注解配置方式有以下几种
1、@Component声明
2、配置类中使用@Bean
3、实现FactoryBean
4、实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
5、实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
最常见的是第1中和第2种。
使用注解的优点:
使用简单
开发效率高
高内聚(类的定义和注解是维护在一个文件内的,不会分散开来)
使用注解的缺点
配置分散。不像xml,配置几种在xml文件中。
对象关系不清晰。
配置修改需要重新编译工程。因为配置在java文件中
注解方式配置bean实践
1、@Component声明
1)增加@Component声明
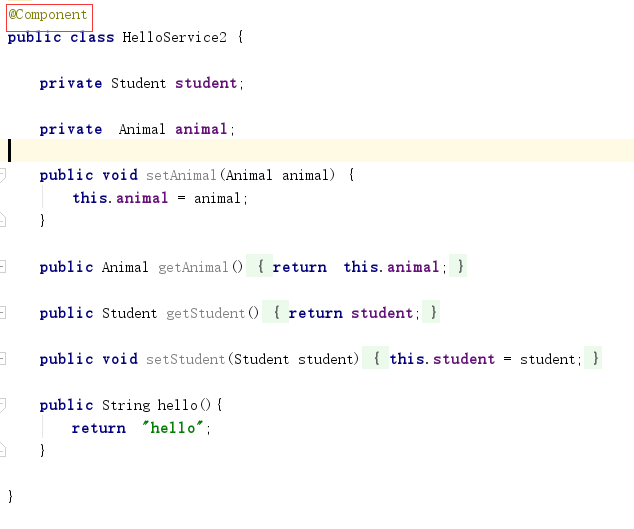
2)在测试类中使用
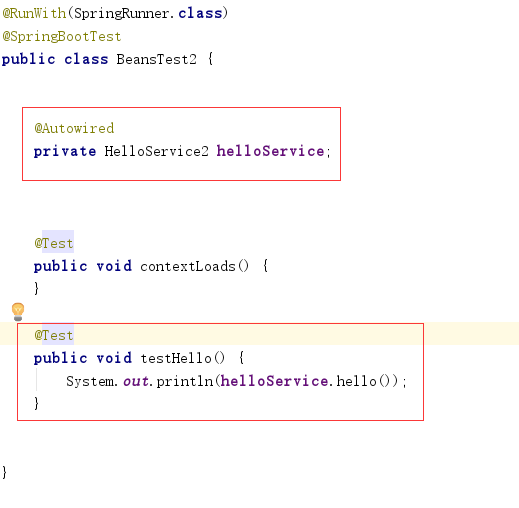
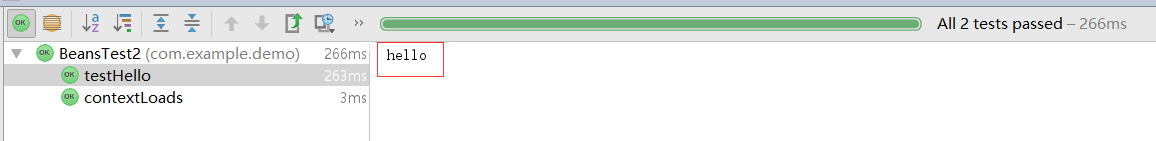
3)输出结果
2、配置类中使用@Bean
1)增加配置文件

Dog类如下
public class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
String getName() {
return "Dog";
}
}
Animal类如下
public abstract class Animal {
abstract String getName();
}
2)在Animal成员变量中增加注解Autowired ,创建hello2方法

3)增加测试类

4)输出结果
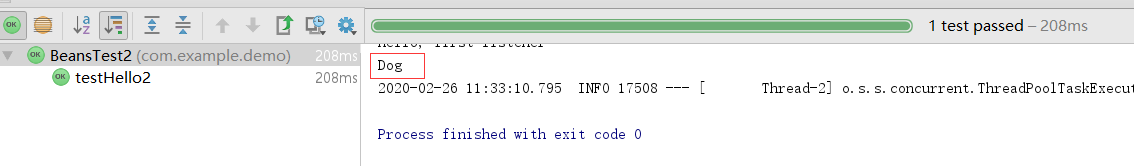
3、实现FactoryBean
1)创建MyCat
@Component
public class MyCat implements FactoryBean<Animal> {
@Nullable
@Override
public Animal getObject() throws Exception {
return new Cat();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Animal.class;
}
}
2)增加Qualifier指定是哪个bean。因此此时会有两个bean
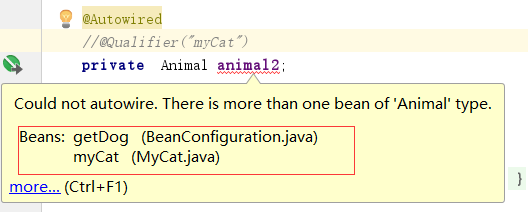
下图是用Qualifier指定是哪个bean

3)运行测试方法testHello2, 输出结果
@Test
public void testHello2() {
System.out.println(helloService.hello2());
}
结果为:

4 实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
1)创建Monkey类
public class Monkey extends Animal {
@Override
String getName() {
return "monkey";
}
}
2)创建MyBeanRegister 类,并实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
@Component
public class MyBeanRegister implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor{
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry) throws BeansException {
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
rootBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(Monkey.class);
beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition("monkey",rootBeanDefinition);
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory configurableListableBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
}
3)修改HelloService2的Qualifier为monkey
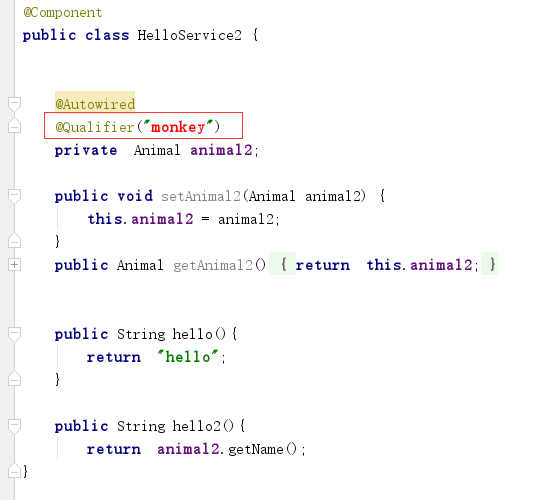
4)运行测试方法testHello2, 输出结果
@Test
public void testHello2() {
System.out.println(helloService.hello2());
}
结果为:

5、实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
1)创建Bird类
public class Bird extends Animal {
@Override
String getName() {
return "bird";
}
}
2)创建类MyBeanImport ,实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口
public class MyBeanImport implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
RootBeanDefinition rootBeanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
rootBeanDefinition.setBeanClass(Bird.class);
registry.registerBeanDefinition("bird",rootBeanDefinition);
}
}
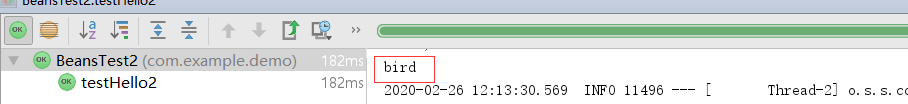
3)修改HelloService2的Qualifier为bird

4)运行测试方法testHello2, 输出结果
@Test
public void testHello2() {
System.out.println(helloService.hello2());
}
结果为: