Java常见的线程安全相关的面试题
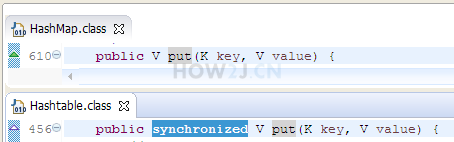
步骤 1 : HashMap和Hashtable的区别
HashMap和Hashtable都实现了Map接口,都是键值对保存数据的方式
区别1:
HashMap可以存放 null
Hashtable不能存放null
区别2:
HashMap不是线程安全的类
Hashtable是线程安全的类
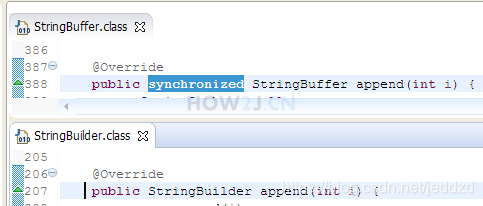
步骤 2 : StringBuffer和StringBuilder的区别
StringBuffer 是线程安全的
StringBuilder 是非线程安全的
所以当进行大量字符串拼接操作的时候,如果是单线程就用StringBuilder会更快些,如果是多线程,就需要用StringBuffer 保证数据的安全性
非线程安全的为什么会比线程安全的 快? 因为不需要同步嘛,省略了些时间
步骤 3 : ArrayList和Vector的区别
通过在eclipse中查看源代码可以得知:
ArrayList类的声明:
public class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.SerializableVector类的声明:
public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable一模一样的~
他们的区别也在于,Vector是线程安全的类,而ArrayList是非线程安全的。
步骤 4 : 把非线程安全的集合转换为线程安全
ArrayList是非线程安全的,换句话说,多个线程可以同时进入一个ArrayList对象的add方法
借助Collections.synchronizedList,可以把ArrayList转换为线程安全的List。
与此类似的,还有HashSet,LinkedList,HashMap等等非线程安全的类,都通过工具类Collections转换为线程安全的
package multiplethread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> list2 = Collections.synchronizedList(list1);
}
}