Logistic Regression
Logistic Regression是一种被广泛使用的分类算法,通过训练数据中的正负样本,学习样本特征到样本标签之间的假设函数。
通常用于将数据映射到不同类别的函数成为阈值函数,常用的阈值函数为Sigmoid函数,形式为:
Sigmoid函数的图像:
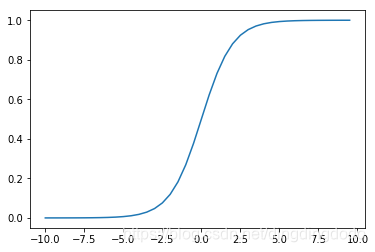
从Sigmoid的图像可以看出函数的值域为(0,1),在0附近变化比较明显
Sigmoid函数的python代码:
def sig(x):
'''Sigmoid函数
input: x(mat):feature * w
output: sigmoid(x)(mat):Sigmoid值
'''
return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
因此对于输入向量X,其属于正例和反例的概率为:
对于Logistic Regression算法来说,如何定义W和b使得算法最优?(什么是最优)
为了求解最优的权重矩阵W和偏置向量b,需要定义损失函数
对于上述的Logistic Regression算法,属于类别 y 的概率是
其中 σ 表示的是Sigmoid函数。
在此用极大似然法进行估计。假设训练数据集有m个训练样本{{X1,Y1},{X2,Y2},……{Xn,Yn}},则其似然函数为:
其中的假设函数
对于似然函数的极大值的求解,通常使用Log似然函数,在Logistic Regression算法中,通常是将负的Log似然函数作为其损失函数,则只需要计算其极小值就行
可以通过梯度下降法求得损失函数的最小值以及其对应的参数值。
利用梯度下降法训练Logistic Regression模型:
上述问题的梯度:
取w0=b,且将偏置项的变量x0设置位1,则上述可合并为:
根据梯度下降法,得到的更新公式:
可以用代码表示出具体的梯度下降法过程:
def lr_train_bgd(feature, label, maxCycle, alpha):
'''利用梯度下降法训练LR模型
input: feature(mat)特征
label(mat)标签
maxCycle(int)最大迭代次数
alpha(float)学习率
output: w(mat):权重
'''
n = np.shape(feature)[1] # 特征个数
w = np.mat(np.ones((n, 1))) # 初始化权重
i = 0
while i <= maxCycle: # 在最大迭代次数的范围内
i += 1 # 当前的迭代次数
h = sig(feature * w) # 计算Sigmoid值
err = label - h
if i % 100 == 0:
print ("\t---------iter=" + str(i) + \
" , train error rate= " + str(error_rate(h, label)))
w = w + alpha * feature.T * err # 权重修正
return w
计算损失值的函数的python代码:

def error_rate(h, label):
'''计算当前的损失函数值
input: h(mat):预测值
label(mat):实际值
output: err/m(float):错误率
'''
m = np.shape(h)[0]
sum_err = 0.0
for i in range(m):
if h[i, 0] > 0 and (1 - h[i, 0]) > 0:
sum_err -= (label[i,0] * np.log(h[i,0]) + \
(1-label[i,0]) * np.log(1-h[i,0]))
else:
sum_err -= 0
return sum_err / m
基于上述操作,可以完成Logistic Regression算法的实践:
- 利用训练样本训练模型
- 利用训练好的模型对新样本进行预测
训练模型的主函数:
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1、导入训练数据
print ("---------- 1.load data ------------")
feature, label = load_data("data.txt")
# 2、训练LR模型
print ("---------- 2.training ------------")
w = lr_train_bgd(feature, label, 1000, 0.01)
# 3、保存最终的模型
print ("---------- 3.save model ------------")
save_model("weights", w)
主要步骤为:
- 导入训练数据
- 利用梯度下降法对训练数据进行训练
- 将权重输出到文件weight中
导入数据的代码:
def load_data(file_name):
'''导入训练数据
input: file_name(string)训练数据的位置
output: feature_data(mat)特征
label_data(mat)标签
'''
f = open(file_name) # 打开文件
feature_data = []
label_data = []
for line in f.readlines():
feature_tmp = []
lable_tmp = []
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
feature_tmp.append(1) # 偏置项
for i in range(len(lines) - 1):
feature_tmp.append(float(lines[i]))
lable_tmp.append(float(lines[-1]))
feature_data.append(feature_tmp)
label_data.append(lable_tmp)
f.close() # 关闭文件
return np.mat(feature_data), np.mat(label_data)
保存最终模型的代码:
def save_model(file_name, w):
'''保存最终的模型
input: file_name(string):模型保存的文件名
w(mat):LR模型的权重
'''
m = np.shape(w)[0]
f_w = open(file_name, "w")
w_array = []
for i in range(m):
w_array.append(str(w[i, 0]))
f_w.write("\t".join(w_array))
f_w.close()
运行可知具体的训练过程:
---------- 1.load data ------------
---------- 2.training ------------
---------iter=100 , train error rate= 0.0011343552118725237
---------iter=200 , train error rate= 0.0009477843077847493
---------iter=300 , train error rate= 0.0008150655965653218
---------iter=400 , train error rate= 0.0007156807636573261
---------iter=500 , train error rate= 0.000638391025133774
---------iter=600 , train error rate= 0.0005765152961049218
---------iter=700 , train error rate= 0.000525828329858299
---------iter=800 , train error rate= 0.0004835251428600975
---------iter=900 , train error rate= 0.0004476693385107426
---------iter=1000 , train error rate= 0.00041688036889435637
---------- 3.save model ------------
可以看到对于训练集的错误率一直在降低。
通过训练后得到的Logistic Regression的模型的权重为
1.3941777508748279 4.527177129107412 -4.793981623770905
对新数据进行预测:
- 包括导入模型
- 导入测试集
- 对数据集进行预测
- 保留结果
测试的代码如下:
# coding:UTF-8
import numpy as np
from lr_train import sig
def load_weight(w):
'''导入LR模型
input: w(string)权重所在的文件位置
output: np.mat(w)(mat)权重的矩阵
'''
f = open(w)
w = []
for line in f.readlines():
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
w_tmp = []
for x in lines:
w_tmp.append(float(x))
w.append(w_tmp)
f.close()
return np.mat(w)
def load_data(file_name, n):
'''导入测试数据
input: file_name(string)测试集的位置
n(int)特征的个数
output: np.mat(feature_data)(mat)测试集的特征
'''
f = open(file_name)
feature_data = []
for line in f.readlines():
feature_tmp = []
lines = line.strip().split("\t")
# print lines[2]
if len(lines) != n - 1:
continue
feature_tmp.append(1)
for x in lines:
# print x
feature_tmp.append(float(x))
feature_data.append(feature_tmp)
f.close()
return np.mat(feature_data)
def predict(data, w):
'''对测试数据进行预测
input: data(mat)测试数据的特征
w(mat)模型的参数
output: h(mat)最终的预测结果
'''
h = sig(data * w.T)#sig
m = np.shape(h)[0]
for i in range(m):
if h[i, 0] < 0.5:
h[i, 0] = 0.0
else:
h[i, 0] = 1.0
return h
def save_result(file_name, result):
'''保存最终的预测结果
input: file_name(string):预测结果保存的文件名
result(mat):预测的结果
'''
m = np.shape(result)[0]
#输出预测结果到文件
tmp = []
for i in range(m):
tmp.append(str(result[i, 0]))
f_result = open(file_name, "w")
f_result.write("\t".join(tmp))
f_result.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 1、导入LR模型
print ("---------- 1.load model ------------")
w = load_weight("weights")
n = np.shape(w)[1]
# 2、导入测试数据
print ("---------- 2.load data ------------")
testData = load_data("test_data", n)
# 3、对测试数据进行预测
print ("---------- 3.get prediction ------------")
h = predict(testData, w)#进行预测
# 4、保存最终的预测结果
print ("---------- 4.save prediction ------------")
save_result("result", h)
数据集和测试数据集:
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1i-0qomeuKqA4I2fcfEuutg
