1 在GeneralTools目录下创建一个常量文件Constants.py
获取短信验证之前需要申请腾讯云短信服务。
"""
腾讯云短信相关常量
"""
# 云短信应用 SDK AppID
SMS_SDK_APP_ID = ''
# 云短信应用 SDK AppKey
SMS_APP_KEY = ''
# 注册短信模板ID
SMS_REGISTER_TEMPLATE_ID = # 输入模板编号
# 短信签名,签名参数使用的是`签名内容`,而不是`签名ID`。
SMS_SIGN = ''
# 验证access_token有效时间: s
VERIFY_ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRES = 300
# 短信验证码的有效期,单位秒
SMS_CODE_REDIS_EXPIRES = 300
# 短信验证码发送间隔,单位秒
SEND_SMS_CODE_INTERVAL = 60
2 GeneralTools目录下创建文件CustomSchema.py
在接口文档中,需要对GET参数进行备注。如图:

此时,需要编写一个公共类,用于在每个视图中增加备注。内容如下:
from rest_framework.schemas import AutoSchema
class CustomSchema(AutoSchema):
"""
自定义AutoSchema,为view手动添加注释
"""
def get_manual_fields(self, path, method):
"""
location有下列可选选项可以选:
path 包含在模板化URI中。例如,url值/products/{product_code}/可以与"path"字段一起使用。
query 包含在URL查询参数中。例如?search=sale。通常用于GET请求。
form 包含在请求正文中,作为JSON对象或HTML表单的单个项目。例如{"colour": "blue", ...}。通常的POST,PUT和PATCH请求。"form"单个链接上可以包含多个字段。
header 包含在请求头中,可以自定义。
{
'get': [
coreapi.Field(name="mobile", required=True, location="path", schema=coreschema.String(description='手机号')),
coreapi.Field(name="name", required=True, location="query", schema=coreschema.String(description='用户名')),
coreapi.Field(name="password", required=True, location="query", schema=coreschema.String(description='密码')),
],
'post': [
coreapi.Field(name="mobile", required=True, location="path", schema=coreschema.String(description='手机号')),
coreapi.Field(name="subject", required=True, location="query", schema=coreschema.String(description='邮件主题')),
coreapi.Field(name="message", required=True, location="query", schema=coreschema.String(description='邮件正文')),
coreapi.Field(name="to_email", required=True, location="query", schema=coreschema.String(description='收件人')),
],
}
"""
# 可能是list,也可能是dict
manual_fields = super(CustomSchema, self).get_manual_fields(path, method)
if type(manual_fields) == list:
return manual_fields
else:
# dict
for k, v in self._manual_fields.items():
if method.lower() == k.lower():
return v
else:
return []
使用方法则是在调用的类中,最前面做声明,声明格式如下:
schema = CustomSchema(
manual_fields={
'get': [
Field(name="mobile", required=True, location="query", schema=String(description='手机号')),
],
}
)
3 在GeneralTools下创建一个用于正则表达式验证的公共方法,名为:Verifications.py 在其中增加一个手机验证方法。
import re
def mobileVerify(mobile):
if re.match(r'^1[3-9]\d{9}$', mobile):
return True
return False
4 在APP下views目录下创建Register.py文件,内容如下:
from rest_framework.views import APIView
import logging
from itsdangerous import TimedJSONWebSignatureSerializer as TJWSSerializer
from django.conf import settings
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import status
from coreapi import Field
from coreschema import String
from GeneralTools.CustomSchema import CustomSchema
from GeneralTools import Constants
from GeneralTools import Verifications
logger = logging.getLogger('tongheng2')
class GetRegisterToken(APIView):
"""
用户注册第一步:获取短信接口access token
"""
schema = CustomSchema(
manual_fields={
'get': [
Field(name="mobile", required=True, location="query", schema=String(description='手机号')),
],
}
)
@classmethod
def get(cls, request):
"""
【功能描述】用户注册第一步:获取短信接口access token </br>
【返回值】返回短信接口access token </br>
"""
mobile = request.query_params.get('mobile')
if not mobile:
return Response(data={'message': '缺少mobile参数'}, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
if not Verifications.mobileVerify(mobile):
return Response(data={'message': '不是有效的有机号'}, status=status.HTTP_400_BAD_REQUEST)
# 创建itsdangerous模型的转换工具
tjwserializer = TJWSSerializer(settings.SECRET_KEY, Constants.VERIFY_ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRES)
access_token = tjwserializer.dumps({'mobile': mobile}) # bytes
access_token = access_token.decode() # str
data = {
'mobile': mobile,
'access_token': access_token
}
return Response(data=data, status=status.HTTP_200_OK)
5 配置Organization urls
from django.urls import path
from .views import Register
urlpatterns = [
path('GetRegisterToken/', Register.GetRegisterToken.as_view()),
]
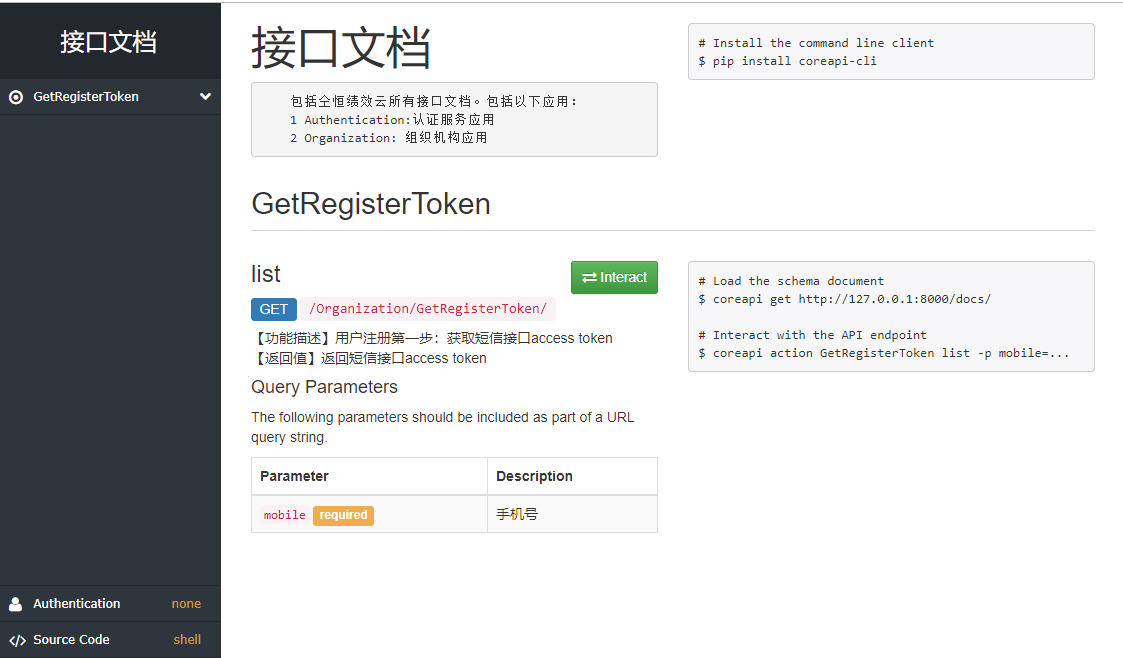
6 运行工程,进入接口文档,可以看到以下效果
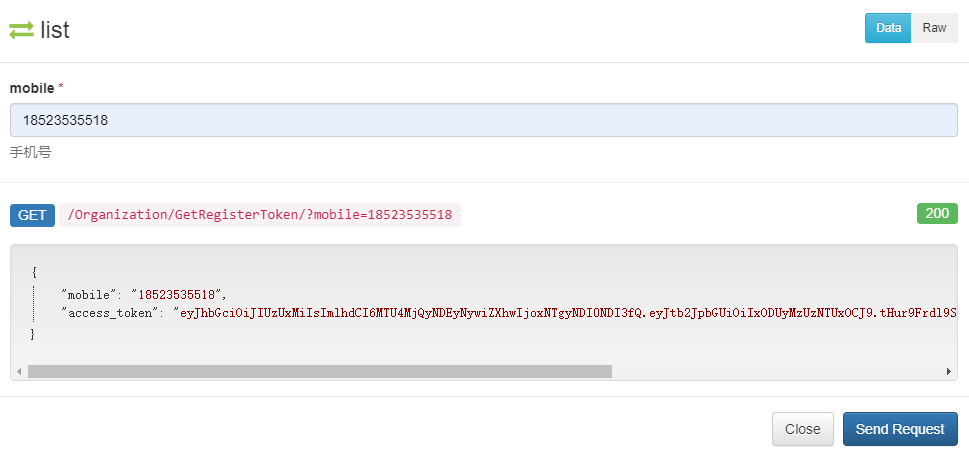
7 点击Interact,即可进行接口测试,即输入手机号,获取获取短信接口access token