很多程序都有记录日志的需求,并且日志中包含的信息即有正常的程序访问日志,还可能有错误、警告等信息输出,python的logging模块提供了标准的日志接口,你可以通过它存储各种格式的日志,logging的日志可以分为 debug()、info()、warning()、 error() 、critical() 5个级别。
import logging
logging.debug("debug message")
logging.info("Input user/passwd")
logging.error("Error")
logging.warning("User already inputed three time username/password!")
logging.critical("The username was locking!")

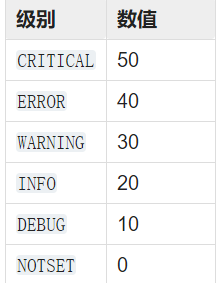
日志级别
把日志写到文件
其中下面这句中的level=loggin.DEBUG意思是,把日志纪录级别设置为DEBUG,也就是说,只有比日志是DEBUG或比DEBUG级别更高的日志才会被记录到文件里
import logging
logging.basicConfig(filename="tesxt.log",level=logging.DEBUG)
logging.debug("debug message")
logging.info("Input user/passwd")
logging.error("Error")
logging.warning("User already inputed three time username/password!")
logging.critical("The username was locking!")
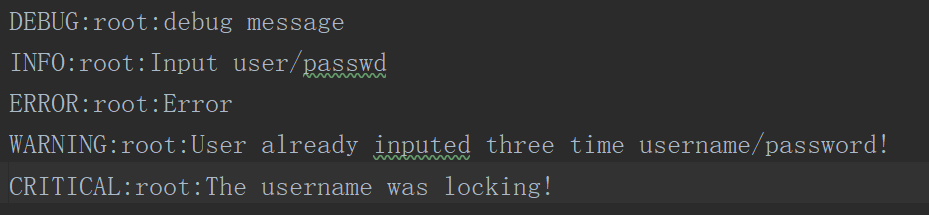
输出结果:
给日志增加时间
import logging
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s %(message)s', datefmt='%m/%d/%Y %I:%M:%S %p')
logging.debug("debug message")
logging.info("Input user/passwd")
logging.error("Error")
logging.warning("User already inputed three time username/password!")
logging.critical("The username was locking!")

日志格式
| %(name)s |
Logger的名字 |
| %(levelno)s |
数字形式的日志级别 |
| %(levelname)s |
文本形式的日志级别 |
| %(pathname)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块的完整路径名,可能没有 |
| %(filename)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块的文件名 |
| %(module)s |
调用日志输出函数的模块名 |
| %(funcName)s |
调用日志输出函数的函数名 |
| %(lineno)d |
调用日志输出函数的语句所在的代码行 |
| %(created)f |
当前时间,用UNIX标准的表示时间的浮 点数表示 |
| %(relativeCreated)d |
输出日志信息时的,自Logger创建以 来的毫秒数 |
| %(asctime)s |
字符串形式的当前时间。默认格式是 “2003-07-08 16:49:45,896”。逗号后面的是毫秒 |
| %(thread)d |
线程ID。可能没有 |
| %(threadName)s |
线程名。可能没有 |
| %(process)d |
进程ID。可能没有 |
| %(message)s |
用户输出的消息 |
把日志打印在屏幕上
import logging
#create logger
logger = logging.getLogger('TEST-LOG')
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create console handler and set level to debug
ch = logging.StreamHandler()
ch.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# create file handler and set level to warning
fh = logging.FileHandler("access.log")
fh.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
# create formatter
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
# add formatter to ch and fh
ch.setFormatter(formatter)
fh.setFormatter(formatter)
# add ch and fh to logger
logger.addHandler(ch)
logger.addHandler(fh)
# 'application' code
logger.debug('debug message')
logger.info('info message')
logger.warn('warn message')
logger.error('error message')
logger.critical('critical message')