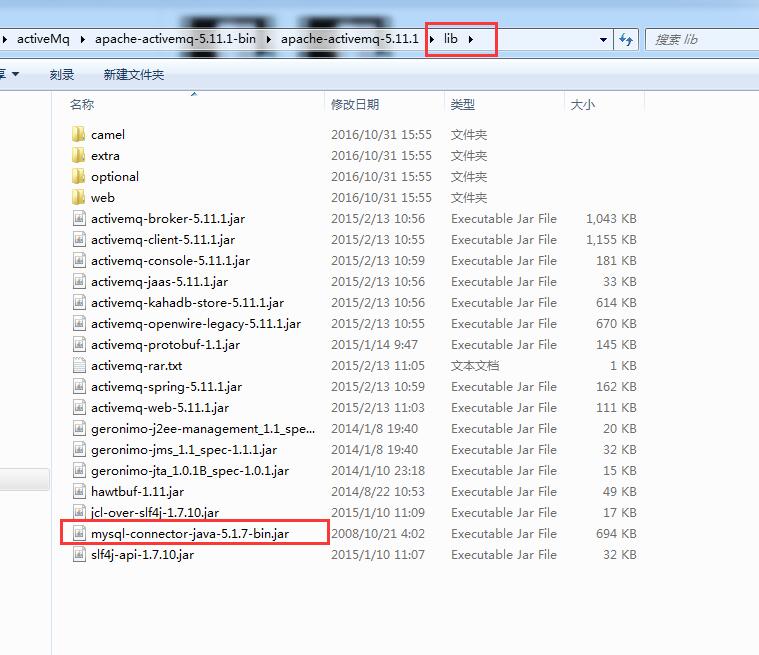
1、将连接Mysql数据库的jar文件,放到ActiveMQ的lib目录下
2、修改ActiveMQ的conf目录下的active.xml文件,修改数据持久化的方式
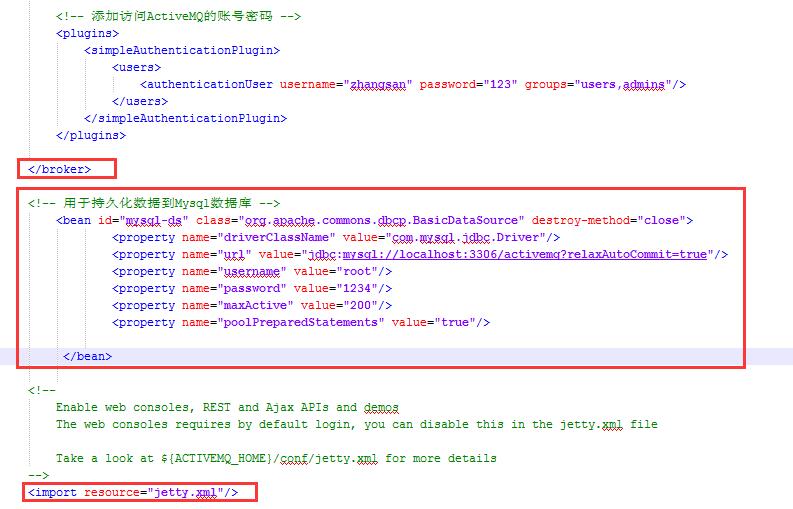
2.1 修改原来的kshadb的持久化数据的方式
<persistenceAdapter>
<!-- <kahaDB directory="${activemq.data}/kahadb"/> -->
<jdbcPersistenceAdapter dataSource="#mysql-ds"/>
</persistenceAdapter>
2.2 连接Mysql的配置(注意配置文件放置的位置)
3、将数据持久化Mysql的运行截图
3.1 重新启动ActiveMQ,并运行程序,放入持久化数据,查看Mysql的active数据库
4、放入持久化数据的代码
import javax.jms.Connection; import javax.jms.ConnectionFactory; import javax.jms.DeliveryMode; import javax.jms.Destination; import javax.jms.MessageProducer; import javax.jms.Session; import javax.jms.TextMessage; import org.apache.activemq.ActiveMQConnectionFactory; public class Sender { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 1、建立ConnectionFactory工厂对象,需要填入用户名,密码,以及连接的地址 // 仅使用默认。端口号为"tcp://localhost:61616" ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ActiveMQConnectionFactory( "zhangsan",// ActiveMQConnectionFactory.DEFAULT_USER, "123",// ActiveMQConnectionFactory.DEFAULT_PASSWORD, "tcp://localhost:61616"); // 2、通过ConnectionFactory工厂对象创建一个Connection连接 // 并且调用Connection的start方法开启连接,Connection默认是不开启的 Connection connection = connectionFactory.createConnection(); connection.start(); // 3、通过Connection对象创建Session会话(上下文环境对象), // 参数一,表示是否开启事务 // 参数二,表示的是签收模式,一般使用的有自动签收和客户端自己确认签收 // 第一个参数设置为true,表示开启事务 // 开启事务后,记得要手动提交事务 Session session = connection.createSession(Boolean.TRUE, Session.CLIENT_ACKNOWLEDGE); // 4、通过Session创建Destination对象,指的是一个客户端用来指定生产消息目标和消费消息来源的对象。 // 在PTP模式中,Destination指的是Queue // 在发布订阅模式中,Destination指的是Topic Destination destination = session.createQueue("queue1"); // 5、使用Session来创建消息对象的生产者或者消费者 MessageProducer messageProducer = session.createProducer(destination); // 6、如果是,生产者,使用MessageProducer的setDeliverMode方法设置,消息的持久化和非持久化 messageProducer.setDeliveryMode(DeliveryMode.PERSISTENT); // 7、最后使用JMS规范的TextMessage形式创建数据(通过Session对象) // 并利用MessageProducer的send方法发送数据 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { TextMessage textMessage = session.createTextMessage(); textMessage.setText("我是消息" + i); messageProducer.send(textMessage); } // 手动提交开启的事务 session.commit(); // 释放连接 if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } }