这里将会写入文字:
1.java字符串:
java字符串的编码时utf-16be,不管是英文还是中文,utf-16be中,英文占两个字节,中文占两个字节,每个字符串都占两个字节。
2.DataOutString写入字符串的方法:
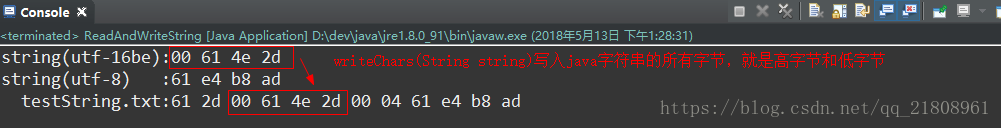
(1)writeBytes(String): 依次写入java字符串中的每一个字符,并且只写入字符的低8位,高字节被抛弃。
(2)writeChars(String): 依次写入java字符串中的每一个字符,字符的2个字节全部写入。
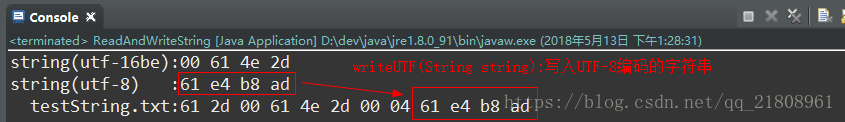
(3)wirteUTF(String) :依次写入utf-8编码的字符,utf-8编码中英文占一个字节,中文占三个字节
(4)先把字符串解析成字符数组:byte[] buf=string.getBytes(),然后使用write(byte[] buf)再写入字节数组
代码:
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ReadAndWriteString
{
public static void pintfHex(String filePath)
{
FileInputStream in;
int b;
byte[] buf=new byte[20];
try
{
in = new FileInputStream(filePath);
while((b=in.read(buf))!=-1)
{
for (int i=0;i<b;i++)
{
if((buf[i]&0xff)<=0xf)
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(buf[i]&0xff)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
} catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void printfHex(byte[] buf)
{
for (byte b : buf)
{
if((b&0xff)<=0xf)
System.out.print("0");
System.out.print(Integer.toHexString(b&0xff)+" ");
}
// System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String packagePath=".\\src\\com\\lan\\dataoutputstream\\";
FileOutputStream in=new FileOutputStream(packagePath+"testString.txt");
DataOutputStream dif=new DataOutputStream(in);
String string="a中";
byte[] bufUtf_16be=string.getBytes("utf-16be");
byte[] bufUtf_8=string.getBytes("utf-8");
// System.out.println();
System.out.print("string(utf-16be):");
printfHex(bufUtf_16be);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("string(utf-8) :");
printfHex(bufUtf_8);
System.out.println();
/*
writeBytes(String) 依次写入java字符串(utf-16be)中的每一个字符,并且只写入字符的低8位,高字节被抛弃。
*/
dif.writeBytes(string);
/*
java字符串(utf-16be)每个字符都占2个字节
riteChars(String) 依次写入java字符串中的每一个字符,字符的2个字节全部写入。
*/
dif.writeChars(string);
dif.writeUTF(string);
dif.close();
System.out.print(" testString.txt:");
pintfHex(packagePath+"testString.txt");
}
}
运行结果:
(1)分析1:writeBytes(String string):
(2)分析2:writeChars(String string):
(3)分析3:writeUTF(String string):
在上面代码的基础上加上write(byte[] buf)方法写入的字符串。:
代码:加入wirte(byte[] buf)方法写字符串之后的main函数:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String packagePath=".\\src\\com\\lan\\dataoutputstream\\";
FileOutputStream in=new FileOutputStream(packagePath+"testString.txt");
DataOutputStream dif=new DataOutputStream(in);
String string="a中";
byte[] bufgbk=string.getBytes();
byte[] bufUtf_16be=string.getBytes("utf-16be");
byte[] bufUtf_8=string.getBytes("utf-8");
// System.out.println();
System.out.print("string(utf-16be):");
printfHex(bufUtf_16be);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("string(utf-8) :");
printfHex(bufUtf_8);
System.out.println();
System.out.print("string(gbk) :");
printfHex(bufgbk);
System.out.println();
dif.writeBytes(string);
dif.writeChars(string);
dif.writeUTF(string);
dif.write(string.getBytes());
dif.write(bufgbk);
dif.close();
System.out.print(" testString.txt:");
pintfHex(packagePath+"testString.txt");
}
运行结果:
在gbk编码中 英文占一个字节,中文占两个字节。
这里顺便来说一下write(int i)和writeInt(int i)的区别:我就不自己写了
出处:Java中write(int)和writeInt(int)的区别,writeBytes(String) 和writeChars(String) 区别:
引用一下前辈的博客:
相同点
write(int)和writeInt(int) 都是接收int参数
write(int)
write(int) 继承自父类OutputStream,接收的虽然是int, 但是它只向输出流里写一个字节。我们知道,在java中,一个int 数子是4个字节组成,write(int) 只写入int的最低位的一个字节,其它3个字节被抛弃。
例如: write(-100),
int -100 的32位二进制码为: 11111111_11111111_11111111_10011100
那么, write(-100),实际上只写了最低的8位到输出流:10011100。
writeInt(int)
writeInt(int),是把整个32位都写入输出流。
那么, write(-100),写了32位到输出流:11111111_11111111_11111111_10011100。
使用DataOutPutStream的writeUTF()和DataInputStream的readUTF()来读写字符串
这里提一下基本类型和字符串之间的相互转换:
1.基本类型转换成String:
(1) 基本类型变量+“”;//基本类型加空字符串即可
(2)String.valueOf(基本类型变量);//
这两个都可以,相比加空字符串的方法,String.valueOf()效率更高。
2.String类型转成基本类型
(1) 调用包装类的parseXXX()方法,
(2) 调用包装类的valueOf()方法,先生成包装类对象,然后再赋值给基本类型(自动拆箱)。
还是直接使用包装类的parseXXX()方法比较好。
注意:char的包装类Character没有parseChar(String str);方法,String转换成char的时候可以使用String.charAt()方法。
FilePath类是我之前写的工具类,可以获取工程下的各种路劲字符串:利用反射动态获取当前工程下的文件路径_解决中文路径乱码问题
通过readUTF()和writeUTF()读写代码:
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import com.lan.filepath.FilePath;
public class ReadAndWriteString2
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
String packagePath=FilePath.getSrcPackagePath(ReadAndWriteString2.class);
System.out.println(packagePath);
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream(packagePath+"TestStringWR.txt");
DataOutputStream dof=new DataOutputStream(out);
byte b=20;//-128~127
short s=80;//
int i=40;
long l=90l;
float f=90.0f;
double d=100.78;
boolean flag=false;
char ch='中';
String string="字符串1";
System.out.println(b);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(l);
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println(ch);
System.out.println(string);
//把基本数据类型转换成String后写入文件,
//String.valueOf()可以将基本类型转换成字符串,
//也可以 b+"";加上一个空字符串就可
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(b));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(s));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(i));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(l));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(f));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(d));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(flag));
dof.writeUTF(String.valueOf(ch));
dof.writeUTF(string);
dof.close();
out.close();
System.out.println("------------------------------");
FileInputStream in=new FileInputStream(packagePath+"TestStringWR.txt");
DataInputStream dif=new DataInputStream(in);
byte btemp;//-128~127
short stemp;//
int itemp;
long ltemp;
float ftemp;
double dtemp;
boolean flagtemp;
char chtemp;
String stringtemp;
//使用包装类的paresXXX()方法可以把String转换成基本类型
btemp=Byte.parseByte(dif.readUTF());
stemp=Short.parseShort(dif.readUTF());
itemp=Integer.parseInt(dif.readUTF());
ltemp=Long.parseLong(dif.readUTF());
ftemp=Float.parseFloat(dif.readUTF());
dtemp=Double.parseDouble(dif.readUTF());
flagtemp=Boolean.parseBoolean(dif.readUTF());
//注意了char的包装类Character没有parseChar()方法
chtemp=dif.readUTF().charAt(0);
stringtemp=dif.readUTF();
System.out.println(btemp);
System.out.println(stemp);
System.out.println(itemp);
System.out.println(ltemp);
System.out.println(ftemp);
System.out.println(dtemp);
System.out.println(flagtemp);
System.out.println(chtemp);
System.out.println(stringtemp);
dif.close();
in.close();
}
}
运行结果:
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\学习8\java\笔记\javaIO\coreJava\src\com\lan\dataoutputstream\ 20 80 40 90 90.0 100.78 false 中 字符串1 ------------------------------ 20 80 40 90 90.0 100.78 false 中 字符串1