写在前面
本次参加了2019年12月7日PAT冬季考试,考点在北京工业大学(土豪大学)。考试时间3个小时。一个半小时AK,其中第一道题提交了5次,第二道题提交2次,第三道题提交1次,第四道题提交1次,总排名好像是30。
这个报名是老早就报的,因为九月参加了一次,报名的时候发现北京赛区已满,只能去保定河北大学考试,成本着实有点高。
这学期其实很忙的,计网实践,算法,数据库,编译原理,操作系统,还有我的CET6。九月份的考试实打实地准备了二十来天,这次考试是完全裸考,本来打算退钱,结果申请的时候,已经不能退了,所有就去参加一下吧。
幸好,我九月份学的到了十二月还没忘掉,考试还算顺利。
第一道题提交多次原因在于我使用了cin而没使用getline,耗费了好长时间,真的烦,直接跳过去了,拐回来的时候脑袋一转,发现了这个问题,哈哈,所以就“打卡”走人。
看着同考场它们都在焦急做题,感觉可还行,有一说一,确实!
下周就要CET6考试,我的英语真的垃圾,本来打算之后好好写写博客,鉴于现在好多人带着不解出的考场,我先把答案放上去,可以先参考一下。
解题的过程
1、读题想算法策略,手动实现题目示例;
2、算法是否可行,时间复杂度度多少?会不会溢出爆栈?这个步骤是必要的,大多数人可能没有进行这一步,这个将直接导致你样例超时,只能拿部分分数,要想拿全分,基本就是另起炉灶,你想你的时间成本有多高,所以一定要计算一下算法时间复杂度;我九月份第一道题就是因为考试没考虑算法时间复杂度
3、思维严谨性 尽一切努力想可能出现的特殊情况,边界情况,这个可能错的多的,经验就多了。这是大多数人花时间最多最懊恼的地方,所有我觉得有时间的话,可以写写博客,总结总结;
4、数据结构使用 在写代码之前,思考需要用到什么,vector<> 还是 数组 ?离散存储还是顺序存储;
5、代码实现,程序员的自我修养,如果你上面的过程都做到了,代码能力好的真的是非常迅速就能完成,一道题也就50行左右的代码量,最多100行。如果给出算法图或者UML图让你写代码你还磨磨唧唧,那我只能说你的代码素养真的需要大量练习(说的这个人就是我,我太菜了)。
7-1 Good in C (20分)
When your interviewer asks you to write “Hello World” using C, can you do as the following figure shows?

Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first part gives the 26 capital English letters A-Z, each in a 7×5 matrix of C’s and .'s. Then a sentence is given in a line, ended by a return. The sentence is formed by several words (no more than 10 continuous capital English letters each), and the words are separated by any characters other than capital English letters.
It is guaranteed that there is at least one word given.
Output Specification:
For each word, print the matrix form of each of its letters in a line, and the letters must be separated by exactly one column of space. There must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the word.
Between two adjacent words, there must be a single empty line to separate them. There must be no extra line at the beginning or the end of the output.
Sample Input:
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
.CCC.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
CCCCC
CCCCC
C....
C....
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
CCCC.
C...C
C....
C.CCC
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
C...C
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
CCCCC
....C
....C
....C
....C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C..C.
C.C..
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
C....
CCCCC
C...C
C...C
CC.CC
C.C.C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
CC..C
C.C.C
C..CC
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
C...C
CCCC.
C....
C....
C....
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
C..CC
.CCC.
CCCC.
C...C
CCCC.
CC...
C.C..
C..C.
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C....
.CCC.
....C
C...C
.CCC.
CCCCC
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.CCC.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
C...C
C...C
C...C
C.C.C
CC.CC
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
.C.C.
C...C
C...C
C...C
C...C
.C.C.
..C..
..C..
..C..
..C..
CCCCC
....C
...C.
..C..
.C...
C....
CCCCC
HELLO~WORLD!
Sample Output:
C...C CCCCC C.... C.... .CCC.
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
CCCCC CCCC. C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C C.... C.... C.... C...C
C...C CCCCC CCCCC CCCCC .CCC.
C...C .CCC. CCCC. C.... CCCC.
C...C C...C C...C C.... C...C
C...C C...C CCCC. C.... C...C
C.C.C C...C CC... C.... C...C
CC.CC C...C C.C.. C.... C...C
C...C C...C C..C. C.... C...C
C...C .CCC. C...C CCCCC CCCC.
题目分析
字符串分割问题,最后一行输入一个句子setence,除了大写字母外,所有的字符都可以是分割符,需要使用getline(cin,str)读取一行,直接cin是不可以的。
字符串处理代码
string setence,buf="";
getline(cin,setence); //需要使用getline,而不是cin,注意空格分隔符
vector<string> vstr;
int len = setence.length();
for(i=0;i<len;i++) //遍历这一行句子
{
if( setence[i]>='A' && setence[i]<='Z')
{
buf += setence[i];
}
else{
if(buf!="")
vstr.push_back(buf);
buf = "";
}
}
if(buf!="") //最后一个不要漏,如果是回车作结束符号
vstr.push_back(buf);
完整代码如下
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
string letter[26][7];
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<26;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<7;j++)
cin>>letter[i][j];
}
getchar();
string setence,buf="";
getline(cin,setence); //需要使用getline,而不是cin,注意空格分隔符
vector<string> vstr;
int len = setence.length();
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if( setence[i]>='A' && setence[i]<='Z')
{
buf += setence[i];
}
else{
if(buf!="")
vstr.push_back(buf);
buf = "";
}
}
if(buf!="") //最后一个不要漏,如果是回车作结束符号
vstr.push_back(buf);
//下面开始输出
int index;
for(k=0;k<vstr.size();k++) //逐个单词输出
{
buf = vstr[k]; //当前单词
len = buf.length();
for(j=0;j<7;j++)
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
index = buf[i]-'A'; // 当前单词的第i个字母
cout<<letter[index][j]; //打印第j行
if(i==len-1)
printf("\n");
else
printf(" ");
}
if(k!=vstr.size()-1) //隔一行
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
7-2 Block Reversing (25分)
Given a singly linked list L. Let us consider every K nodes as a block (if there are less than K nodes at the end of the list, the rest of the nodes are still considered as a block). Your job is to reverse all the blocks in L. For example, given L as 1→2→3→4→5→6→7→8 and K as 3, your output must be 7→8→4→5→6→1→2→3.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains the address of the first node, a positive N (≤10^5) which is the total number of nodes, and a positive K (≤N) which is the size of a block. The address of a node is a 5-digit nonnegative integer, and NULL is represented by −1.
Then N lines follow, each describes a node in the format:
Address Data Next
where Address is the position of the node, Data is an integer, and Next is the position of the next node.
Output Specification:
For each case, output the resulting ordered linked list. Each node occupies a line, and is printed in the same format as in the input.
Sample Input:
00100 8 3
71120 7 88666
00000 4 99999
00100 1 12309
68237 6 71120
33218 3 00000
99999 5 68237
88666 8 -1
12309 2 33218
Sample Output:
71120 7 88666
88666 8 00000
00000 4 99999
99999 5 68237
68237 6 00100
00100 1 12309
12309 2 33218
33218 3 -1
这套题在9月份秋季考试似曾相识,就是对node一遍一遍处理,连起来。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100005;
struct node{
int adr;
int data;
int next;
};
node arr[maxn]; //离散表示
vector<node> v;
vector<node> nv;
int start,N,K;
int main()
{
int i,j;
int adrr;
scanf("%d %d %d",&start,&N,&K);
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&adrr);
arr[adrr].adr = adrr;
scanf("%d %d",&arr[adrr].data,&arr[adrr].next);
}
if(start==-1)
return 0;
adrr = start;
while(adrr!=-1)
{
v.push_back(arr[adrr]);
adrr = arr[adrr].next;
}
int len = v.size();
i = len % K; // i = 2 = 8 % 3
i = len - i; // i = 6
while(i>=0)
{
for(j=i;j<i+K && j<len;j++)
nv.push_back(v[j]);
i-=K;
}
// 下面开始输出
for(i=0;i<len-1;i++) //枚举到倒数第二个,最后一个特殊处理
{
printf("%05d %d %05d\n",nv[i].adr,nv[i].data,nv[i+1].adr);
}
printf("%05d %d -1\n",nv[len-1].adr,nv[len-1].data);
return 0;
}
7-3 Summit (25分)
A summit (峰会) is a meeting of heads of state or government. Arranging the rest areas for the summit is not a simple job. The ideal arrangement of one area is to invite those heads so that everyone is a direct friend of everyone.
Now given a set of tentative arrangements, your job is to tell the organizers whether or not each area is all set.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives two positive integers N (≤ 200), the number of heads in the summit, and M, the number of friendship relations. Then M lines follow, each gives a pair of indices of the heads who are friends to each other. The heads are indexed from 1 to N.
Then there is another positive integer K (≤ 100), and K lines of tentative arrangement of rest areas follow, each first gives a positive number L (≤ N), then followed by a sequence of L distinct indices of the heads. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each of the K areas, print in a line your advice in the following format:
if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, and no friend is missing (that is, no one else is a direct friend of everyone in this area), print Area X is OK…
if in this area everyone is a direct friend of everyone, yet there are some other heads who may also be invited without breaking the ideal arrangement, print Area X may invite more people, such as H. where H is the smallest index of the head who may be invited.
if in this area the arrangement is not an ideal one, then print Area X needs help. so the host can provide some special service to help the heads get to know each other.
Here X is the index of an area, starting from 1 to K.
Sample Input:
8 10
5 6
7 8
6 4
3 6
4 5
2 3
8 2
2 7
5 3
3 4
6
4 5 4 3 6
3 2 8 7
2 2 3
1 1
2 4 6
3 3 2 1
Sample Output:
Area 1 is OK.
Area 2 is OK.
Area 3 is OK.
Area 4 is OK.
Area 5 may invite more people, such as 3.
Area 6 needs help.
感觉这一道题就是遍历,把脑子里想到的方法实现了就行了,当然要估计一下时间复杂度,你自己想的少,机器就要计算的多,它得能计算出来才行,这道题没什么坑点,直接代码实现,时间复杂度也就是O(n2),机器可以接受的。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 205;
int N; // 200
int M;
int K;
bool mates[maxn][maxn]={false};
bool visit[maxn]={false};
vector<int> v;
int flag=0;
void dfs(int curr,int right) // 每个领导人只需要与自己之后的比较,n + n-1 + n-2 + ... 1
//时间复杂度为O(n^2),可行性OK,
{
if(curr>right)
return;
int i;
int a,b;
a = v[curr];
for(i=curr+1;i<=right;i++)
{
b = v[i];
if( !mates[a][b] )
{
flag = -1;
return;
}
}
dfs(curr+1,right);
}
int main()
{
cin>>N>>M;
int i,j,k;
int a,b;
for(i=0;i<M;i++) //输入M个友谊关系
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
mates[a][b]=true;
mates[b][a]=true;
}
cin>>K; //输入K个房间
int L;
for(j=1;j<=K;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&L);
v.clear(); //初始化
flag = 0;
fill(visit,visit+maxn,false);
for(i=0;i<L;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
visit[a]=true; // 表示该区域存在领导人a
v.push_back(a);
}
dfs(0,L-1);
if(flag==-1)
{
printf("Area %d needs help.\n",j);
}
else{ //接下来需要判断是否有新人需要加入
for(k=1;k<=N;k++) //遍历N个领导人
{
if( !visit[k] )
{
for(i=0;i<L;i++)
{
a = v[i];
if( !mates[a][k] ) //领导人k不是其中一个领导人a的朋友
break;
}
if(i==L) //领导人k是该区域内所有人的朋友
{
flag = k;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag==0)
printf("Area %d is OK.\n",j);
else
printf("Area %d may invite more people, such as %d.\n",j,flag);
}
}
return 0;
}
7-4 Cartesian Tree (30分)
A Cartesian tree is a binary tree constructed from a sequence of distinct numbers. The tree is heap-ordered, and an inorder traversal returns the original sequence. For example, given the sequence { 8, 15, 3, 4, 1, 5, 12, 10, 18, 6 }, the min-heap Cartesian tree is shown by the figure.
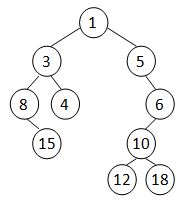
Your job is to output the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. Each case starts from giving a positive integer N (≤30), and then N distinct numbers in the next line, separated by a space. All the numbers are in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print in a line the level-order traversal sequence of the min-heap Cartesian tree. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
10
8 15 3 4 1 5 12 10 18 6
Sample Output:
1 3 5 8 4 6 15 10 12 18
建立树,遍历树。
层次遍历树不知道已经写多少遍了?那几个遍历出现频率都不低。
此题关键在于如何建立二叉树。
因为是堆,所有最小的树的层次越高。
难度不大,手动把输入示例实现一遍,就知道了,很简单的。
左子树 当前节点(当前顺序表中最小) 右子树
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 35;
int N;
int arr[maxn];
struct node{
int data;
node *lchild,*rchild;
};
void createTree(node* &curr,int left,int right)
{
if(left>right)
return;
curr = new node;
curr->lchild = NULL;
curr->rchild = NULL;
int index,minn=0x7fffffff;
int i;
for(i=left;i<=right;i++)
{
if(arr[i]<minn)
{
index = i;
minn = arr[i];
}
}
curr->data = minn;
createTree(curr->lchild,left,index-1);
createTree(curr->rchild,index+1,right);
}
void tra(node* root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return;
queue<node*> que;
que.push(root);
node *curr = NULL;
bool flag = false;
while( !que.empty() )
{
curr = que.front();
que.pop();
if(!flag)
{
printf("%d",curr->data);
flag =true;
}
else
printf(" %d",curr->data);
if( curr->lchild != NULL )
que.push(curr->lchild);
if( curr->rchild != NULL )
que.push(curr->rchild);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
cin>>N;
int i;
for(i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
node *root=NULL;
createTree(root,1,N);
tra(root);
return 0;
}
