首先我们说一下这个lru_cahe是干什么的吧,从名称上就可以猜到,cache缓存,用来缓存信息,如何使用请看下面代码
"""
我分别实现两个fib数列,都使用递归求解的模式,其中一个增加装饰器lru_cache,分别计算其运行时间
"""
import functools
import datetime
@functools.lru_cache()
def fib(n):
if n<3:
return 1
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2)
def fib2(n):
if n<3:
return 1
return fib(n-1)+fib(n-2)
start1 = datetime.datetime.now()
print([fib(i) for i in range(50)])
end1 = (datetime.datetime.now()-start1).total_seconds()
start = datetime.datetime.now()
print([fib2(i) for i in range(50)])
end = (datetime.datetime.now()-start).total_seconds()
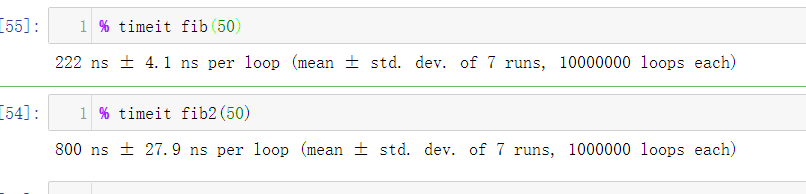
通过运行结果可以知道,lru_cache极大了缩短运行时间,复用了缓存信息
我们Ctrl+鼠标右键进入@functools.lur_cache.
def lru_cache(maxsize=128, typed=False):
# 参数检测
if maxsize is not None and not isinstance(maxsize, int):
raise TypeError('Expected maxsize to be an integer or None')
# 主函数
def decorating_function(user_function):
wrapper = _lru_cache_wrapper(user_function, maxsize, typed, _CacheInfo) # 难点2
return update_wrapper(wrapper, user_function) # 难点1
return decorating_function
难点1:update_wrapper(wrapper, user_function) Ctrl+鼠标右键进入源码
"""wrapper包装函数,wrapped被包装函数,assigned赋值,是用来覆盖的:模快名,限定名,注解,文档,参数注解等属性,经过覆盖包装函数(wrapper)属性就与被包装函数(fn)一致了,updated更新,给字典用的"""
WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS = ('__module__', '__name__', '__qualname__', '__doc__',
'__annotations__')
WRAPPER_UPDATES = ('__dict__',)
def update_wrapper(wrapper,
wrapped,
assigned = WRAPPER_ASSIGNMENTS,
updated = WRAPPER_UPDATES):
for attr in assigned: # 首行元组迭代 拿出的就是,模块,名称,注解,文档
try:
value = getattr(wrapped, attr) # 从被包装函数内取属性attr
except AttributeError:
pass
else: # 如果没有发生异常运行
setattr(wrapper, attr, value) # 把attr的属性值塞给包装函数
for attr in updated:
getattr(wrapper, attr).update(getattr(wrapped, attr, {})) # 字典的更新,如果没有返回空
wrapper.__wrapped__ = wrapped # 添加属性
return wrapper
难点2:_lru_cache_wrapper(user_function, maxsize, typed, _CacheInfo) Ctrl+鼠标右键进入源码
def _lru_cache_wrapper(user_function, maxsize, typed, _CacheInfo):
# Constants shared by all lru cache instances:
sentinel = object() # unique object used to signal cache misses
make_key = _make_key # 从函数参数创建一个key **难点3**
PREV, NEXT, KEY, RESULT = 0, 1, 2, 3 # 连接字段名称
cache = {}
hits = misses = 0
full = False
cache_get = cache.get # bound method to lookup a key or return None
cache_len = cache.__len__ # 不用调用len()获取缓存大小
lock = RLock() # because linkedlist updates aren't threadsafe
root = [] # root of the circular doubly linked list
root[:] = [root, root, None, None] # initialize by pointing to self
if maxsize == 0:
def wrapper(*args, **kwds):
# No caching -- just a statistics update after a successful call
nonlocal misses
result = user_function(*args, **kwds)
misses += 1
return result
elif maxsize is None:
def wrapper(*args, **kwds):
# Simple caching without ordering or size limit
nonlocal hits, misses
key = make_key(args, kwds, typed)
result = cache_get(key, sentinel)
if result is not sentinel:
hits += 1
return result
result = user_function(*args, **kwds)
cache[key] = result
misses += 1
return result
else:
def wrapper(*args, **kwds):
# Size limited caching that tracks accesses by recency
nonlocal root, hits, misses, full
key = make_key(args, kwds, typed)
with lock:
link = cache_get(key)
if link is not None:
# Move the link to the front of the circular queue
link_prev, link_next, _key, result = link
link_prev[NEXT] = link_next
link_next[PREV] = link_prev
last = root[PREV]
last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = link
link[PREV] = last
link[NEXT] = root
hits += 1
return result
result = user_function(*args, **kwds)
with lock:
if key in cache:
# Getting here means that this same key was added to the
# cache while the lock was released. Since the link
# update is already done, we need only return the
# computed result and update the count of misses.
pass
elif full:
# Use the old root to store the new key and result.
oldroot = root
oldroot[KEY] = key
oldroot[RESULT] = result
# Empty the oldest link and make it the new root.
# Keep a reference to the old key and old result to
# prevent their ref counts from going to zero during the
# update. That will prevent potentially arbitrary object
# clean-up code (i.e. __del__) from running while we're
# still adjusting the links.
root = oldroot[NEXT]
oldkey = root[KEY]
oldresult = root[RESULT]
root[KEY] = root[RESULT] = None
# Now update the cache dictionary.
del cache[oldkey]
# Save the potentially reentrant cache[key] assignment
# for last, after the root and links have been put in
# a consistent state.
cache[key] = oldroot
else:
# Put result in a new link at the front of the queue.
last = root[PREV]
link = [last, root, key, result]
last[NEXT] = root[PREV] = cache[key] = link
# Use the cache_len bound method instead of the len() function
# which could potentially be wrapped in an lru_cache itself.
full = (cache_len() >= maxsize)
misses += 1
return result
难点3: make_key = _make_key Ctrl+鼠标右键进入源码
def _make_key(args, kwds, typed,
kwd_mark = (object(),),
fasttypes = {int, str, frozenset, type(None)},
tuple=tuple, type=type, len=len):
key = args # 元组
if kwds:
key += kwd_mark # 元组相加等于的扩展内容
for item in kwds.items():
key += item # 把字典kv对元组添加到key元组中
# 得到一个类似于这样的元组:(4,6,obj,"x",4)
if typed:
key += tuple(type(v) for v in args) # 把args迭代出来的数据类型扩展到key元组中
if kwds:
key += tuple(type(v) for v in kwds.values())
elif len(key) == 1 and type(key[0]) in fasttypes:
return key[0]
return _HashedSeq(key) # 难点4
难点4:_HashedSeq(key)Ctrl+鼠标右键进入源码
class _HashedSeq(list):
"""做了一个这么长的key,很有可能客户传入参数是非法的,所以hash一下,如果非法直接抛异常了,起到的是参数检查的作用"""
__slots__ = 'hashvalue' # 槽
def __init__(self, tup, hash=hash): # 把上面的key拿来传给tup了
self[:] = tup # 他tup赋给他自己了
self.hashvalue = hash(tup) # 求tup hash值
def __hash__(self):
return self.hashvalue
