动态联编和静态联编

静态联编是程序的匹配,连接在编译阶段实现,也称为早期匹配,重载函数使用静态联编
动态联编是指程序联编推迟到运行时进行,所以称为晚期联编(迟绑定)。switch和if语句是动态联编的例子
虚析构函数
// 友元函数.cpp: 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "A() ... " << endl;
this->p = new char[64];
memset(this->p, 0, 64);
strcpy_s(this->p,100, "A string");
}
virtual void ptinftt()
{
cout << "A printff" << this->p << endl;
}
~A()
{
cout << "~A() .." << endl;
if (this->p != NULL)
{
delete[] this->p;
this->p = NULL;
}
}
private:
char *p;
};
class B :public A {
public:
B()//此刻会触发A的无参构造
{
cout << "B()...." << endl;
this->p = new char[64];
memset(this->p, 0, 64);
strcpy_s(this->p, 100,"Bstring");
}
virtual void ptinftt()
{
cout << "B printff" << this->p << endl;
}
~B()
{
cout << "~B() .." << endl;
if (this->p != NULL)
{
delete[] this->p;
this->p = NULL;
}
}
private:
char *p;
};
void func(A *a)
{
a->ptinftt();//在此发生多态
delete a;
}
void test()
{
// A obja;
// func(&obja);
//B objb;
B *bp = new B;
func(bp);
//A *ap = new A;
//func(ap);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
只触发了A的析构函数
没有触发B的析构函数
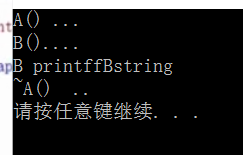
只要把父类的析构函数加上virtual改成虚析构函数即可
重载重写重定义
1.重载一定在同一个作用域下
2.重写一定是虚函数重写,父类是虚函数
3.重定义发生在两个不同的类中,一个是父类, 一个是子类
重定义包括1.普通函数重定义//如果父类的普通函数被子类重写,说是重定义,用子类对象调用这个函数时,一定会调用子类的
2虚函数重写//如果分类的虚函数被子类重写,会发生多态
