17. 电话号码的字母组合
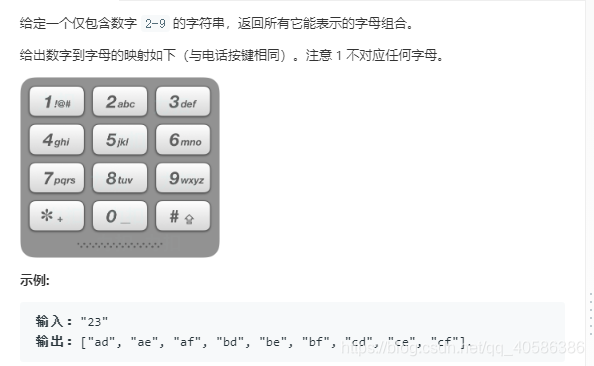
利用bfs搜索算法
BFS:

参考:https://blog.csdn.net/g11d111/article/details/76169861
则本问题代码:
class Solution {
map<char, string> m;
public:
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
// initialize
m['2'] = "abc";
m['3'] = "def";
m['4'] = "ghi";
m['5'] = "jkl";
m['6'] = "mno";
m['7'] = "pqrs";
m['8'] = "tuv";
m['9'] = "wxyz";
int cnt = 0; // Used to determine the number of pop
vector<string> ans;
queue<string> Q;
// BFS
// Enter the queue, then determine the length of the queue and determine the number of loops
// Pop the queue, then join the corresponding the letters, then join the queue
for (int i = 0; i < digits.size(); ++ i){
string ss;
ss.clear();
if (Q.empty()){
for (auto& e : m[digits[i]]){
string tt; tt.push_back(e);
Q.push(tt);
}
cnt = Q.size();
}else {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; ++ j){
ss = Q.front(); Q.pop();
for (auto& e : m[digits[i]]){
string tt = ss; tt.push_back(e);
Q.push(tt);
}
}
cnt = Q.size();
}
}
// from queue to vector<sring>
while (!Q.empty()){
string ss = Q.front(); Q.pop();
ans.push_back(ss);
}
return ans;
}
};
18.四数之和

代码:
利用双指针法,同时加入适当判断条件,尽量减少运行时间。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> fourSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
vector<vector<int>> result;
if(nums.size()<4)
return result;
size_t n_size = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
for(int i=0; i<n_size-3; i++){
// 不存在
if(target<=0 && nums[i]>0) break;
if(nums[i]+nums[i+1]+nums[i+2]+nums[i+3]>target) break;
// 此时条件不满足
if(nums[i]+nums[n_size-3]+nums[n_size-2]+nums[n_size-1]<target) continue;
// 重复项
if(i>0 && nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue;
for(int j=i+1; j<n_size-2; j++){
// 不存在
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[j+1]+nums[j+2]>target) break;
// 此时条件不满足
if(nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[n_size-2]+nums[n_size-1]<target) continue;
// 重复项
if(j>i+1 && nums[j]==nums[j-1]) continue;
int start=j+1, end=n_size-1;
while(start<end){
int sum = nums[i]+nums[j]+nums[start]+nums[end];
if(sum<target) start++;
else if(sum>target) end--;
else{
result.push_back({nums[i], nums[j], nums[start], nums[end]});
int last_start=start, last_end=end;
// 剔除重复项
while(start<end && nums[start] == nums[last_start]) start++;
while(start<end && nums[end] == nums[last_end]) end--;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
};
19.删除链表中的倒数第N个节点

代码:采用双指针法,让一个指针先走N步
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* removeNthFromEnd(ListNode* head, int n) {
ListNode* forehead = new ListNode(0);
forehead->next = head;
ListNode* r = forehead;
ListNode* l = forehead;
for(int i=0;i<n+1;i++){
r = r->next;
}
while(r){
r = r->next;
l = l->next;
}
ListNode* temp;
temp = l->next;
l->next = temp->next;
delete temp;
ListNode*temp1;
temp1 = forehead->next;
delete forehead;
return temp1;
}
};
20.有效的括号

代码:利用栈的先进后出思想进行实现;
class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
vector<char> st;
int le = s.length(),temp;
for(int i=0;i<le;i++){
if(s[i]=='('||s[i]=='['||s[i]=='{')
st.push_back(s[i]);
else{
if(st.size()==0)return false;
temp = st.back();
if(temp == '(' && s[i] == ')' || temp == '[' && s[i] == ']' || temp == '{' && s[i] == '}')
st.pop_back();
else return false;
}
}
return(st.size() == 0);
}
};
21.合并两个有序链表
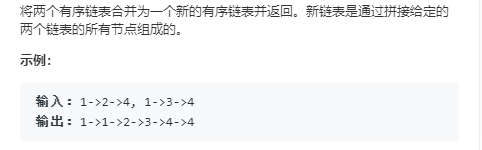
代码:
方法1:利用递归轻易实现
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
if(l1==NULL)return l2;
else if(l2==NULL)return l1;
else if(l1->val<l2->val){
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
return l1;
}
else{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
};
方法二:直接遍历即可
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {
ListNode *prehead = new ListNode(1);
ListNode*prev = prehead;
while(l1!=NULL&&l2!=NULL){
if(l1->val<l2->val){
prev->next = l1;
l1 = l1->next;
}
else{
prev->next = l2;
l2 = l2->next;
}
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = l1==NULL?l2:l1;
return prehead->next;
}
};
22.括号生成

代码:
1.利用递归
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
vector<string> res;
function(res,"",0,0,n);
return res;
}
void function(vector<string>&res,string str,int l ,int r, int n){
if(l>n||r>n||r>l)return;
if(l == n&& r==n){
res.push_back(str);
return;
}
function(res,str+'(',l+1,r,n);
function(res,str+ ')',l,r+1,n);
}
};
2.利用动态规划
n的括号情况为 (q情况)p情况 其中p+q=n-1 维护动态规划数组dp[n+1]即可
代码:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
if(n==0)return{""};
if(n==1)return{"()"};
vector<vector<string>> dp(n+1);
dp[0] = {""};
dp[1] = {"()"};
for(int i=2;i<n+1;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
for(string m:dp[j]){
for(string n :dp[i-1-j]){
string temp = "(" + m + ")" + n;
dp[i].push_back(temp);
}
}
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
23.合并k个有序链表

方法1:利用合并两个链表方法,但复杂度较高
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
int size = lists.size();
if(size == 0) return nullptr;
if(size == 1) return lists[0];
ListNode* res = lists[0];
for(int i=1;i<size;i++){
res = merge2list(res,lists[i]);
}
return res;
}
ListNode* merge2list(ListNode*m,ListNode*n){
ListNode* pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode*result = pre;
while(m&&n){
if(m->val<n->val){
pre->next = m;
m = m->next;
}
else{
pre->next = n;
n = n->next;
}
pre = pre->next;
}
pre->next = m==NULL?n:m;
return result->next;
}
};
方法2:将vector转换为queue,可加快运行速度
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists) {
int size = lists.size();
if(size == 0) return nullptr;
if(size == 1) return lists[0];
queue<ListNode*>waiting(deque<ListNode*>(lists.begin(),lists.end()));
while(waiting.size()>1){
ListNode*l1=waiting.front();
waiting.pop();
ListNode*l2 = waiting.front();
waiting.pop();
waiting.push(merge2list(l1,l2));
}
return waiting.front();
}
ListNode* merge2list(ListNode*m,ListNode*n){
ListNode* pre = new ListNode(0);
ListNode*result = pre;
while(m&&n){
if(m->val<n->val){
pre->next = m;
m = m->next;
}
else{
pre->next = n;
n = n->next;
}
pre = pre->next;
}
pre->next = m==NULL?n:m;
return result->next;
}
};
24.交换链表中两两节点

方法1:直接根据链表之间对应关系即可:
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
ListNode*pre = new ListNode(0);
pre->next = head;
ListNode*tem = pre;
ListNode*p;
while(tem->next!=NULL&&tem->next->next!=NULL){
p=tem->next;
tem->next = p->next;
p->next = p->next->next;
tem->next->next = p;
tem = p;
}
return pre->next;
}
};
方法2:利用递归,清楚递归三要素:终止条件,单元作用,以及返回值
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)return head;
ListNode* ne = head->next;
head->next = swapPairs(ne->next);
ne->next = head;
return ne;
}
};
25.K 个一组翻转链表

方法一:
k个一组,分组翻转
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode *dummy = new ListNode(-1), *pre = dummy, *cur = pre;
dummy->next = head;
int num = 0;
while (cur = cur->next) ++num;//链表长度
while (num >= k) {
cur = pre->next;
//依次交换节点元素
for (int i = 1; i < k; ++i) {
ListNode *t = cur->next;
cur->next = t->next;
t->next = pre->next;
pre->next = t;
}
pre = cur;
num -= k;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};
方法二:递归调用
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseKGroup(ListNode* head, int k) {
ListNode* cur =head;
int count = 0;
while(count!=k&&cur!=NULL){
cur = cur->next;
count++;
}
if(count ==k){
cur = reverseKGroup(cur,k);
while(count!=0){
count--;
ListNode* tep = head->next;
head->next = cur;
cur = head;
head = tep;
}
head = cur;
}
return head;
}
};
26.删除排序数组中的重复项
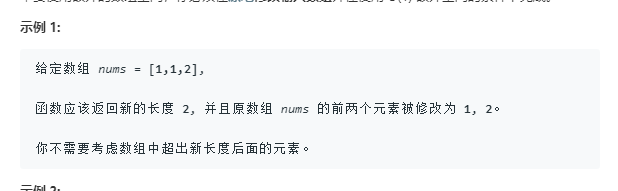
代码:利用双指针即可
class Solution {
public:
int removeDuplicates(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.size()<2)return nums.size();
int i=0,j=1;
while(j<nums.size()){
if(nums[i]==nums[j]){
j++;
}
else{
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
j++;
}
}
return i+1;
}
};
27.移除元素

代码:利用双指针法求解,设置两个指针变量即可
class Solution {
public:
int removeElement(vector<int>& nums, int val) {
int len = nums.size();
int i=0;
int j = 0;
int res = len;
while(j<len){
if(nums[j]==val){
j++;
res--;
}
else{
nums[i] = nums[j];
i++;
j++;
}
}return res;
}
};
28.实现strStr()

方法1:暴力匹配
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
if(needle.size()==0)return 0;
if(needle.size()>haystack.size())return -1;
for(int i=0;i<haystack.size()-needle.size()+1;i++){
int j=0;
for( j=0;j<needle.size();j++){
if(haystack[i+j]!=needle[j]){
break;
}
}
if(j==needle.size()){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
方法2:KMP算法
参考文章https://blog.csdn.net/f1033774377/article/details/82556438
代码:
29.两数相除

处理数字的暂时不想看就这样
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int subDivide(int dividend, int divisor, bool minus)
{
int i = 0, times = 1;
int originDivisor = divisor;
while (dividend <= divisor && dividend <= 0)
{
dividend -= divisor;
i += times;
if (dividend >= divisor)
{
break;
}
divisor += divisor;
times += times;
}
if (dividend > originDivisor)
{
if (minus)
return -i;
else
return i;
}
else
{
if (minus)
return -i + subDivide(dividend, originDivisor, minus);
else
return i + subDivide(dividend, originDivisor, minus);
}
}
int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
int i = 0, times = 1, left = 0;
bool minus = false;
if (dividend == INT_MIN)
{
if (divisor == -1)
return INT_MAX;
else if (divisor == 1)
return INT_MIN;
else if (divisor == INT_MIN)
return 1;
}
else if (divisor == INT_MIN)
return 0;
else if (divisor == 1)
return dividend;
else if (divisor == -1)
return -dividend;
if (dividend < 0 && divisor > 0)
{
minus = true;
divisor = -divisor;
}
else if (dividend > 0 && divisor < 0)
{
minus = true;
dividend = -dividend;
}
else if (dividend > 0 && divisor > 0)
{
divisor = -divisor;
dividend = -dividend;
}
return subDivide(dividend, divisor, minus);
}
};
30.串联所有单词的子串

代码1:暴力法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
if(s.empty()||words.empty())return{};
vector<int> res;
int n = words.size();
int len = words[0].size();
unordered_map<string,int> wordcout;
for(auto&e:words) ++wordcout[e];//记录所给单词出现次数
for(int i=0;i<=(int)s.size()-n*len;i++){
unordered_map<string,int> strcnt;
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
string find = s.substr(i+j*len,len);//将所要匹配字符串分割
strcnt[find]++;
if(!wordcout.count(find))break;//加快收敛速度
if(strcnt==wordcout){
res.push_back(i);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
代码二:滑动窗口
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findSubstring(string s, vector<string>& words) {
if(s.empty()||words.empty())return{};
vector<int> res;
int n = words.size();
int len = words[0].size();
unordered_map<string,int> wordcount;
for(auto&e:words) ++wordcount[e];
for(int i=0;i<len;i++){
int left = i,right = i,count = 0;//左右边界
unordered_map<string,int> strcount;
while(right+len<=s.size()){//滑动窗口
string temp = s.substr(right,len);
right+=len;
if(wordcount.count(temp)==0){//跳过此单词
left = right;
strcount.clear();
}
else{//若匹配成功
strcount[temp]++;
while(strcount.at(temp)>wordcount.at(temp)){//如果相同单词匹配多次,则缩小左边界
string temp_1 = s.substr(left,len);
strcount[temp_1]--;
left+=len;
}
if(strcount==wordcount)res.push_back(left);
}
}
}
return res;
}
};
31.下一个排列

代码:逆序找出i<i+1,之后找出最接近i的点,交换两点后,将i之后逆序,找出大于所给数字的最小值。
class Solution {
public:
void nextPermutation(vector<int>& nums) {
int len = nums.size();
int j=len-1,i=len-2;
while((i>=0)&&nums[i]>=nums[j]){
i--;
j--;
}
if(i>=0){
j = len -1;
while(nums[i]>=nums[j]&&j>=0)j--;
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
i++;
j = nums.size()-1;
while(i<j){
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
i++;
j--;
}
}
};
