串的定义:
字符串或串(String)是由数字、字母、下划线组成的一串字符。一般记为 s=“a1a2···an”(n>=0)。它是编程语言中表示文本的数据类型。在程序设计中,字符串(string)为符号或数值的一个连续序列,如符号串(一串字符)或二进制数字串(一串二进制数字)。
通常以串的整体作为操作对象,如:在串中查找某个子串、求取一个子串、在串的某个位置上插入一个子串以及删除一个子串等。两个字符串相等的充要条件是:长度相等,并且各个对应位置上的字符都相等。设p、q是两个串,求q在p中首次出现的位置的运算叫做模式匹配。串的两种最基本的存储方式是顺序存储方式和链接存储方式。
字符串的基本操作的实现:
对于字符串来说使用顺序存储方式比使用链式存储方式节约空间,且很容易实现,所有下面的代码实现的是字符串的顺序存方式。
注意:规定在串值后面加一个不计入串长度的结束标记字符,比如“\0”来表示串值终结。如果不加“\0”,输出时可能会出现乱码!
base.h
//base.h
//-----公用的常量和类型----------
#include<iostream>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
#include<malloc.h>
#include<string.h>
//函数结果状态代码
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;String.h
//string.h
//字符串的基本操作
//---------串的堆分配存储表示----------
typedef struct{
char *ch; //若是非空串,则按串长分配空间,否则ch为NULL
int length; //串的长度
}String;
//--------串基本操作的函数原型说明--------
//生成一个其值等于chars的串
Status StrAssign(String &T, char *chars){
if(T.ch)
free(T.ch);
int i;
for(i = 0; *(chars+i); ++i){}
if(!i){
cout<<"空字符!"<<endl;
T.ch = NULL;
T.length = 0;
}else{
if(!(T.ch = (char *)malloc(i * sizeof(char))))
exit(OVERFLOW);
int j;
for(j = 0; j < i; j++){
T.ch[j] = chars[j];
T.length = i;
}
T.ch[T.length] = '\0';
}
return OK;
}//StrAssign
//返回串内元素个数,串长度
int StrLength(String S){
return S.length;
}//StrLength
//字符串比较,若S>T,则返回>0;若S=T,则返回=0;若S<T,则返回<0;
int StrCompare(String S, String T){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < S.length && i < T.length; ++i)
if(S.ch[i] != T.ch[i])
return S.ch[i] - T.ch[i];
return S.length - T.length;
}
//将串S清空
Status ClearString(String &S){
if(S.ch){
free(S.ch);
S.ch = NULL;
}
S.length = 0;
return OK;
}//ClearString
//用T返回由S1和S2连接而成的新串
Status Concat(String &T, String S1, String S2){
if(T.ch)
free(T.ch); //释放旧空间
if(!(T.ch = (char*)malloc((S1.length + S2.length) * sizeof(char))))
exit(OVERFLOW);
int i;
for(i = 0; i < S1.length; i++)
T.ch[i] = S1.ch[i];
T.length = S1.length + S2.length;
int j;
for( i = 0, j = S1.length; j < T.length; j++, i++)
T.ch[j] = S2.ch[i];
T.ch[T.length] = '\0';
return OK;
}//Concat
//初始条件:串S存在,1<=pos<=StrLength(S) 且 0<=len<=StrLength(S)-pos+1
//用Sub返回串S的第pos个字符起长度为len的子串
Status SubString(String &Sub, String S, int pos, int len){
if(pos < 1 || pos > S.length || len < 0 || len > S.length - pos + 1)
return ERROR;
if(Sub.ch)
free(Sub.ch);
if(!len){
cout<<"Sub不存在!"<<endl;
Sub.ch = NULL;
Sub.length = 0;
}else{
Sub.ch = (char *)malloc(len * sizeof(char));
int i;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++){
Sub.ch[i] = S.ch [pos + i - 1];
Sub.length = len;
}
S.ch[S.length] = '\0';
return OK;
}
return OK;
}//SubSting
//判空
Status StrEmpty(String S){
if(S.length == 0)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}//StrEmpty
//串复制
Status StrCopy(String &T, String S){
if(!(T.ch = (char*)malloc(S.length * sizeof(char))))
exit(OVERFLOW);
T.ch = S.ch;
T.length = S.length;
return OK;
}//StrCopy
//若主串S中存在和串T相同的子串,则返回它在主串中的
//第pos个字符之后的第一次出现的位置,否则函数值为0
Status Index(String S, String T, int pos){
if(pos >= 0){
String Sub;
int n, m;
n = StrLength(S);
m = StrLength(T);
int i = pos;
while(i <= (n-m+1)){
SubString(Sub, S, i, m);
if(StrCompare(Sub, T) != 0)
++i;
else
return i;
}//while
}//if
return 0;
}//Index
//初始条件:串S存在,1<=pos<=StrLength(S)+1
//操作结果:在串S的第pos个字符之前插入串T
Status StrInsert(String &S, int pos, String T){
if(pos < 1 || pos > S.length + 1) //pos不合法
return ERROR;
if(T.length){ //T非空,则重新分配空间,插入T
if(!(S.ch = (char *)realloc(S.ch,(S.length + T.length) * sizeof(char))))
exit(OVERFLOW);
int i;
for(i = S.length-1; i >= pos-1; --i) //为插入T而腾出位置
S.ch[i+T.length] = S.ch[i];
for(i = 0; i < T.length; i++) //插入T
S.ch[pos+i] = T.ch[i];
S.length += T.length;
S.ch[S.length] = '\0';
}
return OK;
}//StrInsert
//初始条件:串S存在,1<=pos<=StrLength(S)-len+1
//操作结果:从串S中删除第pos个字符起长度为len的子串
Status StrDelete(String &S, int pos, int len){
if(pos < 1 || pos > (StrLength(S)-len+1)) //pos不合法
return ERROR;
if(S.length){ //T非空,则重新分配空间,插入T
int i;
for(i=pos-1; i < (StrLength(S)-len+1); i++)
S.ch[i] = S.ch[len+i];
S.length -= len;
S.ch[S.length] = '\0';
}
return OK;
}//StrInsert
//初始条件:串S,T,V存在,T是非空串
//操作结果:用V替换主串S中出现的所有与T相等的不重叠的子串
Status Replace(String &S, String T, String V){
int i;
for(i = 0; i < (StrLength(S)-StrLength(T)); i++){
int j = Index(S, T , 0);
if(j){
StrDelete(S, j, StrLength(T));
StrInsert(S, j-1, V);
}
}
return OK;
}//Replace
//销毁串
Status DestroyString(String &S){
if(!S.ch)
cout<<"字符串不存在,不需要销毁!"<<endl;
else{
free(S.ch);
S.ch = NULL;
S.length = 0;
cout<<"字符串销毁成功!"<<endl;
}
return OK;
}//DestroyString
main.cpp
//用来测试基本操作
#include "base.h"
#include "string.h"
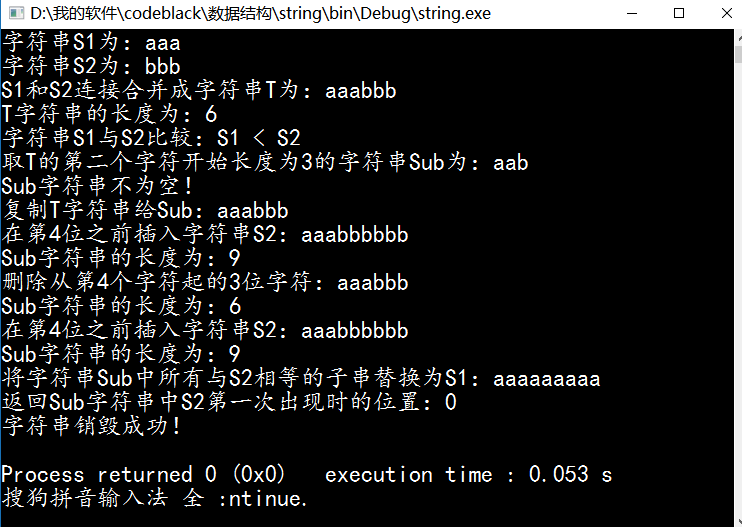
int main(){
String S1,S2, T, Sub;
char str1[] = {"aaa"};
char str2[] = {"bbb"};
StrAssign(S1, str1); //生成字符串
StrAssign(S2, str2);
cout<<"字符串S1为:"<<S1.ch<<endl;//输出字符串
cout<<"字符串S2为:"<<S2.ch<<endl;
Concat(T, S1, S2);
cout<<"S1和S2连接合并成字符串T为:"<<T.ch<<endl;
cout<<"T字符串的长度为:"<<StrLength(T)<<endl;
cout<<"字符串S1与S2比较:";
if(StrCompare(S1, S2) < 0)
cout<<"S1 < S2"<<endl;
else if(StrCompare(S1, S2) == 0)
cout<<"S1 = S2"<<endl;
else
cout<<"S1 > S2"<<endl;
SubString(Sub, T, 2, 3);
cout<<"取T的第二个字符开始长度为3的字符串Sub为:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
if(StrEmpty(Sub))
cout<<"Sub字符串为空!"<<endl;
else
cout<<"Sub字符串不为空!"<<endl;
StrCopy(Sub, T);
cout<<"复制T字符串给Sub:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
StrInsert(Sub, 3, S2);
cout<<"在第4位之前插入字符串S2:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
cout<<"Sub字符串的长度为:"<<StrLength(Sub)<<endl;
StrDelete(Sub, 4 , 3);
cout<<"删除从第4个字符起的3位字符:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
cout<<"Sub字符串的长度为:"<<StrLength(Sub)<<endl;
StrInsert(Sub, 3, S2);
cout<<"在第4位之前插入字符串S2:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
cout<<"Sub字符串的长度为:"<<StrLength(Sub)<<endl;
Replace(Sub, S2, S1);
cout<<"将字符串Sub中所有与S2相等的子串替换为S1:"<<Sub.ch<<endl;
cout<<"返回Sub字符串中S2第一次出现时的位置:"<<Index(Sub, S2, 0)<<endl;
DestroyString(Sub);
return 0;
}字符串操作测试结果: