一、查询语法
查询语句语法:
[WITH CommonTableExpression (, CommonTableExpression)*]
Only available
starting with Hive 0.13.0)
SELECT [ALL | DISTINCT] select_expr, select_expr, ...
FROM table_reference
[WHERE where_condition]
[GROUP BY col_list]
[ORDER BY col_list]
[CLUSTER BY col_list
| [DISTRIBUTE BY col_list] [SORT BY col_list]
]
[LIMIT number]
官方文档:
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+Select
二、基本查询(select … from)
2.1 全表和特定列查询
1、全表查询
hive (default)> select * from emp;
OK
emp.empno emp.ename emp.job emp.mgr emp.hiredate emp.sal emp.comm emp.deptno
7369 SMITH CLERK 7902 1980-12-17 800.0 NULL 20
7499 ALLEN SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-20 1600.0 300.0 30
7521 WARD SALESMAN 7698 1981-2-22 1250.0 500.0 30
7566 JONES MANAGER 7839 1981-4-2 2975.0 NULL 20
7654 MARTIN SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-28 1250.0 1400.0 30
7698 BLAKE MANAGER 7839 1981-5-1 2850.0 NULL 30
7782 CLARK MANAGER 7839 1981-6-9 2450.0 NULL 10
7788 SCOTT ANALYST 7566 1987-4-19 3000.0 NULL 20
7839 KING PRESIDENT NULL 1981-11-17 5000.0 NULL 10
7844 TURNER SALESMAN 7698 1981-9-8 1500.0 0.0 30
7876 ADAMS CLERK 7788 1987-5-23 1100.0 NULL 20
7900 JAMES CLERK 7698 1981-12-3 950.0 NULL 30
7902 FORD ANALYST 7566 1981-12-3 3000.0 NULL 20
7934 MILLER CLERK 7782 1982-1-23 1300.0 NULL 10
Time taken: 2.619 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
2、选择特定列查询
hive (default)> select empno, ename from emp;
OK
empno ename
7369 SMITH
7499 ALLEN
7521 WARD
7566 JONES
7654 MARTIN
7698 BLAKE
7782 CLARK
7788 SCOTT
7839 KING
7844 TURNER
7876 ADAMS
7900 JAMES
7902 FORD
7934 MILLER
Time taken: 0.141 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
注意:
(1) SQL 语言大小写不敏感
(2) SQL 可以写在一行或者多行
(3) 关键字不能被缩写也不能分行
(4) 各子句一般要分行写
(5) 使用缩进提高语句的可读性
2.2 列别名
hive (default)> select ename AS name, deptno dn from emp;
OK
name dn
SMITH 20
ALLEN 30
WARD 30
JONES 20
MARTIN 30
BLAKE 30
CLARK 10
SCOTT 20
KING 10
TURNER 30
ADAMS 20
JAMES 30
FORD 20
MILLER 10
Time taken: 0.101 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
2.3 算数运算符
例子:
查询出所有员工的薪水后加1显示
hive (default)> select sal+1 as sal from emp;
OK
sal
801.0
1601.0
1251.0
2976.0
1251.0
2851.0
2451.0
3001.0
5001.0
1501.0
1101.0
951.0
3001.0
1301.0
Time taken: 0.096 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
2.4 常用函数
1、求总行数(count)
hive (default)> select count(*) cnt from emp;
2、求工资的最大值(max)
hive (default)> select max(sal) max_sal from emp;
3、求工资的最小值(min)
hive (default)> select min(sal) min_sal from emp;
4、求工资的总和(sum)
hive (default)> select sum(sal) sum_sal from emp;
5、求工资的平均值(avg)
hive (default)> select avg(sal) avg_sal from emp;
2.5 limit 语句
limit 子句用于限制返回的行数
hive (default)> select * from emp limit 5;
三、where 语句
3.1 基本用法
1、使用 where 子句,将不满足条件的行过滤掉
2、where 子句紧随 from 子句
3、案例
查询出薪水大于 800 的所有员工
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal > 800;
3.2 比较运算符(between/ in/ is null)
1、介绍
下面表中描述了谓词操作符,这些操作符也可以用于 join…on 和 having 语句中。
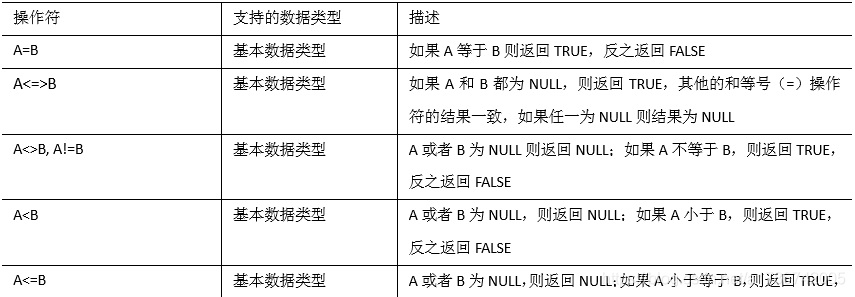
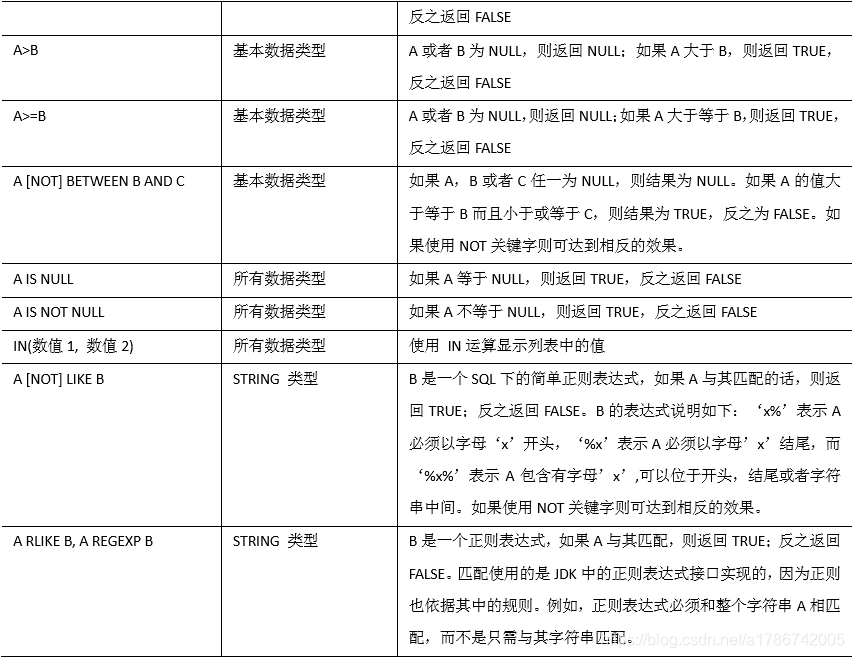 2、案例
2、案例
(1) 查询出薪水等于 5000 的所有员工
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal =5000;
(2) 查询出工资在 500 到 1000 员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal between 500 and 1000;
(3) 查询 comm 为空的所有员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where comm is null;
(4) 查询工资是1500 或 5000 的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal IN (1500, 5000);
3.3 like 和 rlike
1、用法介绍
(1) 使用 LIKE 运算选择类似的值
(2) 选择条件可以包含字符或数字
% 代表零个或多个字符(任意个字符)
_ 代表一个字符
(3) RLIKE 子句是 Hive 中这个功能的一个扩展其可以通过正则表达式来指定匹配条件
2、案例
(1) 查询以 2 开头薪水的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE '2%';
(2) 查询第二个数值为 2 的薪水的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal LIKE '_2%';
(3) 查找薪水中含有 2 的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal RLIKE '[2]';
3.4 逻辑运算符(and/ or/ not)
1、介绍
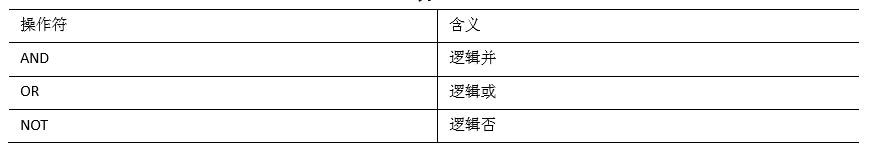 2、案例
2、案例
(1) 查询薪水大于 1000,部门是 30
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 and deptno=30;
(2) 查询薪水大于 1000,或者部门是 30
hive (default)> select * from emp where sal>1000 or deptno=30;
(3) 查询除了 20 部门和 30 部门以外的员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp where deptno not IN(30, 20);
四、分组
4.1 group by 语句
1、介绍
GROUP BY 语句通常会和聚合函数一起使用按照一个或者多个列队结果进行分组,然后对每个组执行聚合操作。
2、案例
(1) 计算 emp 表每个部门的平均工资
hive (default)> select t.deptno, avg(t.sal) avg_sal from emp t group by t.deptno;
(2) 计算 emp 每个部门中每个岗位的最高薪水
hive (default)> select t.deptno, t.job, max(t.sal) max_sal from emp t group by t.deptno, t.job;
4.2 having 语句
1、having 与 where 不同点
(1) where 针对表中的列发挥作用,查询数据;having 针对查询结果中的列发挥作用,筛选数据。
(2) where 后面不能写聚合函数,而 having 后面可以使用聚合函数。
(3) having 只用于 group by 分组统计语句。
2、案例
(1) 求每个部门的平均薪水大于 2000 的部门
A、求每个部门的平均工资
hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) from emp group by deptno;
B、求每个部门的平均工资大于 2000 的部门
hive (default)> select deptno, avg(sal) avg_sal from emp group by deptno having avg_sal > 2000;
五、join语句
5.1 等值 join
1、介绍
hive 支持通常的 sql join 语句,但是 只支持等值连接,不支持非等值连接 。
2、案例
(1) 根据员工表和部门表中的部门编号相等,查询员工编号、员工名称和部门名称
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno, d.dname from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.2 表的别名
1、好处
(1) 使用别名可以简化查询
(2) 使用表名前缀可以提高执行效率
2、案例
合并员工表和部门表
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.3 内连接
1、内连接介绍
只有进行连接的两个表中都存在与连接条件相匹配的数据才会被保留下来。
2、案例
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.4 左外连接
1、左外连接介绍
join 操作符左边表中符合 where 子句的所有记录将会被返回。
2、案例
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e left join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.5 右外连接
1、右外连接介绍
join 操作符右边表中符合 where 子句的所有记录将会被返回。
2、案例
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e right join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.6 满外连接
1、满外连接介绍
将会返回所有表中符合 where 语句条件的所有记录。如果任一表的指定 字段没有符合条件的值话,那么就使用 null 值替代。
2、案例
hive (default)> select e.empno, e.ename, d.deptno from emp e full join dept d on e.deptno = d.deptno;
5.7 多表连接
1、多表连接介绍
连接 n 个表,至少需要 n - 1 个连接条件。
2、案例
(1) 创建表
create table if not exists default.location(
loc int,
loc_name string )
row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
(2) 导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/location.txt' into table default.location;
(3) 多表连接查询
hive (default)>SELECT e.ename, d.deptno, l.loc_name
FROM emp e
JOIN dept d
ON d.deptno = e.deptno
JOIN location l
ON d.loc = l.loc;
大多数情况下,Hive 会对每对 JOIN 连接对象启动一个 MapReduce 任务。本例中会首先启动一个 MapReduce job 对表 e 和表 d 进行连接操作,然后会再启动一个 MapReduce job 将第一个 MapReduce job 的输出和表 l 进行连接操作。
注意:为什么不是表 d 和表 l 先进行连接操作呢?这是因为 Hive 总是按照从左到右的
顺序执行的。
5.8 笛卡尔积
1、笛卡尔积会在下面条件下产生
(1) 省略连接条件
(2) 连接条件无效
(3) 所有表中的所有行互相连接
2、案例
hive (default)> select empno, dname from emp, dept;
5.9 连接谓词中不支持 or
使用后会报错
六、排序
6.1 全局排序(order by)
order by:全局排序,一个 Reducer
1、使用 order by 子句排序
asc(ascend):升序(默认)
desc(descend):降序
2、order by 子句在 select 语句的结尾
3、例子
(1) 查询员工信息按照工资升序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal;
(2) 查询员工信息按照工资降序排列
hive (default)> select * from emp order by sal desc;
6.2 按照别名排序
按照员工薪水的两倍排序
hive (default)> select ename, sal*2 twosal from emp order by twosal;
6.3 多个列排序
按照部门和工资升序排序
hive (default)> select ename, deptno, sal from emp order by deptno, sal;
6.4 每个 mapreduce 内部排序(Sort By)
Sort By:每个 Reducer 内部进行排序,对全局结果集来说不是排序。
1、设置 reduce 个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
2、查看设置 reduce 个数
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces;
3、根据部门编号降序查看员工信息
hive (default)> select * from emp sort by empno desc;
6.5 分区排序(distribute by)
1、介绍
Distribute By:类似 MR 中 partition,进行分区,结合 sort by 使用。
注意,Hive 要求 DISTRIBUTE BY 语句要写在 SORT BY 语句之前。
对于 distribute by 进行测试,一定要分配多 reduce 进行处理,否则无法看到 distribute by
的效果。
2、案例
先按照部门编号分区,再按照员工编号降序排序
hive (default)> set mapreduce.job.reduces=3;
hive (default)> insert overwrite local directory '/opt/module/datas/distribute-result' select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by empno desc;
6.6 cluster by
1、介绍
当 distribute by 和 sorts by 字段相同时,可以使用 cluster by 方式。 cluster by 除了具有 distribute by 的功能外还兼具 sort by 的功能。但是排序只能是升序排序,不能指定排序规则为 ASC 或者 DESC。
2、以下两种写法等价
hive (default)> select * from emp cluster by deptno;
hive (default)> select * from emp distribute by deptno sort by deptno;
注意:按照部门编号分区,不一定就是固定死的数值,可以是 20 号和 30 号部门分到一个分区里面去。
七、分桶及抽样查询
7.1 分桶表数据储存
1、介绍
(1) 分区针对的是数据的存储路径;分桶针对的是数据文件。
(2) 分区提供一个隔离数据和优化查询的便利方式。不过,并非所有的数据集都可形成合理
的分区,特别是之前所提到过的要确定合适的划分大小这个疑虑。
(3) 分桶是将数据集分解成更容易管理的若干部分的另一个技术。
2、案例
(1) 先创建分桶表,通过直接导入数据文件的方式
A、先创建分桶表
hive (default)> create table stu_buck(id int, name string) clustered by(id) into 4 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
B、查看表结构
hive (default)> desc formatted stu_buck; Num Buckets: 4
C、查看数据
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ cat student.txt
1 a
2 b
3 c
4 d
5 e
6 f
D、导入数据到分桶表中
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/student.txt' into table stu_buck;
E、查看创建的分桶表是否分成 4 个桶
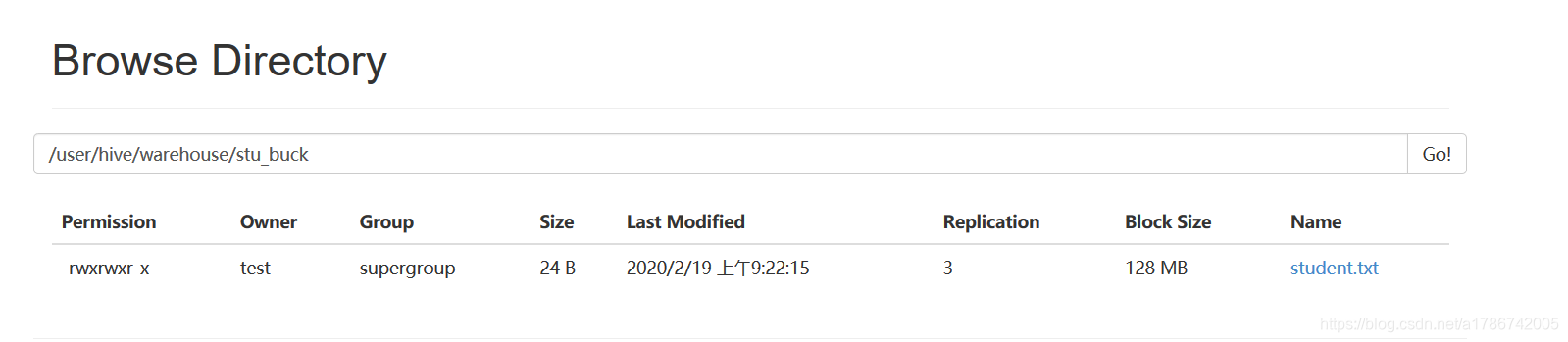 没有分成 4 个桶,请继续往下看。
没有分成 4 个桶,请继续往下看。
(2) 创建分桶表时,数据通过子查询的方式导入
A、先建一个普通的 stu 表
hive (default) create table stu(id int, name string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t';
B、向普通的 stu 表中导入数据
hive (default)> load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/student.txt' into table stu;
C、清空 stu_buck 表中数据
hive (default)> truncate table stu_buck;
D、导入数据到分桶表,通过子查询的方式
hive (default)> insert into table stu_buck select id, name from stu;
E、发现还是只有一个分桶
F、设置一个属性
hive (default)> set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
hive (default)> insert into table stu_buck select id, name from stu;
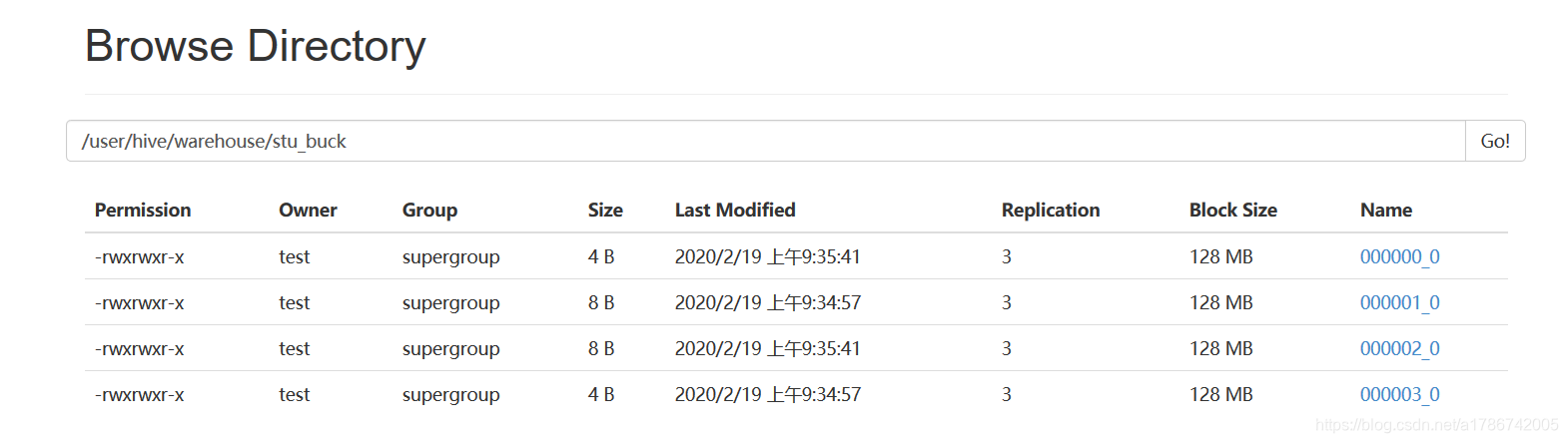
G、查询分桶的数据
hive (default)> select * from stu_buck;
OK
stu_buck.id stu_buck.name
4 d
5 e
1 a
6 f
2 b
3 c
Time taken: 0.215 seconds, Fetched: 6 row(s)
7.2 分桶抽样查询
1、介绍
对于非常大的数据集,有时用户需要使用的是一个具有代表性的查询结果而不是全部结果。Hive 可以通过对表进行抽样来满足这个需求。
2、案例
hive (default)> select * from stu_buck tablesample(bucket 1 out of 4 on id);
A、注:tablesample 是抽样语句,法:TABLESAMPLE(BUCKET x OUT OF y) 。
B、y 必须是 table 总 bucket 数的倍数或者因子。hive 根据 y 的大小,决定抽样的比例。例如,table 总共分了 4 份,当 y=2 时,抽取(4/2=)2 个 bucket 的数据,当 y=8 时,抽取(4/8=)1/2 个 bucket 的数据。
C、x 表示从哪个 bucket 开始抽取,如果需要取多个分区,以后的分区号为当前分区号加上y。例如,table 总 bucket 数为 4,tablesample(bucket 1 out of 2),表示总共抽取(4/2=)2 个bucket 的数据,抽取第 1(x)个和第 3(x+y)个 bucket 的数据。
D、注意:x 的值必须小于等于 y 的值,否则报错。
八、其他常用查询函数
8.1 空字段赋值
1、函数说明
NVL:给值为 NULL 的数据赋值,它的格式是 NVL( string1, replace_with)。它的功能是如果 string1 为 NULL,则 NVL 函数返回 replace_with 的值,否则返回 string1 的值,如果两个参数都为 NULL,则返回 NULL。
2、案例
(1) 查询如果员工的 comm 为 null,用 -1 代替
hive (default)> select nvl(comm,-1) from emp;
OK
_c0
-1.0
300.0
500.0
-1.0
1400.0
-1.0
-1.0
-1.0
-1.0
0.0
-1.0
-1.0
-1.0
-1.0
Time taken: 0.361 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
(2) 查询如果员工的 comm 为 null,则用领导 id 代替
hive (default)> select nvl(comm,mgr) from emp;
OK
_c0
7902.0
300.0
500.0
7839.0
1400.0
7839.0
7839.0
7566.0
NULL
0.0
7788.0
7698.0
7566.0
7782.0
Time taken: 0.083 seconds, Fetched: 14 row(s)
8.2 时间类
1、date_format:格式化时间
hive (default)> select date_format('2019-06-29','yyyy-MM-dd');
OK
_c0
2019-06-29
Time taken: 0.558 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
2、date_add:时间和天数相加
hive (default)> select date_add('2019-06-29',5); OK _c0 2019-07-04
hive (default)> select date_add('2019-06-29',-5); OK _c0 2019-06-24
3、date_sub:时间和天数相减
hive (default)> select date_sub('2019-06-29',5); OK _c0 2019-06-24
hive (default)> select date_sub('2019-06-29 12:12:12',5); OK _c0 2019-06-24
hive (default)> select date_sub('2019-06-29',-5); OK _c0 2019-07-04
4、datediff:两个时间相减
hive (default)> select datediff('2019-06-29','2019-06-24');
OK
_c0
5
Time taken: 0.236 seconds, Fetched: 1 row(s)
8.3 case when
1、准备数据
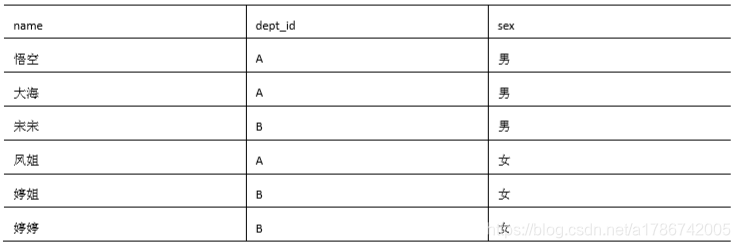
2、需求
求出不同部门男女各多少人,结果如下:

3、创建本地 emp_sex.txt,添加数据
4、创建 hive 表并导入数据
create table emp_sex(
name string,
dept_id string,
sex string)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/emp_sex.txt' into table emp_sex;
5、编写 HQL 语句
select
dept_id,
sum(case sex when '男' then 1 else 0 end) male_count,
sum(case sex when '女' then 1 else 0 end) female_count
from
emp_sex group by
dept_id;
8.4 行转列
1、相关函数说明
(1) CONCAT(string A/col, string B/col…):返回输入字符串连接后的结果,支持任意个输入字符串。
(2) CONCAT_WS(separator, str1, str2,…):它是一个特殊形式的 CONCAT()。第一个参数剩余参数间的分隔符。分隔符可以是与剩余参数一样的字符串。如果分隔符是 NULL,返回值也将为 NULL。这个函数会跳过分隔符参数后的任何 NULL 和空字符串。分隔符将被加到被连接的字符串之间;
(3) COLLECT_SET(col):函数只接受基本数据类型,它的主要作用是将某字段的值进行去重汇总,产生 array 类型字段。
2、案例
(1) 数据准备
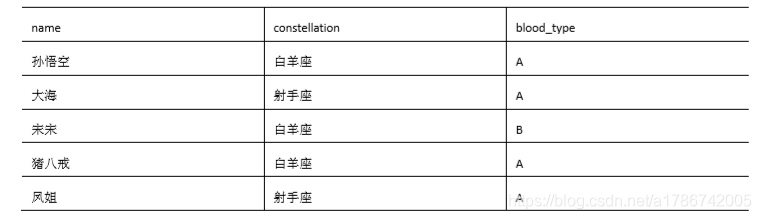
(2) 需求
把星座和血型一样的人归类到一起,结果如下:

(3) 创建本地文件 constellation.txt,导入数据
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ vi constellation.txt
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ cat constellation.txt
孙悟空 白羊座 A
大海 射手座 A
宋宋 白羊座 B
猪八戒 白羊座 A
凤姐 射手座 A
(4) 创建 hive 表并导入数据
create table person_info(
name string,
constellation string,
blood_type string)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
hive (default)> load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/constellation.txt" into table person_info;
(5) 按需求查询数据
select
t1.base,
concat_ws('|', collect_set(t1.name)) name from
(select
name,
concat(constellation, ",", blood_type) base
from
person_info) t1
group by t1.base;
8.5 列转行
1、函数说明
(1) EXPLODE(col):将 hive 一列中复杂的 array 或者 map 结构拆分成多行。
(2) LATERAL VIEW
用法:LATERAL VIEW udtf(expression) tableAlias AS columnAlias
解释:用于和 split, explode 等 UDTF 一起使用,它能够将一列数据拆成多行数据,在此基础上可以对拆分后的数据进行聚合。
2、案例
(1) 数据准备
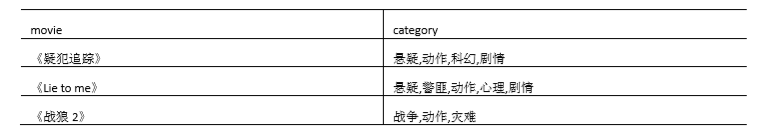
(2) 需求
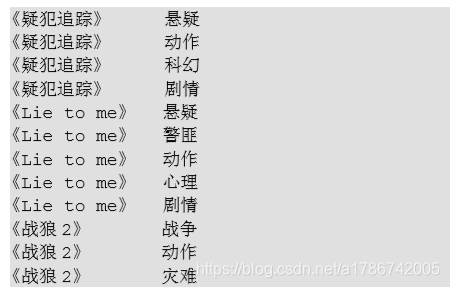
将电影分类中的数组数据展开,结果如下:
(3) 创建本地 movie.txt,导入数据
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ vim movie.txt
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ cat movie.txt
《疑犯追踪》 悬疑,动作,科幻,剧情
《Lie to me》 悬疑,警匪,动作,心理,剧情
《战狼 2》 战争,动作,灾难
(4) 创建 hive 表并导入数据
create table movie_info(
movie string,
category array<string>)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t"
collection items terminated by ",";
load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/movie.txt" into table movie_info;
(5) 编写 HQL 语句查询数据
select
movie,
category_name
from
movie_info lateral view explode(category) table_tmp as
category_name;
8.6 窗口函数
1、相关函数说明
OVER():指定分析函数工作的数据窗口大小,这个数据窗口大小可能会随着行的变化而变化;
CURRENT ROW:当前行;
n PRECEDING:往前 n 行数据;
n FOLLOWING:往后 n 行数据;
UNBOUNDED:起点,UNBOUNDED PRECEDING 表示从前面的起点, UNBOUNDED
FOLLOWING 表示到后面的终点;
LAG(col,n):往前第 n 行数据;
LEAD(col,n):往后第 n 行数据;
NTILE(n):把有序分区中的行分发到指定数据的组中,各个组有编号,编号从 1 开始,
对于每一行,NTILE 返回此行所属的组的编号。注意:n 必须为 int 类型。
2、案例
(1) 数据准备
三列分别为:name、orderdate、cost
jack,2017-01-01,10
tony,2017-01-02,15
jack,2017-02-03,23
tony,2017-01-04,29
jack,2017-01-05,46
jack,2017-04-06,42
tony,2017-01-07,50
jack,2017-01-08,55
mart,2017-04-08,62
mart,2017-04-09,68
neil,2017-05-10,12
mart,2017-04-11,75
neil,2017-06-12,80
mart,2017-04-13,94
(2) 需求
A、查询在 2017 年 4 月份购买过的顾客及总人数
B、查询顾客的购买明细及购买总额
C、上述的场景,要将 cost 按照日期进行累加
D、查询顾客上次的购买时间
E、查询前 20%时间的订单信息
(3) 创建本地文件 business.txt,导入数据
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ vim business.txt
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ cat business.txt
jack,2017-01-01,10
tony,2017-01-02,15
jack,2017-02-03,23
tony,2017-01-04,29
jack,2017-01-05,46
jack,2017-04-06,42
tony,2017-01-07,50
jack,2017-01-08,55
mart,2017-04-08,62
mart,2017-04-09,68
neil,2017-05-10,12
mart,2017-04-11,75
neil,2017-06-12,80
mart,2017-04-13,94
(4) 创建 hive 表并导入数据
create table business(
name string,
orderdate string,
cost int )
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED FIELDS TERMINATED BY ',';
load data local inpath "/opt/module/datas/business.txt" into table business;
(5) 按需求查询数据
A、查询在 2017 年 4 月份购买过的顾客及总人数
select name,count(*) over ()
from business
where substring(orderdate,1,7) = '2017-04'
group by name;
B、查询顾客的购买明细及月购买总额
select name,orderdate,cost,sum(cost)
over(partition by month(orderdate))
from business;
C、上述场景,将 cost 按照日期进行累加
select name,orderdate,cost,
sum(cost) over() as sample1,--所有行相加
sum(cost) over(partition by name) as sample2,--按 name 分组,组内 数据相加
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate) as sample3,-按 name 分组,组内数据累加
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between UNBOUNDED PRECEDING and current row ) as sample4 ,--和 sample3一样,由起点到当前行的聚合
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between 1 PRECEDING and current row) as sample5, --当前行和前面一行做聚合
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between1 PRECEDING AND 1 FOLLOWING ) as sample6,--当前行和前边一行及后面一行
sum(cost) over(partition by name order by orderdate rows between current row and UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING ) as sample7 --当前行及后面所有行
from business;
D、查看顾客上次的购买时间
select name,orderdate,cost,
lag(orderdate,1,'1900-01-01')
over(partition by name order by orderdate)
as time1, lag(orderdate,2)
over (partition by name order by orderdate) as time2
from business;
E、查询前 20% 时间的订单信息
select * from (
select name,orderdate,cost, ntile(5) over(order by orderdate)
sorted from business )
t where sorted = 1;
8.7 rank
1、函数说明
RANK() 排序相同时会重复,总数不会变
DENSE_RANK() 排序相同时会重复,总数会减少
ROW_NUMBER() 会根据顺序计算
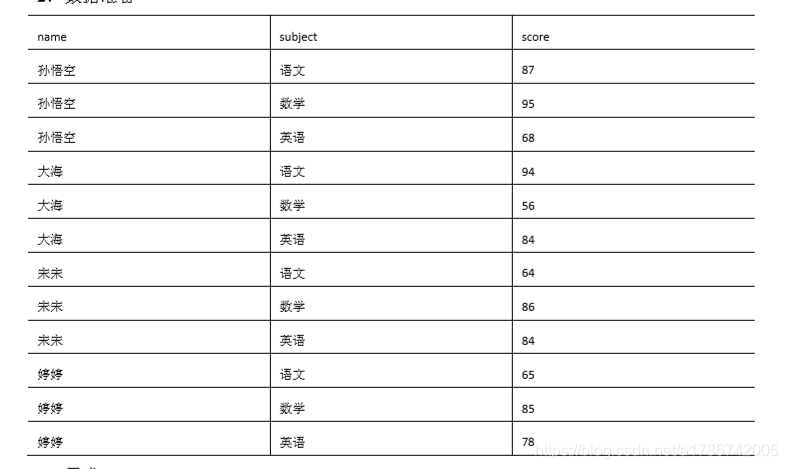
2、数据准备
3、需求
计算每门学科成绩排名
4、创建本地文件 movie.txt,导入数据
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ vim score.txt
[test@hadoop151 datas]$ cat score.txt
孙悟空 语文 87
孙悟空 数学 95
孙悟空 英语 68
大海 语文 94
大海 数学 56
大海 英语 84
宋宋 语文 64
宋宋 数学 86
宋宋 英语 84
婷婷 语文 65
婷婷 数学 85
婷婷 英语 78
5、创建 hive 表并导入数据
create table score(
name string,
subject string,
score int)
row format delimited fields terminated by "\t";
load data local inpath '/opt/module/datas/score.txt' into table score;
6、按照需求查询数据
select name,
subject,
score,
rank()
over(partition by subject order by score desc) rp, dense_rank()
over(partition by subject order by score desc) drp, row_number()
over(partition by subject order by score desc) rmp
from score;
结果为:
name subject score rp drp rmp
孙悟空 数学 95 1 1 1
宋宋 数学 86 2 2 2
婷婷 数学 85 3 3 3
大海 数学 56 4 4 4
宋宋 英语 84 1 1 1
大海 英语 84 1 1 2
婷婷 英语 78 3 2 3
孙悟空 英语 68 4 3 4
大海 语文 94 1 1 1
孙悟空 语文 87 2 2 2
婷婷 语文 65 3 3 3
宋宋 语文 64 4 4 4
