最近在做全景拼接项目,有有六张来自于六目摄像头的图片,分别来自不同方向上的图片,摄像头示意图如下:
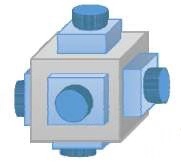
各方向上图片的位置示意图如下:

假设相对应位置的图片为拼接起来后(此处我们用代码进行了拼接,而且需要这样结构拼接起来作为输入):

球面变换和拼接的代码如下:
from PIL import Image
import math
import numpy as np
import cv2
def spherical_coordinates(i, j, w, h):
""" Returns spherical coordinates of the pixel from the output image. """
theta = 2*float(i)/float(w)-1
phi = 2*float(j)/float(h)-1
# phi = lat, theta = long
return phi*(math.pi/2), theta*math.pi
def vector_coordinates(phi, theta):
""" Returns 3D vector which points to the pixel location inside a sphere. """
return (math.cos(phi) * math.cos(theta), # X
math.sin(phi), # Y
math.cos(phi) * math.sin(theta)) # Z
# Assign identifiers to the faces of the cube
FACE_Z_POS = 1 # Left
FACE_Z_NEG = 2 # Right
FACE_Y_POS = 3 # Top
FACE_Y_NEG = 4 # Bottom
FACE_X_NEG = 5 # Front
FACE_X_POS = 6 # Back
def get_face(x, y, z):
""" Uses 3D vector to find which cube face the pixel lies on. """
largest_magnitude = max(abs(x), abs(y), abs(z))
if largest_magnitude - abs(x) < 0.00001:
return FACE_X_POS if x < 0 else FACE_X_NEG
elif largest_magnitude - abs(y) < 0.00001:
return FACE_Y_POS if y < 0 else FACE_Y_NEG
elif largest_magnitude - abs(z) < 0.00001:
return FACE_Z_POS if z < 0 else FACE_Z_NEG
def raw_face_coordinates(face, x, y, z):
"""
Return coordinates with necessary sign (- or +) depending on which face they lie on.
From Open-GL specification (chapter 3.8.10) https://www.opengl.org/registry/doc/glspec41.core.20100725.pdf
"""
if face == FACE_X_NEG:
xc = z
yc = y
ma = x
return xc, yc, ma
elif face == FACE_X_POS:
xc = -z
yc = y
ma = x
return xc, yc, ma
elif face == FACE_Y_NEG:
xc = z
yc = -x
ma = y
return xc, yc, ma
elif face == FACE_Y_POS:
xc = z
yc = x
ma = y
return xc, yc, ma
elif face == FACE_Z_POS:
xc = x
yc = y
ma = z
return xc, yc, ma
elif face == FACE_Z_NEG:
xc = -x
yc = y
ma = z
return xc, yc, ma
def raw_coordinates(xc, yc, ma):
""" Return 2D coordinates on the specified face relative to the bottom-left corner of the face. Also from Open-GL spec."""
return (float(xc)/abs(float(ma)) + 1) / 2, (float(yc)/abs(float(ma)) + 1) / 2
def face_origin_coordinates(face, n):
""" Return bottom-left coordinate of specified face in the input image. """
if face == FACE_X_NEG:
return n, n
elif face == FACE_X_POS:
return 3*n, n
elif face == FACE_Z_NEG:
return 2*n, n
elif face == FACE_Z_POS:
return 0, n
elif face == FACE_Y_POS:
return n, 0
elif face == FACE_Y_NEG:
return n, 2*n
def normalized_coordinates(face, x, y, n):
""" Return pixel coordinates in the input image where the specified pixel lies. """
face_coords = face_origin_coordinates(face, n)
normalized_x = math.floor(x*n)
normalized_y = math.floor(y*n)
# Stop out of bound behaviour
if normalized_x < 0:
normalized_x = 0
elif normalized_x >= n:
normalized_x = n-1
if normalized_y < 0:
normalized_x = 0
elif normalized_y >= n:
normalized_y = n-1
return face_coords[0] + normalized_x, face_coords[1] + normalized_y
def find_corresponding_pixel(i, j, w, h, n):
"""
:param i: X coordinate of output image pixel
:param j: Y coordinate of output image pixel
:param w: Width of output image
:param h: Height of output image
:param n: Height/Width of each square face
:return: Pixel coordinates for the input image that a specified pixel in the output image maps to.
"""
spherical = spherical_coordinates(i, j, w, h)
vector_coords = vector_coordinates(spherical[0], spherical[1])
face = get_face(vector_coords[0], vector_coords[1], vector_coords[2])
raw_face_coords = raw_face_coordinates(face, vector_coords[0], vector_coords[1], vector_coords[2])
cube_coords = raw_coordinates(raw_face_coords[0], raw_face_coords[1], raw_face_coords[2])
return normalized_coordinates(face, cube_coords[0], cube_coords[1], n)
def get_six_pics_stitching(val_resize):
size_t = val_resize
# generate a (512,512) black image
target = np.zeros((size_t, size_t), dtype=np.uint8)
ret = cv2.cvtColor(target, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
imgs_index = ["top", "left", "front", "right", "back", "down"]
imgs_set = []
# read all the images from target file
for i in range(6):
img = cv2.imread("./pics/{}.jpg".format(imgs_index[i]))
img_res = cv2.resize(img, (size_t, size_t))
imgs_set.append(img_res)
# first row stitching
ret_pano1 = np.concatenate((ret, imgs_set[0]), axis=1)
for i in range(2):
ret_pano1 = np.concatenate((ret_pano1, ret), axis=1)
# Second row stitching
imgs_mid_four = imgs_set[1:5]
ret_pano2 = imgs_mid_four[0]
for i in range(3):
ret_pano2 = np.concatenate((ret_pano2, imgs_mid_four[i + 1]), axis=1)
# Third row stitching
ret_pano3 = np.concatenate((ret, imgs_set[5]), axis=1)
for i in range(2):
ret_pano3 = np.concatenate((ret_pano3, ret), axis=1)
# whole image sitiching
ret_pano = np.concatenate((ret_pano1, ret_pano2), axis=0)
ret_pano = np.concatenate((ret_pano, ret_pano3), axis=0)
cv2.imwrite('six_pics_stitching.jpg',ret_pano)
def convert_img(infile, outfile):
inimg = Image.open(infile)
wo, ho = inimg.size
# Calculate height and width of output image, and size of each square face
h = int(wo/3)
w = 2*h
n = int(ho/3)
# Create new image with width w, and height h
outimg = Image.new('RGB', (w, h))
# For each pixel in output image find colour value from input image
for ycoord in range(0, h):
for xcoord in range(0, w):
corrx, corry = find_corresponding_pixel(xcoord, ycoord, w, h, n)
outimg.putpixel((xcoord, ycoord), inimg.getpixel((corrx, corry)))
# Print progress percentage
print(str(round((float(ycoord)/float(h))*100, 2)) + '%')
outimg.save(outfile, 'PNG')
if __name__ == '__main__':
val_resize = 512
# you need put your images in the file"./pics/" or you can define by yourself.
get_six_pics_stitching(val_resize)
convert_img('six_pics_stitching.jpg', 'output.jpg')
# out_img = cv2.imread('output.jpg')
# cv2.imshow('out_img', out_img)
# cv2.waitKey()
拼接后的效果如图:

