以找到链表中的其它结点,使得表处理更加方便灵活。

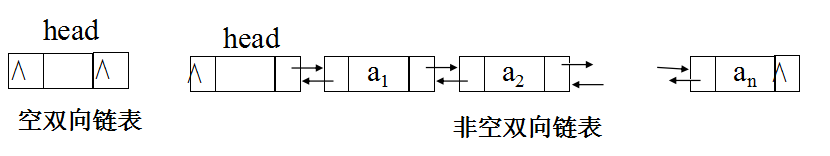
双向链表
双向链表指的是构成链表的每个结点中设立两个指针域:一个指向其直接前趋的指针域prior,一个指向其直接后继
的指针域next。这样形成的链表中有两个方向不同的链,故称为双向链表。
typedef struct Dulnode
{
ElemType data ;
struct Dulnode *prior ,*next ;
}DulNode ;节点形式

1.2 对线性表的认识及学习体会。
优点:
无需为表示表中元素之间的逻辑关系而增加额外的存储空间
可以快速地存取表中任一位置的元素
缺点:
插入删除操作需要移动大量元素
当线性表长度变化较大时,难以确定存储空间的容量
造成内存碎片
学习体会:
对于线性表的操作最重要的在于循环条件的判断,需要根据具体题目具体分析。
2.PTA实验作业
2.1 7-2 一元多项式的乘法与加法运算
2.1.1代码截图
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
static int a[1000];
static int b[1000];
static int c[1000];
static int d[1000];
int n, i, j, k,x,y;
int flag = 0;
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x >> y;
a[y] += x;//下标指数,内容系数
}
cin >> n;
while (n--)
{
cin >> x >> y;
b[y] += x;
}
k = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)//乘法
{
if (a[i])
{
for (j = 0; j < 1000; j++)
{
if (b[j])
{
c[i + j] += a[i] * b[j];
}
}
}
}
for (i = 999; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (c[i])
{
if (flag)
{
cout << " ";
}
cout << c[i] << " " << i;
flag++;
}
}
if (flag == 0) cout << "0 0";
cout << endl;
flag = 0;
for (i = 999; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (a[i])
{
d[i] += a[i];
}
}
for (j = 999; j >= 0; j--)
{
if (b[j])
{
d[j] += b[j];
}
}
for (i = 999; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (d[i])
{
if (flag)
{
cout << " ";
}
cout << d[i] << " " << i;
flag++;
}
}
if (flag == 0) cout << "0 0";
cout << -1;
return 0;
}2.1.2 本题PTA提交列表说明

答案错误:没有搞懂对零多项式的理解与处理。
解决方法:零多项式即没有任何项。