前言
记录学习历程,使用IDEA编程
SpringMVC常用注解包括@Controller、@RequestMapping、@PathVariable、@RequestParam、@SessionAttributes、@ModelAttribute、@RequestBody等
基于注解的处理器
在SpringMVC中,处理器是基于@Controller和@RequestMapping这两个注解,@Controller用于声明一个控制器类,@RequestMapping用于声明对应请求的映射关系
例:一个HelloWorld
(1)在IDEA创建SpringMVC项目,修改web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!--配置dispatcherServlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
让Web容器使用SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet,通过设置url-pattern为“/”让所有的url请求都映射到这个前端控制器
(2)在src下创建SpringMVC配置文件springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!--配置自动扫描的包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.springmvc"/>
<!--配置视图解析器,将控制器方法返回的逻辑视图解析为物理视图-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!--设置JSP文件的目录位置-->
<!--配置前缀属性路径-->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"/>
<!--配置后缀属性路径-->
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
context:component-scan元素设置自动扫描包内的被注释的类,然后注册到Spring IoC容器中
配置视图解析器
(3)src下创建包springmvc.controller,创建类HelloController
package com.springmvc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(){
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
return "success";
}
}
通过@Controller注解将HelloController声明为一个处理器类,通过@RequestMapping注解将sayHello方法的请求映射为/hello,这种映射是根据请求的URL进行映射
(4)编写视图
index.jsp
<body>
<a href="/hello">Hello SpringMVC</a>
</body>
在WEB-INF下创建视图层包views
创建success.jsp
<body>
欢迎光临
</body>
(5)启动TomCat
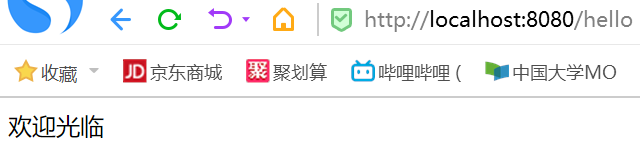
点击超链接后跳转到新界面
(6)@RequestMapping也可以修饰类
在HelloController上注释@RequestMapping
package com.springmvc.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@RequestMapping("/springmvc")
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello(){
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
return "success";
}
}
index.jsp超链接地址修改:
<a href="/springmvc/hello">Hello SpringMVC</a>
也运行成功
